- Information
- Symbol: BC1
- MSU: LOC_Os03g30250
- RAPdb: Os03g0416200
- PSP score
- LOC_Os03g30250.1: 0.8567
- PLAAC score
- LOC_Os03g30250.1: 0
- pLDDT score
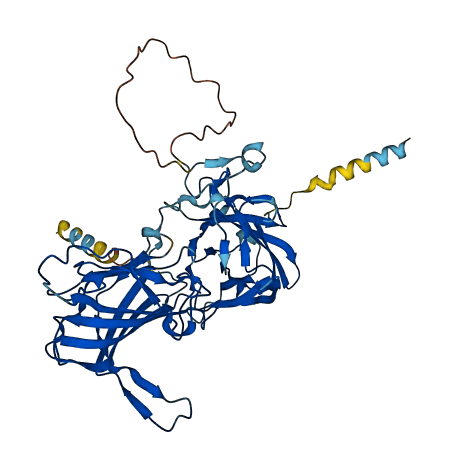
- 84.86
- Protein Structure from AlphaFold and UniProt
- MolPhase score
- LOC_Os03g30250.1: 0.95886057
- MolPhase Result
- Publication
- Rice Brittle culm 6 encodes a dominant-negative form of CesA protein that perturbs cellulose synthesis in secondary cell walls, 2011, J Exp Bot.
- BRITTLE CULM1, Which Encodes a COBRA-Like Protein, Affects the Mechanical Properties of Rice Plants, 2003, The Plant Cell Online.
- The carbohydrate-binding module CBM-like sequence is crucial for rice CWA1/BC1 function in proper assembly of secondary cell wall materials, 2010, Plant Signal Behav.
- Isolation of a novel cell wall architecture mutant of rice with defective Arabidopsis COBL4 ortholog BC1 required for regulated deposition of secondary cell wall components, 2010, Planta.
- Genbank accession number
- Key message
- In these types of cells, mutations in BC1 cause not only a reduction in cell wall thickness and cellulose content but also an increase in lignin level, suggesting that BC1, a gene that controls the mechanical strength of monocots, plays an important role in the biosynthesis of the cell walls of mechanical tissues
- This expression pattern was highly similar to that of BC1, which encodes a COBRA-like protein involved in cellulose synthesis in secondary cell walls in rice
- Genetic analysis showed that cwa1 is allelic to brittle culm1 (bc1), which encodes the glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored COBRA-like protein specifically in plants
- BC1 is known as a regulator that controls the culm mechanical strength and cellulose content in the secondary cell walls of sclerenchyma, but the precise function of BC1 has not been resolved
- BC1, which encodes a COBRA-like protein, is expressed mainly in developing sclerenchyma cells and in vascular bundles of rice
- Our results suggest that CWA1/BC1 has an essential role in assembling cell wall constituents at their appropriate sites, thereby enabling synthesis of solid and flexible internodes in rice
- Isolation of a novel cell wall architecture mutant of rice with defective Arabidopsis COBL4 ortholog BC1 required for regulated deposition of secondary cell wall components
- To understand the molecular mechanism that controls the plant mechanical strength of crops, we characterized the classic rice mutant brittle culm1 (bc1) and isolated BC1 using a map-based cloning approach
- Our results suggested that CWA1/BC1 plays a role in assembling secondary cell wall materials at appropriate sites, enabling synthesis of highly ordered secondary cell wall structure with solid and flexible internodes in rice
- To investigate the importance of the CBM-like sequence of CWA1/BC1 in the assembly of secondary cell wall materials, Trp residues in the CBM-like sequence, which is important for carbohydrate binding, were substituted for Val residues and introduced into the cwa1 mutant
- CWA1/BC1 with the mutated sequence did not complement the abnormal secondary cell walls seen in the cwa1 mutant, indicating that the CBM-like sequence is essential for the proper function of CWA1/BC1, including assembly of secondary cell wall materials
- The carbohydrate-binding module (CBM)-like sequence is crucial for rice CWA1/BC1 function in proper assembly of secondary cell wall materials
- Connection
- BC1, OsMYB103L~CEF1, CEF1/OsMYB103L is involved in GA-mediated regulation of secondary wall biosynthesis in rice., OsMYB103L mediates cellulose biosynthesis and secondary walls formation mainly through directly binding the CESA4, CESA7, CESA9 and BC1 promoters and regulating their expression
Prev Next