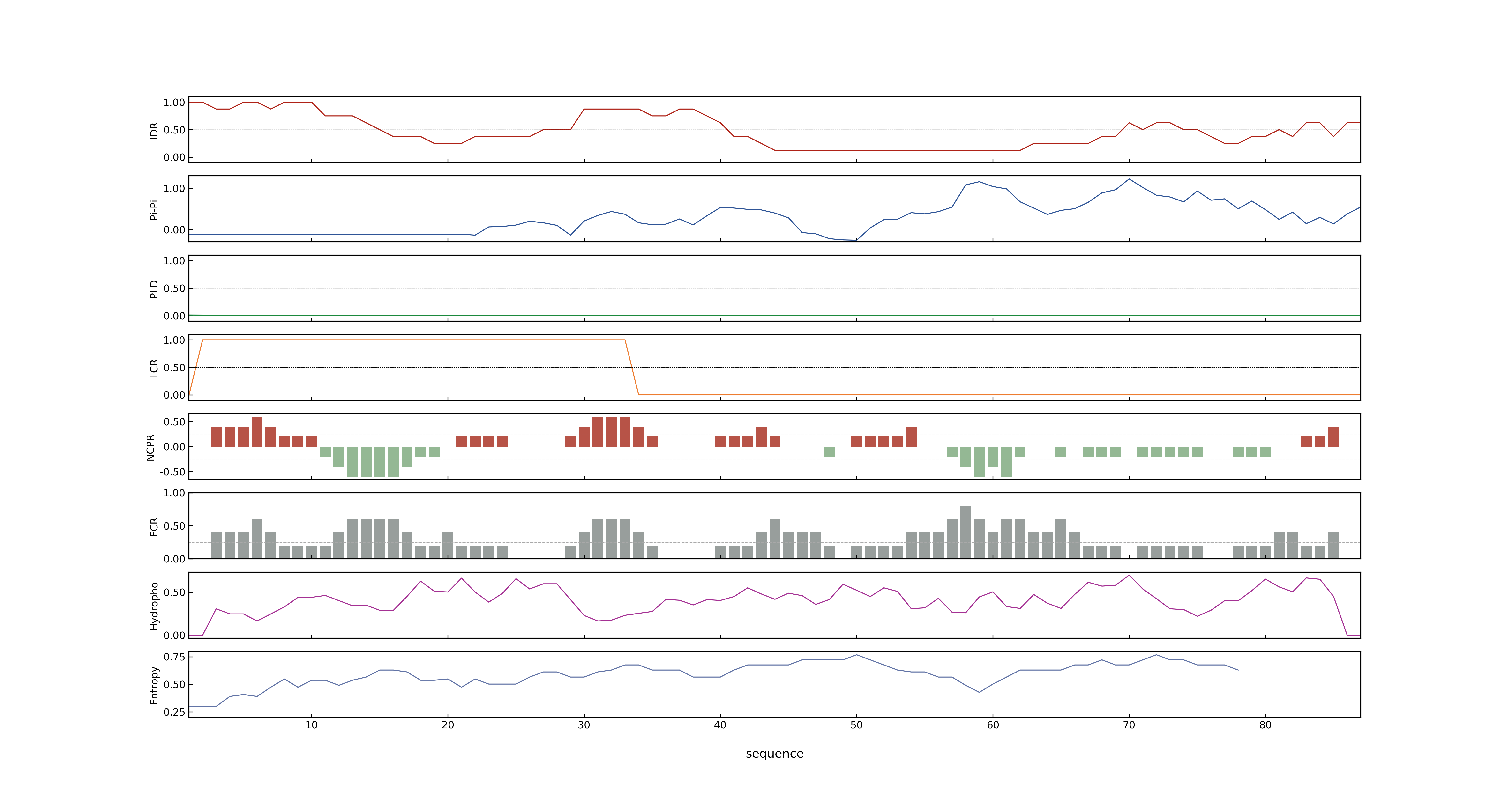
- Information
- Symbol: BU1
- MSU: LOC_Os06g12210
- RAPdb: Os06g0226500
- PSP score
- LOC_Os06g12210.1: 0.218
- PLAAC score
- LOC_Os06g12210.1: 0
- pLDDT score
- NA
- MolPhase score
- LOC_Os06g12210.1: 0.22494632
- MolPhase Result
- Publication
- H3K36 methylation is critical for brassinosteroid-regulated plant growth and development in rice, 2012, Plant J.
- BRASSINOSTEROID UPREGULATED1, encoding a helix-loop-helix protein, is a novel gene involved in brassinosteroid signaling and controls bending of the lamina joint in rice, 2009, Plant Physiol.
- Genbank accession number
- Key message
- These results indicate that BU1 protein is a positive regulator of BR response: it controls bending of the lamina joint in rice and it is a novel primary response gene that participates in two BR signaling pathways through OsBRI1 and RGA1
- Rice plants overexpressing BU1 (BU1:OX) showed enhanced bending of the lamina joint, increased grain size, and resistance to brassinazole, an inhibitor of BR biosynthesis
- Consistently, transcriptome analyses revealed that SDG725 depletion results in down-regulation by more than two-fold of over 1000 genes, including D11, BRI1 and BU1, which are known to be involved in brassinosteroid biosynthesis or signaling pathways
- In addition, compared to the wild type, the induction of BU1 by exogenous brassinolide did not require de novo protein synthesis and it was weaker in a BR receptor mutant OsbriI (Oryza sativa brassinosteroid insensitive1, d61) and a rice G protein alpha subunit (RGA1) mutant d1
- These results indicate that BU1 may participate in some other unknown processes modulated by BR in rice
- Furthermore, expression analyses showed that BU1 is expressed in several organs including lamina joint, phloem, and epithelial cells in embryos
- In contrast to BU1:OX, RNAi plants designed to repress both BU1 and its homologs displayed erect leaves
- Here, we describe a novel BR-induced rice gene BRASSINOSTEROID UPREGULATED1 (BU1), encoding a helix-loop-helix protein
- Connection
- BU1, D11~CPB1~CYP724B1~GNS4, H3K36 methylation is critical for brassinosteroid-regulated plant growth and development in rice, Consistently, transcriptome analyses revealed that SDG725 depletion results in down-regulation by more than two-fold of over 1000 genes, including D11, BRI1 and BU1, which are known to be involved in brassinosteroid biosynthesis or signaling pathways
- BU1, D61~OsBRI1, H3K36 methylation is critical for brassinosteroid-regulated plant growth and development in rice, Consistently, transcriptome analyses revealed that SDG725 depletion results in down-regulation by more than two-fold of over 1000 genes, including D11, BRI1 and BU1, which are known to be involved in brassinosteroid biosynthesis or signaling pathways
- BU1, SDG725, H3K36 methylation is critical for brassinosteroid-regulated plant growth and development in rice, Consistently, transcriptome analyses revealed that SDG725 depletion results in down-regulation by more than two-fold of over 1000 genes, including D11, BRI1 and BU1, which are known to be involved in brassinosteroid biosynthesis or signaling pathways
- BU1, D1~RGA1, BRASSINOSTEROID UPREGULATED1, encoding a helix-loop-helix protein, is a novel gene involved in brassinosteroid signaling and controls bending of the lamina joint in rice, In addition, compared to the wild type, the induction of BU1 by exogenous brassinolide did not require de novo protein synthesis and it was weaker in a BR receptor mutant OsbriI (Oryza sativa brassinosteroid insensitive1, d61) and a rice G protein alpha subunit (RGA1) mutant d1
- BU1, D1~RGA1, BRASSINOSTEROID UPREGULATED1, encoding a helix-loop-helix protein, is a novel gene involved in brassinosteroid signaling and controls bending of the lamina joint in rice, These results indicate that BU1 protein is a positive regulator of BR response: it controls bending of the lamina joint in rice and it is a novel primary response gene that participates in two BR signaling pathways through OsBRI1 and RGA1
- BU1, D61~OsBRI1, BRASSINOSTEROID UPREGULATED1, encoding a helix-loop-helix protein, is a novel gene involved in brassinosteroid signaling and controls bending of the lamina joint in rice, In addition, compared to the wild type, the induction of BU1 by exogenous brassinolide did not require de novo protein synthesis and it was weaker in a BR receptor mutant OsbriI (Oryza sativa brassinosteroid insensitive1, d61) and a rice G protein alpha subunit (RGA1) mutant d1
- BU1, D61~OsBRI1, BRASSINOSTEROID UPREGULATED1, encoding a helix-loop-helix protein, is a novel gene involved in brassinosteroid signaling and controls bending of the lamina joint in rice, These results indicate that BU1 protein is a positive regulator of BR response: it controls bending of the lamina joint in rice and it is a novel primary response gene that participates in two BR signaling pathways through OsBRI1 and RGA1
- BU1, MRG702, MRG702, a reader protein of H3K4me3 and H3K36me3, is involved in brassinosteroid-regulated growth and flowering time control in rice., Gene transcription analyses showed that MRG702 knock-down resulted in the down-regulation of BR-related genes, including D11, BRI1, and BU1, and several flowering genes including Ehd1, Ehd2/OsID1/RID1, Ehd3,OsMADS50, Hd3a, and RFT1
Prev Next