- Information
- Symbol: Bc6,OsCesA9
- MSU: LOC_Os09g25490
- RAPdb: Os09g0422500
- PSP score
- LOC_Os09g25490.1: 0.3563
- PLAAC score
- LOC_Os09g25490.1: 0
- pLDDT score
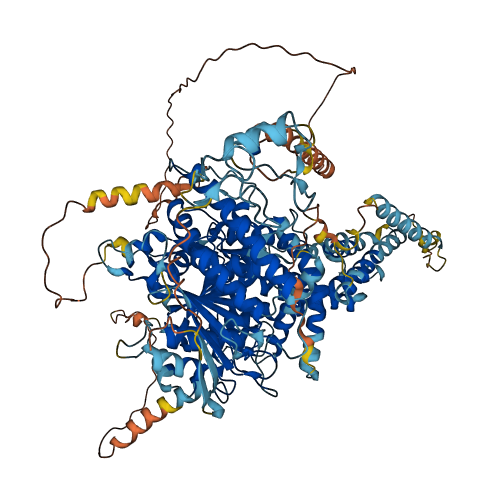
- 76.79
- Protein Structure from AlphaFold and UniProt
- MolPhase score
- LOC_Os09g25490.1: 0.98904687
- MolPhase Result
- Publication
- A missense mutation in the transmembrane domain of CESA9 affects cell wall biosynthesis and plant growth in rice, 2012, Plant Sci.
- Three Distinct Rice Cellulose Synthase Catalytic Subunit Genes Required for Cellulose Synthesis in the Secondary Wall, 2003, Plant Physiol.
- Rice Brittle culm 6 encodes a dominant-negative form of CesA protein that perturbs cellulose synthesis in secondary cell walls, 2011, J Exp Bot.
- OsCESA9 conserved-site mutation leads to largely enhanced plant lodging resistance and biomass enzymatic saccharification by reducing cellulose DP and crystallinity in rice., 2017, Plant Biotechnol J.
- Two Complementary Mechanisms Underpin Cell Wall Patterning during Xylem Vessel Development., 2017, Plant Cell.
- Genbank accession number
- Key message
- In rice expressing a reporter construct, BC6 promoter activity was detected in the culms, nodes, and flowers, and was localized primarily in xylem tissues
- These results indicate that OsCESA9 plays an important role in cell wall biosynthesis and plant growth
- Bc6 encodes a cellulose synthase catalytic subunit, OsCesA9, and has a missense mutation in its highly conserved region
- Transmission electron microscopy analysis revealed that Bc6 mutation reduced the cell wall thickness of sclerenchymal cells in culms
- These results indicate that BC6 is a secondary cell wall-specific CesA that plays an important role in proper deposition of cellulose in the secondary cell walls
- In culms of the Bc6 mutant, the proportion of cellulose was reduced by 38%, while that of hemicellulose was increased by 34%
- Introduction of the semi-dominant Bc6 mutant gene into wild-type rice significantly reduced the percentage of cellulose, causing brittle phenotypes
- The OsCESA9 gene is predominantly expressed in the culms of mature stage plants, consistent with the brittle phenotype in the culm
- Genetic analysis and map-based cloning showed that all the phenotype of S1-60 mutant was caused by a recessive point mutation in the OsCESA9 gene, which encodes the cellulose synthase A subunit 9
- We show here that the genes responsible for three distinct brittle mutations of rice, induced by the insertion of the endogenous retrotransposon Tos17, correspond to CesA (cellulose synthase catalytic subunit) genes, OsCesA4, OsCesA7 and OsCesA9
- OsCESA9 conserved-site mutation leads to largely enhanced plant lodging resistance and biomass enzymatic saccharification by reducing cellulose DP and crystallinity in rice.
- Connection
- Bc6~OsCesA9, OsCesA4~Bc7~bc11, Three Distinct Rice Cellulose Synthase Catalytic Subunit Genes Required for Cellulose Synthesis in the Secondary Wall, We show here that the genes responsible for three distinct brittle mutations of rice, induced by the insertion of the endogenous retrotransposon Tos17, correspond to CesA (cellulose synthase catalytic subunit) genes, OsCesA4, OsCesA7 and OsCesA9
- Bc6~OsCesA9, OsCesA7, Three Distinct Rice Cellulose Synthase Catalytic Subunit Genes Required for Cellulose Synthesis in the Secondary Wall, We show here that the genes responsible for three distinct brittle mutations of rice, induced by the insertion of the endogenous retrotransposon Tos17, correspond to CesA (cellulose synthase catalytic subunit) genes, OsCesA4, OsCesA7 and OsCesA9
- Bc6~OsCesA9, OsMYB103L~CEF1, CEF1/OsMYB103L is involved in GA-mediated regulation of secondary wall biosynthesis in rice, OsMYB103L mediates cellulose biosynthesis and secondary walls formation mainly through directly binding the CESA4, CESA7, CESA9 and BC1 promoters and regulating their expression
Prev Next