- Information
- Symbol: Bph14
- MSU: LOC_Os03g63150
- RAPdb: Os03g0848700
- PSP score
- LOC_Os03g63150.1: 0.0471
- LOC_Os03g63150.2: 0.0471
- PLAAC score
- LOC_Os03g63150.1: 0
- LOC_Os03g63150.2: 0
- pLDDT score
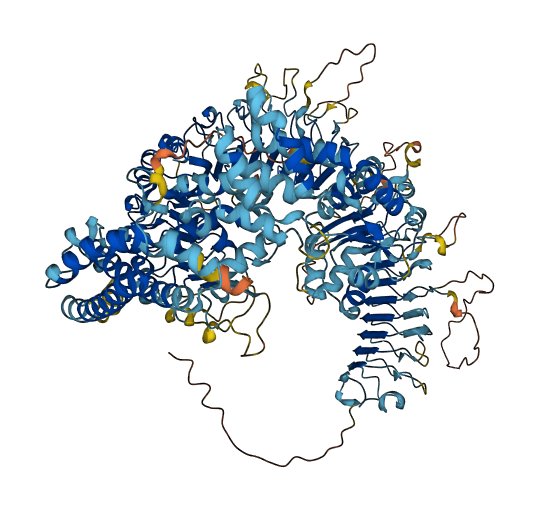
- 79.62
- Protein Structure from AlphaFold and UniProt
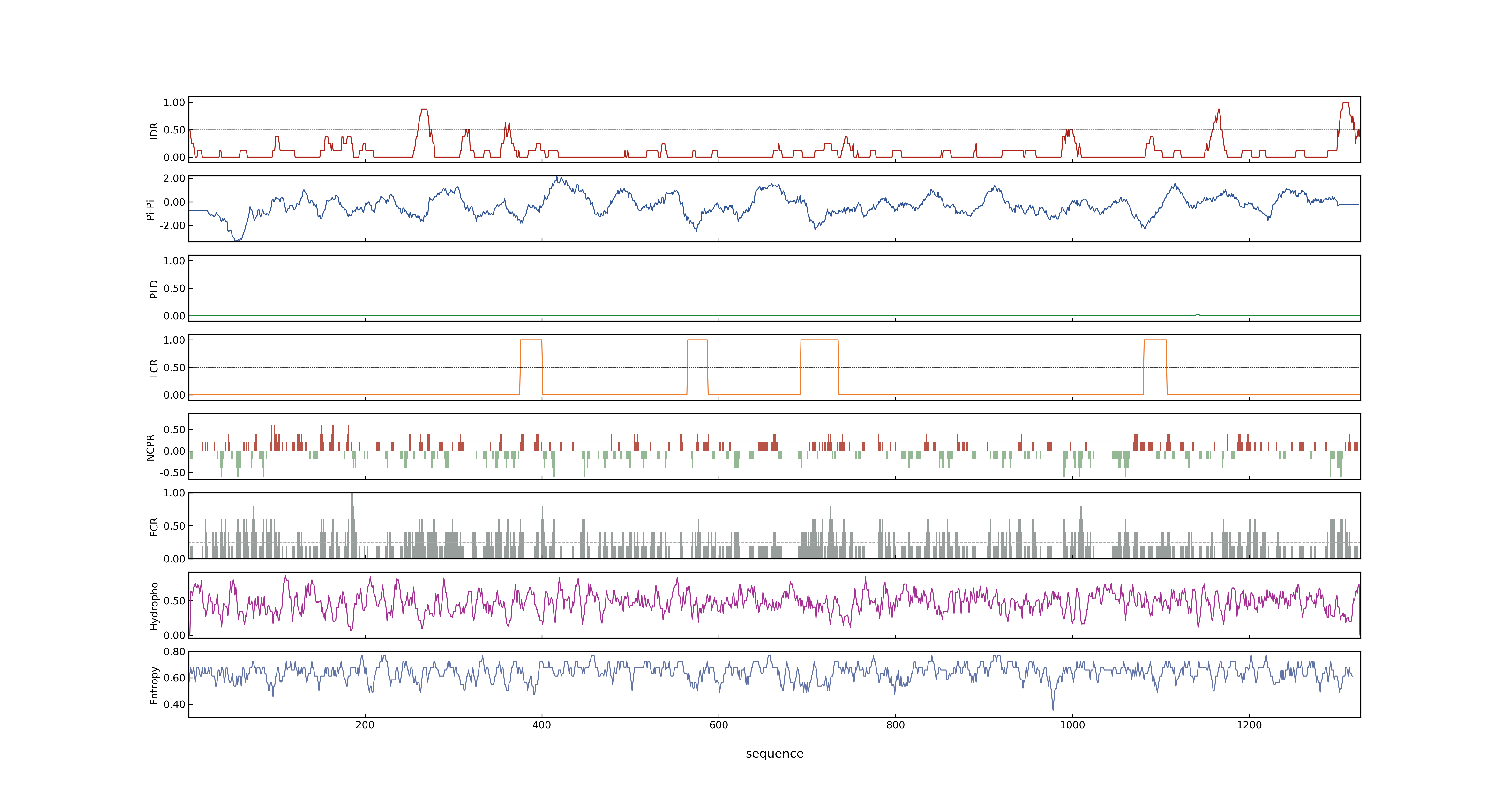
- MolPhase score
- LOC_Os03g63150.1: 0.99083471
- LOC_Os03g63150.2: 0.99083471
- MolPhase Result
- Publication
- Identification and mapping of two brown planthopper resistance genes in rice, 2001, TAG Theoretical and Applied Genetics.
- Identification and characterization of Bph14, a gene conferring resistance to brown planthopper in rice, 2009, Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A.
- Genbank accession number
- Key message
- Expression of Bph14 activates the salicylic acid signaling pathway and induces callose deposition in phloem cells and trypsin inhibitor production after planthopper infestation, thus reducing the feeding, growth rate, and longevity of the BPH insects
- Sequence comparison indicates that Bph14 carries a unique LRR domain that might function in recognition of the BPH insect invasion and activating the defense response
- Identification and characterization of Bph14, a gene conferring resistance to brown planthopper in rice
- Bph14 is predominantly expressed in vascular bundles, the site of BPH feeding
- In this study, we cloned Bph14, a gene conferring resistance to BPH at seedling and maturity stages of the rice plant, using a map-base cloning approach
- Connection
Prev Next