- Information
- Symbol: D2,CYP90D2,SMG11
- MSU: LOC_Os01g10040
- RAPdb: Os01g0197100
- PSP score
- LOC_Os01g10040.1: 0.0314
- LOC_Os01g10040.2: 0.0027
- PLAAC score
- LOC_Os01g10040.1: 0
- LOC_Os01g10040.2: 0
- pLDDT score
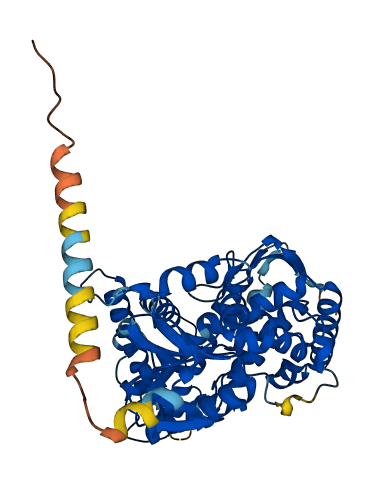
- 89.61
- Protein Structure from AlphaFold and UniProt
- MolPhase score
- LOC_Os01g10040.1: 0.15923377
- LOC_Os01g10040.2: 0.01127554
- MolPhase Result
- Publication
- Rice CYP90D2 and CYP90D3 catalyze C-23 hydroxylation of brassinosteroids in vitro, 2012, Plant Physiol Biochem.
- Proteomic identification of small, copper-responsive proteins in germinating embryos of Oryza sativa, 2009, Ann Bot.
- A comprehensive genetic study reveals a crucial role of CYP90D2/D2 in regulating plant architecture in rice Oryza sativa, 2013, New Phytol.
- A rice brassinosteroid-deficient mutant, ebisu dwarf d2, is caused by a loss of function of a new member of cytochrome P450, 2003, Plant Cell.
- RAV-Like1 maintains brassinosteroid homeostasis via the coordinated activation of BRI1 and biosynthetic genes in rice, 2010, Plant Cell.
- SMALL GRAIN 11 Controls Grain Size, Grain Number and Grain Yield in Rice., 2016, Rice (N Y).
- Genbank accession number
- Key message
- Our chemical analysis suggested that CYP90D2/D2 might catalyze C-3 dehydrogenation step in BR biosynthesis
- The accumulation profile of BR intermediates in the d2 mutants confirmed that these plants are deficient in late BR biosynthesis
- The D2 gene encoded a novel cytochrome P450 classified in CYP90D that is highly similar to the reported BR synthesis enzymes
- Based on these results, we conclude that D2/CYP90D2 catalyzes the steps from 6-deoxoteasterone to 3-dehydro-6-deoxoteasterone and from teasterone to 3-dehydroteasterone in the late BR biosynthesis pathway
- Furthermore, RAVL1 is also required for the expression of the BR biosynthetic genes D2, D11, and BRD1 that are subject to BR negative feedback
- Allelic mutations of CYP90D2/D2 confer varying degrees of dwarfism and leaf angle, thus providing useful information for molecular breeding in grain crop plants
- In feeding experiments, 3-dehydro-6-deoxoteasterone, 3-dehydroteasterone, and brassinolide effectively caused the lamina joints of the d2 plants to bend, whereas more upstream compounds did not cause bending
- However, in vitro biochemical assays using baculovirus/insect cell-produced proteins revealed that both CYP90D2 and CYP90D3 catalyze C-23 hydroxylation of various 22-hydroxylated brassinosteroids, but with markedly different catalytic efficiencies
- We showed that the severe dwarf phenotype was caused by a complete deletion of a cytochrome P450 gene, CYP90D2/D2, which was further confirmed in two independent T-DNA insertion lines in different genetic backgrounds and by RNA interference
- A comprehensive genetic study reveals a crucial role of CYP90D2/D2 in regulating plant architecture in rice (Oryza sativa)
- A rice brassinosteroid-deficient mutant, ebisu dwarf (d2), is caused by a loss of function of a new member of cytochrome P450
- A rice dwarf mutant, ebisu dwarf (d2), which contains a defective copy of CYP90D2, is known to be a brassinosteroid-deficient mutant, and CYP90D2 has been considered to act as a C-3 dehydrogenase
- We characterized a rice dwarf mutant, ebisu dwarf (d2)
- The dwarf phenotype of d2 was rescued by exogenous brassinolide treatment
- We report the biochemical characterization of two brassinosteroid-biosynthetic P450s from rice: CYP90D2 and CYP90D3
- These results indicate that CYP90D2 and CYP90D3 can act as brassinosteroid C-23 hydroxylases in rice
- Rice CYP90D2 and CYP90D3 catalyze C-23 hydroxylation of brassinosteroids in vitro
- SMG11 controls grain size by promoting cell expansion in grain hulls
- SMG11 regulates cell expansion, at least in part, by influencing expression of several grain size genes involved in the regulation of cell expansion
- The suitable expression of SMG11 increases grain size, grain weight and grain yield
- Cloning and sequence analyses of the SMG11 gene reveal that smg11 is a new allele of DWARF2 (D2), which encodes a cytochrome P450 (CYP90D2) involved in brassinosteroid biosynthetic pathway
- Connection
- CYP90D3, D2~CYP90D2~SMG11, Rice CYP90D2 and CYP90D3 catalyze C-23 hydroxylation of brassinosteroids in vitro, We report the biochemical characterization of two brassinosteroid-biosynthetic P450s from rice: CYP90D2 and CYP90D3
- CYP90D3, D2~CYP90D2~SMG11, Rice CYP90D2 and CYP90D3 catalyze C-23 hydroxylation of brassinosteroids in vitro, However, in vitro biochemical assays using baculovirus/insect cell-produced proteins revealed that both CYP90D2 and CYP90D3 catalyze C-23 hydroxylation of various 22-hydroxylated brassinosteroids, but with markedly different catalytic efficiencies
- CYP90D3, D2~CYP90D2~SMG11, Rice CYP90D2 and CYP90D3 catalyze C-23 hydroxylation of brassinosteroids in vitro, These results indicate that CYP90D2 and CYP90D3 can act as brassinosteroid C-23 hydroxylases in rice
- CYP90D3, D2~CYP90D2~SMG11, Rice CYP90D2 and CYP90D3 catalyze C-23 hydroxylation of brassinosteroids in vitro, Rice CYP90D2 and CYP90D3 catalyze C-23 hydroxylation of brassinosteroids in vitro
- D11~CPB1~CYP724B1~GNS4, D2~CYP90D2~SMG11, RAV-Like1 maintains brassinosteroid homeostasis via the coordinated activation of BRI1 and biosynthetic genes in rice, Furthermore, RAVL1 is also required for the expression of the BR biosynthetic genes D2, D11, and BRD1 that are subject to BR negative feedback
- D2~CYP90D2~SMG11, RAVL1, RAV-Like1 maintains brassinosteroid homeostasis via the coordinated activation of BRI1 and biosynthetic genes in rice, Furthermore, RAVL1 is also required for the expression of the BR biosynthetic genes D2, D11, and BRD1 that are subject to BR negative feedback
- D2~CYP90D2~SMG11, LPA1, Loose Plant Architecture1 LPA1 determines lamina joint bending by suppressing auxin signalling that interacts with C-22-hydroxylated and 6-deoxo brassinosteroids in rice., A strong synergic effect is detected between lpa1 and d2 (the defective mutant for catalysis of C-23-hydroxylated BRs) during IAA-mediated lamina inclination
- D2~CYP90D2~SMG11, TAC3, A Novel Tiller Angle Gene, TAC3, together with TAC1 and D2 Largely Determine the Natural Variation of Tiller Angle in Rice Cultivars., A Novel Tiller Angle Gene, TAC3, together with TAC1 and D2 Largely Determine the Natural Variation of Tiller Angle in Rice Cultivars.
- D2~CYP90D2~SMG11, TAC3, A Novel Tiller Angle Gene, TAC3, together with TAC1 and D2 Largely Determine the Natural Variation of Tiller Angle in Rice Cultivars., A nucleotide diversity analysis revealed that TAC3, D2 and TAC1 have been subjected to selection during japonica domestication
- D2~CYP90D2~SMG11, TAC3, A Novel Tiller Angle Gene, TAC3, together with TAC1 and D2 Largely Determine the Natural Variation of Tiller Angle in Rice Cultivars., A haplotype analysis identified favorable alleles of TAC3, D2 and TAC1, which may be used for breeding plants with an ideal architecture
- D2~CYP90D2~SMG11, TAC3, A Novel Tiller Angle Gene, TAC3, together with TAC1 and D2 Largely Determine the Natural Variation of Tiller Angle in Rice Cultivars., In conclusion, there is a diverse genetic basis for tiller angle between the two subpopulations, and it is the novel gene TAC3 together with TAC1, D2, and other newly identified genes in this study that controls tiller angle in rice cultivars
Prev Next