- Information
- Symbol: D3
- MSU: LOC_Os06g06050
- RAPdb: Os06g0154200
- PSP score
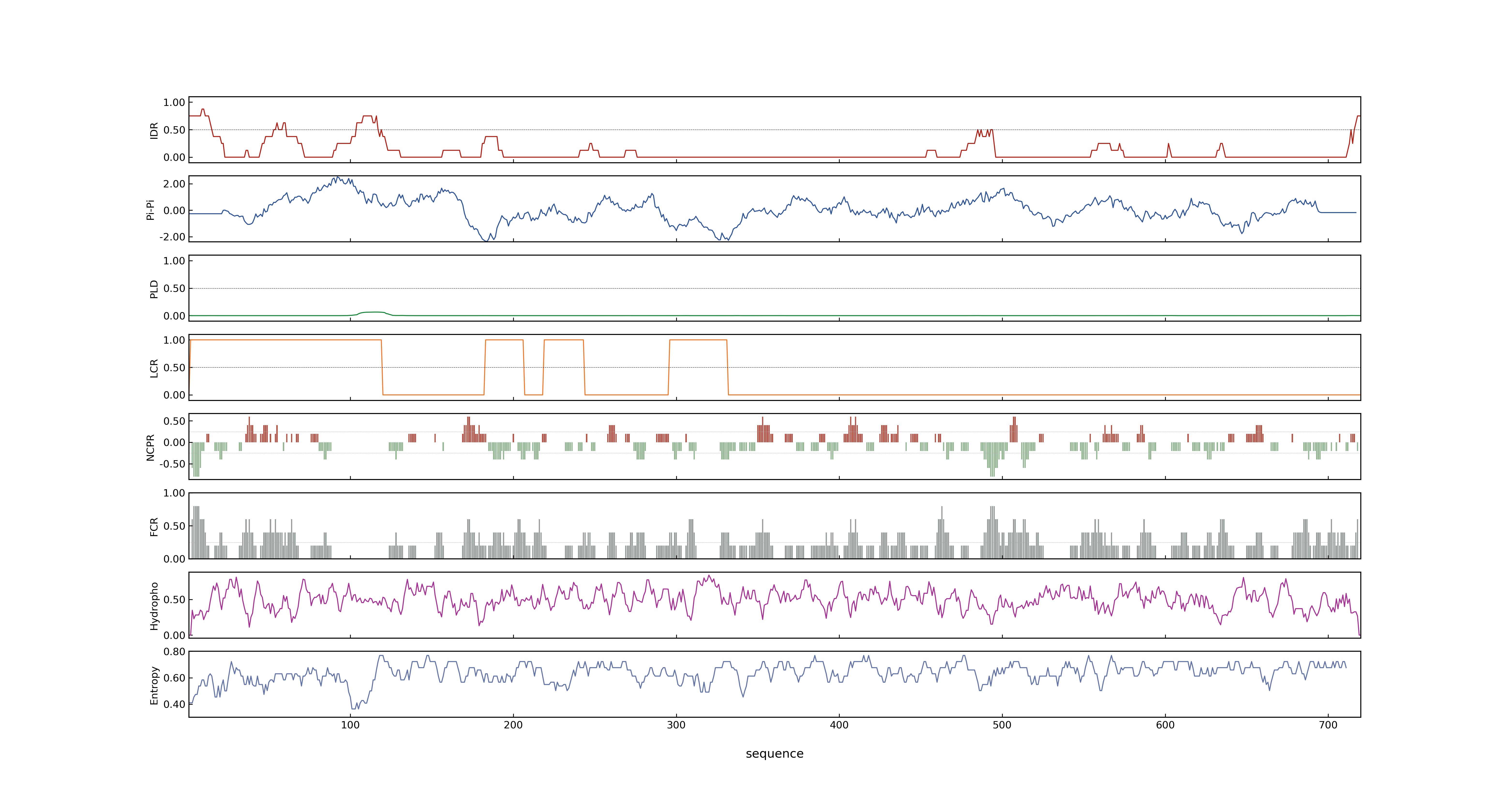
- LOC_Os06g06050.1: 0.2117
- PLAAC score
- LOC_Os06g06050.1: 0
- pLDDT score
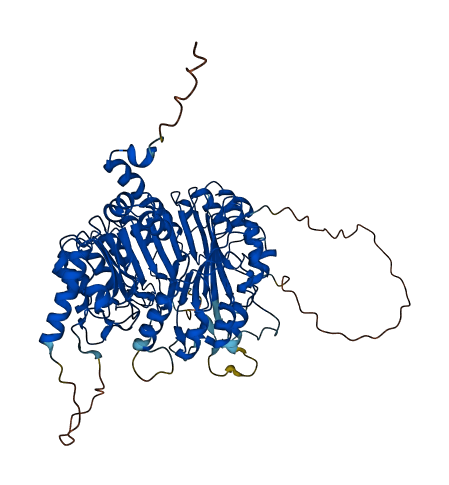
- 87.55
- Protein Structure from AlphaFold and UniProt
- MolPhase score
- LOC_Os06g06050.1: 0.82416284
- MolPhase Result
- Publication
- Identification and characterization of HTD2: a novel gene negatively regulating tiller bud outgrowth in rice, 2009, Planta.
- Rice tillering dwarf mutant dwarf3 has increased leaf longevity during darkness-induced senescence or hydrogen peroxide-induced cell death, 2007, Genes Genet Syst.
- Genetic interaction between 2 tillering genes, reduced culm number 1 rcn1 and tillering dwarf gene d3, in rice, 2007, J Hered.
- The rice HIGH-TILLERING DWARF1 encoding an ortholog of Arabidopsis MAX3 is required for negative regulation of the outgrowth of axillary buds, 2006, Plant J.
- DWARF10, an RMS1/MAX4/DAD1 ortholog, controls lateral bud outgrowth in rice, 2007, Plant J.
- DWARF 53 acts as a repressor of strigolactone signalling in rice, 2013, Nature.
- D14-SCFD3-dependent degradation of D53 regulates strigolactone signalling, 2013, Nature.
- Suppression of tiller bud activity in tillering dwarf mutants of rice, 2005, Plant Cell Physiol.
- Destabilization of strigolactone receptor DWARF14 by binding of ligand and E3-ligase signaling effector DWARF3., 2015, Cell Res.
- Genbank accession number
- Key message
- The D53 gene product shares predicted features with the class I Clp ATPase proteins and can form a complex with the alpha/beta hydrolase protein DWARF 14 (D14) and the F-box protein DWARF 3 (D3), two previously identified signalling components potentially responsible for SL perception
- We found that darkness-induced senescence or H2O2-induced cell death in the third leaf [as measured by chlorophyll degradation, membrane ion leakage and expression of senescence-associated genes (SAGs)] in a d3 rice mutant was delayed by 1~3 d compared to that in its reference line Shiokari
- These results suggest that D3 protein in rice, like MAX2/ORE9 in Arabidopsis, is involved in leaf senescence or cell death
- Treatments with GR24, a synthetic SL analogue, cause D53 degradation via the proteasome in a manner that requires D14 and the SCF(D3) ubiquitin ligase, whereas the dominant form of D53 is resistant to SL-mediated degradation
- Mutant genes, reduced culm number 1 (rcn1) and bunketsuwaito tillering dwarf (d3), affect tiller number in rice (Oryza sativa L
- The reduction in tillering by the rcn1 mutation was independent of the d3 genotype, and tillering number of d3rcn1 double mutant was between those of the d3 and rcn1 mutants
- These results demonstrated that the Rcn1 gene was not involved in the D3-associated pathway in tillering control
- Genetic interaction between 2 tillering genes, reduced culm number 1 (rcn1) and tillering dwarf gene d3, in rice
- SL signalling requires the hormone-dependent interaction of DWARF 14 (D14), a probable candidate SL receptor, with DWARF 3 (D3), an F-box component of the Skp-Cullin-F-box (SCF) E3 ubiquitin ligase complex
- Here we report the characterization of a dominant SL-insensitive rice (Oryza sativa) mutant dwarf 53 (d53) and the cloning of D53, which encodes a substrate of the SCF(D3) ubiquitination complex and functions as a repressor of SL signalling
- The d3 mutant was reported to increase tiller number and reduce plant stature
- Moreover, D10 expression is upregulated in six branching mutants, d3, d10, d14, d17, d27 and high tillering dwarf (htd1)
- ) gene DWARF3 (D3) is orthologous to MAX2/ORE9, we wished to know whether disruption of D3 also results in increased longevity in leaves
- Moreover, the mRNA levels of D3, HTD1 and D10, which are orthologs of Arabidopsis MAX2/ORE9, MAX3 and MAX4, respectively, increased during cell death
- Loss of function of HTD2 resulted in a significantly increased expression of HTD1, D10 and D3, which were involved in the strigolactone biosynthetic pathway
- We demonstrate that, in a D14- and D3-dependent manner, SLs induce D53 degradation by the proteasome and abrogate its activity in promoting axillary bud outgrowth
- D14-SCF(D3)-dependent degradation of D53 regulates strigolactone signalling
- Connection
- D3, HTD2~D88~D14, Identification and characterization of HTD2: a novel gene negatively regulating tiller bud outgrowth in rice, Loss of function of HTD2 resulted in a significantly increased expression of HTD1, D10 and D3, which were involved in the strigolactone biosynthetic pathway
- D10~OsCCD8~OsCCD8b, D3, Identification and characterization of HTD2: a novel gene negatively regulating tiller bud outgrowth in rice, Loss of function of HTD2 resulted in a significantly increased expression of HTD1, D10 and D3, which were involved in the strigolactone biosynthetic pathway
- D3, HTD1~OsCCD7, Identification and characterization of HTD2: a novel gene negatively regulating tiller bud outgrowth in rice, Loss of function of HTD2 resulted in a significantly increased expression of HTD1, D10 and D3, which were involved in the strigolactone biosynthetic pathway
- D10~OsCCD8~OsCCD8b, D3, Rice tillering dwarf mutant dwarf3 has increased leaf longevity during darkness-induced senescence or hydrogen peroxide-induced cell death, Moreover, the mRNA levels of D3, HTD1 and D10, which are orthologs of Arabidopsis MAX2/ORE9, MAX3 and MAX4, respectively, increased during cell death
- D3, HTD1~OsCCD7, Rice tillering dwarf mutant dwarf3 has increased leaf longevity during darkness-induced senescence or hydrogen peroxide-induced cell death, Moreover, the mRNA levels of D3, HTD1 and D10, which are orthologs of Arabidopsis MAX2/ORE9, MAX3 and MAX4, respectively, increased during cell death
- D3, Rcn1~OsABCG5, Genetic interaction between 2 tillering genes, reduced culm number 1 rcn1 and tillering dwarf gene d3, in rice, Mutant genes, reduced culm number 1 (rcn1) and bunketsuwaito tillering dwarf (d3), affect tiller number in rice (Oryza sativa L
- D3, Rcn1~OsABCG5, Genetic interaction between 2 tillering genes, reduced culm number 1 rcn1 and tillering dwarf gene d3, in rice, Our objective was to compare the phenotype of the d3rcn1 double mutant with each single mutant and parental rice cultivar “Shiokari” and to clarify whether the Rcn1 gene interacted with the D3 gene
- D3, Rcn1~OsABCG5, Genetic interaction between 2 tillering genes, reduced culm number 1 rcn1 and tillering dwarf gene d3, in rice, We recovered a new rcn1 mutant from Shiokari and developed d3rcn1 double mutant with Shiokari genetic background
- D3, Rcn1~OsABCG5, Genetic interaction between 2 tillering genes, reduced culm number 1 rcn1 and tillering dwarf gene d3, in rice, Three near-isogenic lines, rcn1 mutant, d3 mutant, and d3rcn1 double mutant, were grown together with the parental Shiokari
- D3, Rcn1~OsABCG5, Genetic interaction between 2 tillering genes, reduced culm number 1 rcn1 and tillering dwarf gene d3, in rice, The reduction in tillering by the rcn1 mutation was independent of the d3 genotype, and tillering number of d3rcn1 double mutant was between those of the d3 and rcn1 mutants
- D3, Rcn1~OsABCG5, Genetic interaction between 2 tillering genes, reduced culm number 1 rcn1 and tillering dwarf gene d3, in rice, These results demonstrated that the Rcn1 gene was not involved in the D3-associated pathway in tillering control
- D3, Rcn1~OsABCG5, Genetic interaction between 2 tillering genes, reduced culm number 1 rcn1 and tillering dwarf gene d3, in rice, Genetic interaction between 2 tillering genes, reduced culm number 1 (rcn1) and tillering dwarf gene d3, in rice
- D3, HTD1~OsCCD7, The rice HIGH-TILLERING DWARF1 encoding an ortholog of Arabidopsis MAX3 is required for negative regulation of the outgrowth of axillary buds, In addition, the expression of HTD1, D3 and OsCCD8a in the htd1 and d3 mutants suggests a feedback mechanism may exist for the synthesis and perception of the carotenoid-derived signal in rice
- D27, D3, DWARF10, an RMS1/MAX4/DAD1 ortholog, controls lateral bud outgrowth in rice, Moreover, D10 expression is upregulated in six branching mutants, d3, d10, d14, d17, d27 and high tillering dwarf (htd1)
- D10~OsCCD8~OsCCD8b, D3, DWARF10, an RMS1/MAX4/DAD1 ortholog, controls lateral bud outgrowth in rice, Moreover, D10 expression is upregulated in six branching mutants, d3, d10, d14, d17, d27 and high tillering dwarf (htd1)
- D3, HTD2~D88~D14, DWARF10, an RMS1/MAX4/DAD1 ortholog, controls lateral bud outgrowth in rice, Moreover, D10 expression is upregulated in six branching mutants, d3, d10, d14, d17, d27 and high tillering dwarf (htd1)
- D3, HTD1~OsCCD7, DWARF10, an RMS1/MAX4/DAD1 ortholog, controls lateral bud outgrowth in rice, Moreover, D10 expression is upregulated in six branching mutants, d3, d10, d14, d17, d27 and high tillering dwarf (htd1)
- D3, HTD1~OsCCD7, DWARF10, an RMS1/MAX4/DAD1 ortholog, controls lateral bud outgrowth in rice, No such effects were found for D3 or HTD1, the MAX2 and MAX3 orthologs, respectively, of rice
- D3, D53, DWARF 53 acts as a repressor of strigolactone signalling in rice, Here we report the characterization of a dominant SL-insensitive rice (Oryza sativa) mutant dwarf 53 (d53) and the cloning of D53, which encodes a substrate of the SCF(D3) ubiquitination complex and functions as a repressor of SL signalling
- D3, D53, DWARF 53 acts as a repressor of strigolactone signalling in rice, Treatments with GR24, a synthetic SL analogue, cause D53 degradation via the proteasome in a manner that requires D14 and the SCF(D3) ubiquitin ligase, whereas the dominant form of D53 is resistant to SL-mediated degradation
- D3, D53, DWARF 53 acts as a repressor of strigolactone signalling in rice, Our results suggest a model of SL signalling that involves SL-dependent degradation of the D53 repressor mediated by the D14-D3 complex
- D3, HTD2~D88~D14, DWARF 53 acts as a repressor of strigolactone signalling in rice, SL signalling requires the hormone-dependent interaction of DWARF 14 (D14), a probable candidate SL receptor, with DWARF 3 (D3), an F-box component of the Skp-Cullin-F-box (SCF) E3 ubiquitin ligase complex
- D3, HTD2~D88~D14, DWARF 53 acts as a repressor of strigolactone signalling in rice, Treatments with GR24, a synthetic SL analogue, cause D53 degradation via the proteasome in a manner that requires D14 and the SCF(D3) ubiquitin ligase, whereas the dominant form of D53 is resistant to SL-mediated degradation
- D3, HTD2~D88~D14, DWARF 53 acts as a repressor of strigolactone signalling in rice, Our results suggest a model of SL signalling that involves SL-dependent degradation of the D53 repressor mediated by the D14-D3 complex
- D3, D53, D14-SCFD3-dependent degradation of D53 regulates strigolactone signalling, The D53 gene product shares predicted features with the class I Clp ATPase proteins and can form a complex with the alpha/beta hydrolase protein DWARF 14 (D14) and the F-box protein DWARF 3 (D3), two previously identified signalling components potentially responsible for SL perception
- D3, D53, D14-SCFD3-dependent degradation of D53 regulates strigolactone signalling, We demonstrate that, in a D14- and D3-dependent manner, SLs induce D53 degradation by the proteasome and abrogate its activity in promoting axillary bud outgrowth
- D3, D53, D14-SCFD3-dependent degradation of D53 regulates strigolactone signalling, D14-SCF(D3)-dependent degradation of D53 regulates strigolactone signalling
- D3, HTD2~D88~D14, D14-SCFD3-dependent degradation of D53 regulates strigolactone signalling, The D53 gene product shares predicted features with the class I Clp ATPase proteins and can form a complex with the alpha/beta hydrolase protein DWARF 14 (D14) and the F-box protein DWARF 3 (D3), two previously identified signalling components potentially responsible for SL perception
- D3, HTD2~D88~D14, D14-SCFD3-dependent degradation of D53 regulates strigolactone signalling, We demonstrate that, in a D14- and D3-dependent manner, SLs induce D53 degradation by the proteasome and abrogate its activity in promoting axillary bud outgrowth
- D3, HTD2~D88~D14, D14-SCFD3-dependent degradation of D53 regulates strigolactone signalling, D14-SCF(D3)-dependent degradation of D53 regulates strigolactone signalling
- D3, RFL~APO2~SSC, Functions for rice RFL in vegetative axillary meristem specification and outgrowth., The relationship between RFL, strigolactone signalling, and bud outgrowth was studied by transcript analyses and by the tillering phenotype of transgenic plants knocked down for both RFL and D3
- D3, HTD2~D88~D14, Destabilization of strigolactone receptor DWARF14 by binding of ligand and E3-ligase signaling effector DWARF3., Key mediators of the SL signaling pathway in rice include the ÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂñ/ÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂò-fold hydrolase DWARF 14 (D14) and the F-box component DWARF 3 (D3) of the ubiquitin ligase SCF(D3) that mediate ligand-dependent degradation of downstream signaling repressors
- D3, HTD2~D88~D14, Destabilization of strigolactone receptor DWARF14 by binding of ligand and E3-ligase signaling effector DWARF3., More importantly, D14 is destabilized upon the binding of ligands and D3, thus revealing an unusual mechanism of SL recognition and signaling, in which the hormone, the receptor, and the downstream effectors are systematically destabilized during the signal transduction process
- D3, HTD2~D88~D14, Identification and Molecular Mapping of Indica High-tillering Dwarf Mutant htd4, a Mild Phenotype Allelic Mutant of D14 in Rice Oryza sativa L.., Quantitative RT-PCR analyses revealed that expression levels of the genes D10, D17, D27, D3, and D14 increased significantly while expression of D53 decreased in htd4, compared to the wild type
- D3, HTD2~D88~D14, Identification and Molecular Mapping of Indica High-tillering Dwarf Mutant htd4, a Mild Phenotype Allelic Mutant of D14 in Rice Oryza sativa L.., However, a BiFC assay suggested that the mutant-type D14 could not interact with D3
Prev Next