- Information
- Symbol: D53
- MSU: LOC_Os11g01330
- RAPdb: Os11g0104300,Os11g0104350
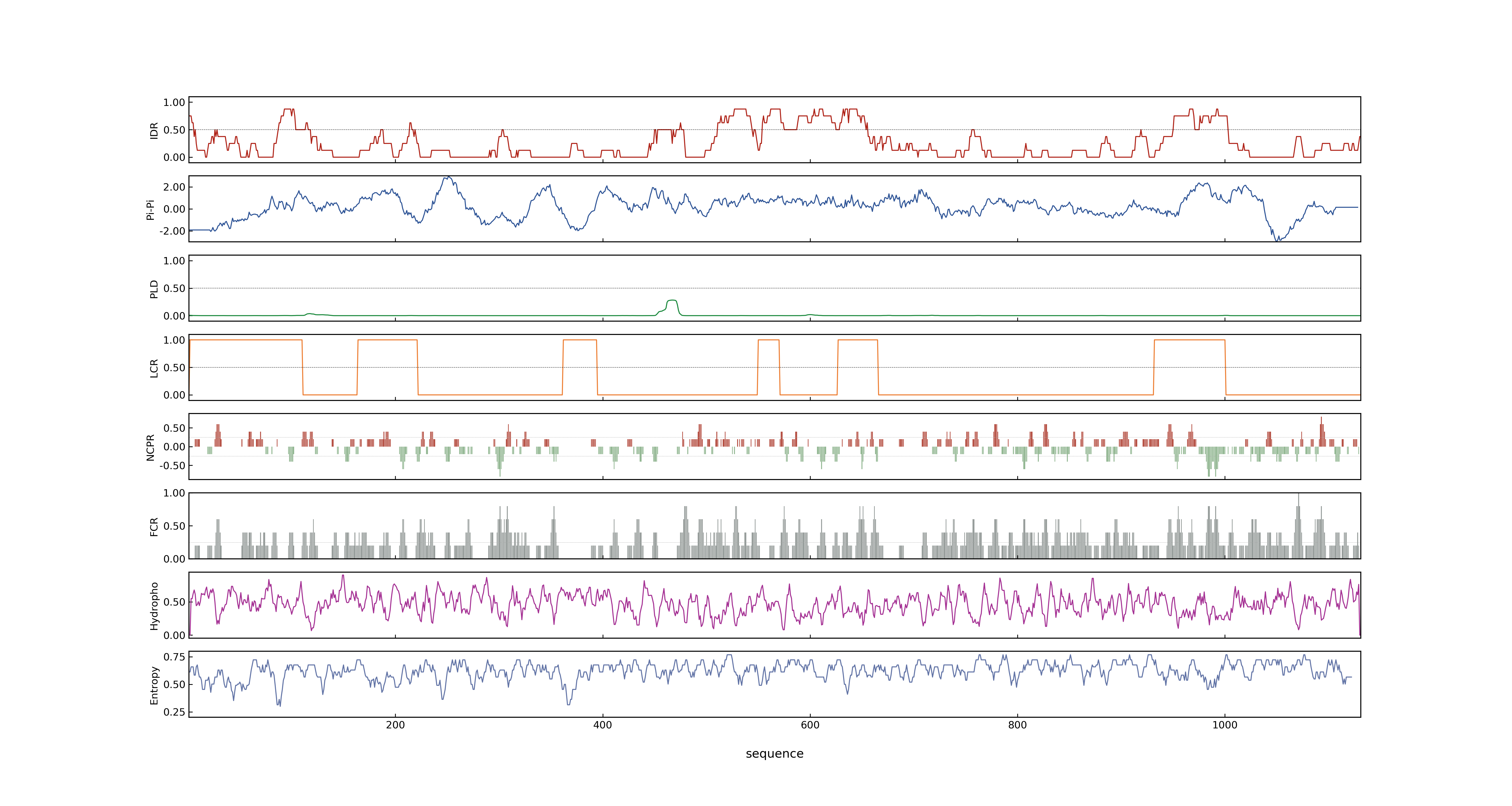
- PSP score
- LOC_Os11g01330.1: 0.9425
- PLAAC score
- LOC_Os11g01330.1: 0
- pLDDT score
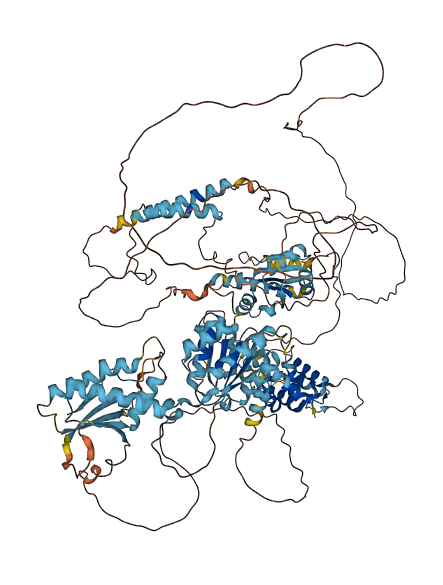
- 61.36
- Protein Structure from AlphaFold and UniProt
- MolPhase score
- LOC_Os11g01330.1: 0.99975234
- MolPhase Result
- Publication
- DWARF 53 acts as a repressor of strigolactone signalling in rice, 2013, Nature.
- D14-SCFD3-dependent degradation of D53 regulates strigolactone signalling, 2013, Nature.
- A D53 repression motif induces oligomerization of TOPLESS corepressors and promotes assembly of a corepressor-nucleosome complex., 2017, Sci Adv.
- Genbank accession number
- Key message
- D14-SCF(D3)-dependent degradation of D53 regulates strigolactone signalling
- We demonstrate that, in a D14- and D3-dependent manner, SLs induce D53 degradation by the proteasome and abrogate its activity in promoting axillary bud outgrowth
- Here we report the characterization of a dominant SL-insensitive rice (Oryza sativa) mutant dwarf 53 (d53) and the cloning of D53, which encodes a substrate of the SCF(D3) ubiquitination complex and functions as a repressor of SL signalling
- Here we show that DWARF 53 (D53) acts as a repressor of SL signalling and that SLs induce its degradation
- The D53 gene product shares predicted features with the class I Clp ATPase proteins and can form a complex with the alpha/beta hydrolase protein DWARF 14 (D14) and the F-box protein DWARF 3 (D3), two previously identified signalling components potentially responsible for SL perception
- We find that the rice (Oryza sativa) d53 mutant, which produces an exaggerated number of tillers compared to wild-type plants, is caused by a gain-of-function mutation and is insensitive to exogenous SL treatment
- Treatments with GR24, a synthetic SL analogue, cause D53 degradation via the proteasome in a manner that requires D14 and the SCF(D3) ubiquitin ligase, whereas the dominant form of D53 is resistant to SL-mediated degradation
- Connection
- D3, D53, DWARF 53 acts as a repressor of strigolactone signalling in rice, Here we report the characterization of a dominant SL-insensitive rice (Oryza sativa) mutant dwarf 53 (d53) and the cloning of D53, which encodes a substrate of the SCF(D3) ubiquitination complex and functions as a repressor of SL signalling
- D3, D53, DWARF 53 acts as a repressor of strigolactone signalling in rice, Treatments with GR24, a synthetic SL analogue, cause D53 degradation via the proteasome in a manner that requires D14 and the SCF(D3) ubiquitin ligase, whereas the dominant form of D53 is resistant to SL-mediated degradation
- D3, D53, DWARF 53 acts as a repressor of strigolactone signalling in rice, Our results suggest a model of SL signalling that involves SL-dependent degradation of the D53 repressor mediated by the D14-D3 complex
- D53, HTD2~D88~D14, DWARF 53 acts as a repressor of strigolactone signalling in rice, Treatments with GR24, a synthetic SL analogue, cause D53 degradation via the proteasome in a manner that requires D14 and the SCF(D3) ubiquitin ligase, whereas the dominant form of D53 is resistant to SL-mediated degradation
- D53, HTD2~D88~D14, DWARF 53 acts as a repressor of strigolactone signalling in rice, Our results suggest a model of SL signalling that involves SL-dependent degradation of the D53 repressor mediated by the D14-D3 complex
- D3, D53, D14-SCFD3-dependent degradation of D53 regulates strigolactone signalling, The D53 gene product shares predicted features with the class I Clp ATPase proteins and can form a complex with the alpha/beta hydrolase protein DWARF 14 (D14) and the F-box protein DWARF 3 (D3), two previously identified signalling components potentially responsible for SL perception
- D3, D53, D14-SCFD3-dependent degradation of D53 regulates strigolactone signalling, We demonstrate that, in a D14- and D3-dependent manner, SLs induce D53 degradation by the proteasome and abrogate its activity in promoting axillary bud outgrowth
- D3, D53, D14-SCFD3-dependent degradation of D53 regulates strigolactone signalling, D14-SCF(D3)-dependent degradation of D53 regulates strigolactone signalling
- D53, HTD2~D88~D14, D14-SCFD3-dependent degradation of D53 regulates strigolactone signalling, The D53 gene product shares predicted features with the class I Clp ATPase proteins and can form a complex with the alpha/beta hydrolase protein DWARF 14 (D14) and the F-box protein DWARF 3 (D3), two previously identified signalling components potentially responsible for SL perception
- D53, HTD2~D88~D14, D14-SCFD3-dependent degradation of D53 regulates strigolactone signalling, We demonstrate that, in a D14- and D3-dependent manner, SLs induce D53 degradation by the proteasome and abrogate its activity in promoting axillary bud outgrowth
- D53, HTD2~D88~D14, D14-SCFD3-dependent degradation of D53 regulates strigolactone signalling, D14-SCF(D3)-dependent degradation of D53 regulates strigolactone signalling
- D53, HTD2~D88~D14, Identification and Molecular Mapping of Indica High-tillering Dwarf Mutant htd4, a Mild Phenotype Allelic Mutant of D14 in Rice Oryza sativa L.., Quantitative RT-PCR analyses revealed that expression levels of the genes D10, D17, D27, D3, and D14 increased significantly while expression of D53 decreased in htd4, compared to the wild type
- D53, OsSPL14~IPA1~WFP, IPA1 functions as a downstream transcription factor repressed by D53 in strigolactone signaling in rice., IPA1 functions as a downstream transcription factor repressed by D53 in strigolactone signaling in rice.
- D53, OsSPL14~IPA1~WFP, IPA1 functions as a downstream transcription factor repressed by D53 in strigolactone signaling in rice., Here we report that Ideal Plant Architecture 1 (IPA1), a key regulator of the plant architecture in rice, functions as a direct downstream component of D53 in regulating tiller number and SL-induced gene expression
- D53, OsSPL14~IPA1~WFP, IPA1 functions as a downstream transcription factor repressed by D53 in strigolactone signaling in rice., We showed that D53 interacts with IPA1 in vivo and in vitro and suppresses the transcriptional activation activity of IPA1
- D53, OsSPL14~IPA1~WFP, IPA1 functions as a downstream transcription factor repressed by D53 in strigolactone signaling in rice., We further showed that IPA1 could directly bind to the D53 promoter and plays a critical role in the feedback regulation of SL-induced D53 expression
- D53, OsSPL14~IPA1~WFP, IPA1 functions as a downstream transcription factor repressed by D53 in strigolactone signaling in rice., These findings reveal that IPA1 is likely one of the long-speculated transcription factors that act with D53 to mediate the SL-regulated tiller development in rice
Prev Next