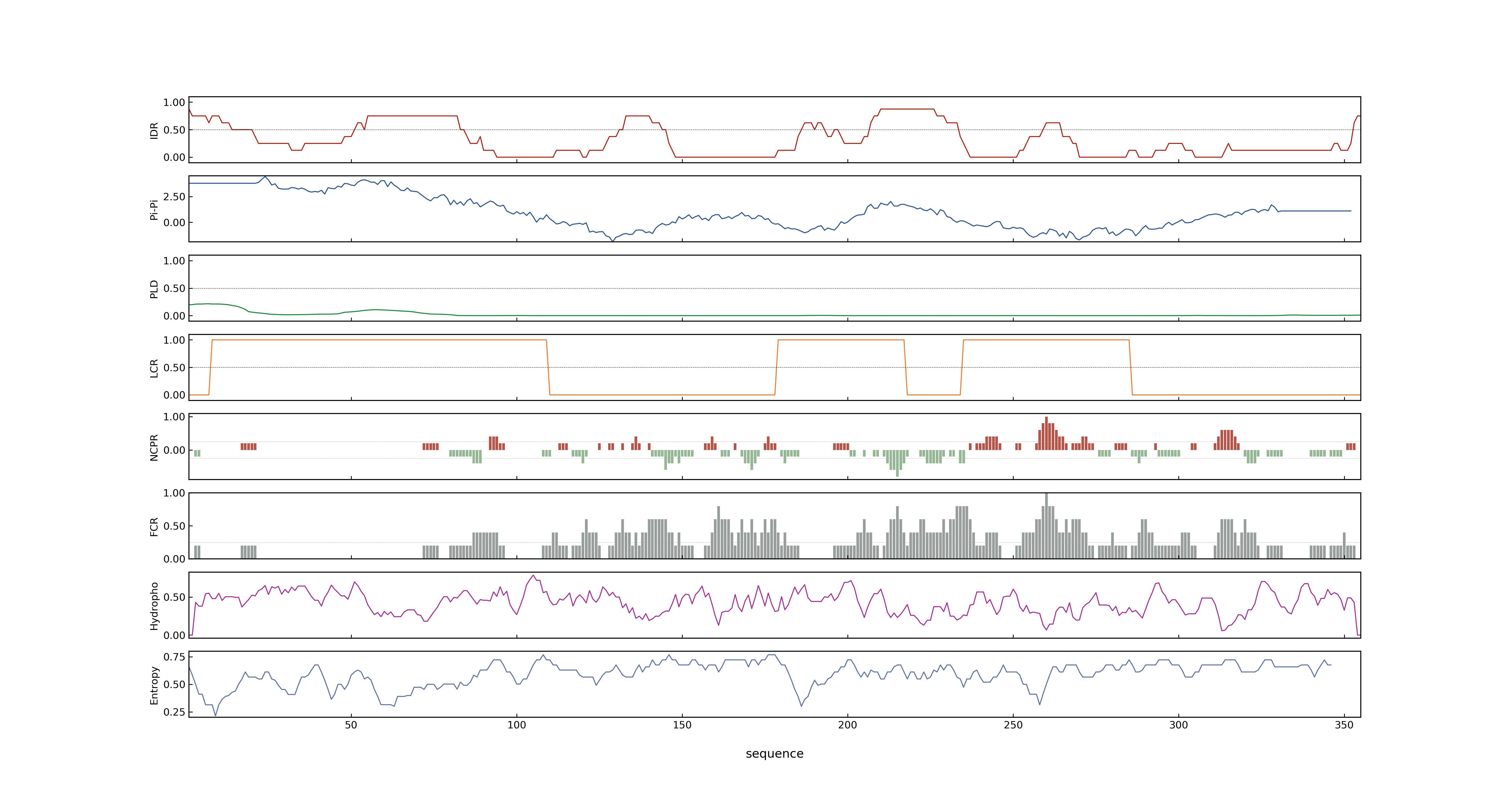
- Information
- Symbol: D6,OSH15,Oskn3
- MSU: LOC_Os07g03770
- RAPdb: Os07g0129700
- PSP score
- LOC_Os07g03770.1: 0.4075
- PLAAC score
- LOC_Os07g03770.1: 0
- pLDDT score
- NA
- MolPhase score
- LOC_Os07g03770.1: 0.99733847
- MolPhase Result
- Publication
- Loss-of-function mutations in the rice homeobox gene OSH15 affect the architecture of internodes resulting in dwarf plants, 1999, EMBO J.
- Overexpression of rice OSH genes induces ectopic shoots on leaf sheaths of transgenic rice plants, 2000, Dev Biol.
- Disruption of KNOX gene suppression in leaf by introducing its cDNA in rice, 2008, Plant Science.
- SUI-family genes encode phosphatidylserine synthases and regulate stem development in rice, 2013, Planta.
- Isolation and characterization of a rice homebox gene, OSH15, 1998, Plant Mol Biol.
- Characterization of the KNOX class homeobox genes Oskn2 and Oskn3 identified in a collection of cDNA libraries covering the early stages of rice embryogenesis, 1999, Plant Mol Biol.
- Developmental regulation and downstream effects of the knox class homeobox genes Oskn2 and Oskn3 from rice, 2002, Plant Mol Biol.
- KNOX homeobox genes are sufficient in maintaining cultured cells in an undifferentiated state in rice, 2001, Genesis.
- Regional expression of the rice KN1-type homeobox gene family during embryo, shoot, and flower development, 1999, Plant Cell.
- Positive autoregulation of a KNOX gene is essential for shoot apical meristem maintenance in rice, 2011, Plant Cell.
- Functional analysis of the conserved domains of a rice KNOX homeodomain protein, OSH15, 2001, Plant Cell.
- KNOX Protein OSH15 Induces Grain Shattering by Repressing Lignin Biosynthesis Genes., 2017, Plant Physiol.
- Genbank accession number
- Key message
- Whereas Oskn3 transformants showed the most pronounced phenotypic effects during vegetative development, Oskn2 transformants showed relatively mild alterations in the vegetative phase but a more severely affected flower morphology
- Overexpression of SUI1 and SUI2 caused outgrowths of internodes during vegetative development, and we showed that expression patterns of Oryza Sativa Homeobox 15 (OSH15) and Histone4 were impaired
- We produced transgenic rice calli, which constitutively express each of four KNOX family class 1 homeobox genes of rice, OSH1, OSH16, OSH15, and OSH71, and found that constitutive and ectopic expression of such genes inhibits normal regeneration from transformed calli, which showed continuous growth around their shoot-regenerating stages
- Whereas the expression of OSH1 continued within the shoot apical meristem, OSH15 expression within the shoot apical meristem ceased but became observable in a ring shaped pattern at the boundaries of some embryonic organs
- RNA in situ localization data suggest that OSH15 may play roles in the shoot organization during early embryogenesis and thereafter, OSH15 may be involved in morphogenetic events around the shoot apical meristem
- Loss-of-function mutations in the rice homeobox gene OSH15 affect the architecture of internodes resulting in dwarf plants
- Ectopic expression of Oskn2 or Oskn3 induced similar defects in panicle branching
- In transgenic plants carrying the OSH15 promoter-GUS reporter construct, the reporter gene was preferentially expressed in the AZ during young spikelet development
- The RNA in situ hybridization experiment also showed that OSH15 mRNAs were abundant in the AZ during spikelet development
- KNOX Protein OSH15 Induces Grain Shattering by Repressing Lignin Biosynthesis Genes.
- Knockdown mutations of OSH15 showed reduced seed shattering phenotypes
- Analyses of osh15 SH5-D double mutants showed that SH5 could not increase the degree of seed shattering when OSH15 was absent, indicating that SH5 functions together with OSH15
- In addition to the seed shattering phenotype, osh15 mutants displayed dwarfism and accumulated a higher amount of lignin in internodes due to increased expression of the genes involved in lignin biosynthesis
- We conclude that OSH15 and SH5 form a dimer that enhances seed shattering by directly inhibiting lignin biosynthesis genes
- Connection
- D6~OSH15~Oskn3, SUI2, SUI-family genes encode phosphatidylserine synthases and regulate stem development in rice, Overexpression of SUI1 and SUI2 caused outgrowths of internodes during vegetative development, and we showed that expression patterns of Oryza Sativa Homeobox 15 (OSH15) and Histone4 were impaired
- D6~OSH15~Oskn3, OsSUI1~OsPSS, SUI-family genes encode phosphatidylserine synthases and regulate stem development in rice, Overexpression of SUI1 and SUI2 caused outgrowths of internodes during vegetative development, and we showed that expression patterns of Oryza Sativa Homeobox 15 (OSH15) and Histone4 were impaired
- D6~OSH15~Oskn3, OSH1~Oskn1, Isolation and characterization of a rice homebox gene, OSH15, We analyzed the in situ mRNA localization of OSH15 through the whole plant life cycle, comparing the expression pattern with that of another rice homeobox gene, OSH1
- D6~OSH15~Oskn3, OSH1~Oskn1, Isolation and characterization of a rice homebox gene, OSH15, Whereas the expression of OSH1 continued within the shoot apical meristem, OSH15 expression within the shoot apical meristem ceased but became observable in a ring shaped pattern at the boundaries of some embryonic organs
- D6~OSH15~Oskn3, OSH1~Oskn1, Characterization of the KNOX class homeobox genes Oskn2 and Oskn3 identified in a collection of cDNA libraries covering the early stages of rice embryogenesis, Two of these, Oskn2 and Oskn3, encode newly described KNOX genes, whereas the third (Oskn1) corresponds to the previously described OSH1 gene
- D6~OSH15~Oskn3, OSH1~Oskn1, Characterization of the KNOX class homeobox genes Oskn2 and Oskn3 identified in a collection of cDNA libraries covering the early stages of rice embryogenesis, Whereas OSH1 was previously proposed to function also in SAM maintenance, Oskn3 may be involved in patterning organ positions, as its expression was found to mark the boundaries of different embryonic organs following SAM formation
- D6~OSH15~Oskn3, OSH1~Oskn1, Characterization of the KNOX class homeobox genes Oskn2 and Oskn3 identified in a collection of cDNA libraries covering the early stages of rice embryogenesis, Transgenic expression of Oskn2 and Oskn3 in tobacco further supported their involvement in cell fate determination, like previously reported for Knotted1 and OSH1 ectopic expression
- D6~OSH15~Oskn3, OSH71~Oskn2, Characterization of the KNOX class homeobox genes Oskn2 and Oskn3 identified in a collection of cDNA libraries covering the early stages of rice embryogenesis, Two of these, Oskn2 and Oskn3, encode newly described KNOX genes, whereas the third (Oskn1) corresponds to the previously described OSH1 gene
- D6~OSH15~Oskn3, OSH71~Oskn2, Characterization of the KNOX class homeobox genes Oskn2 and Oskn3 identified in a collection of cDNA libraries covering the early stages of rice embryogenesis, Transgenic expression of Oskn2 and Oskn3 in tobacco further supported their involvement in cell fate determination, like previously reported for Knotted1 and OSH1 ectopic expression
- D6~OSH15~Oskn3, OSH71~Oskn2, Characterization of the KNOX class homeobox genes Oskn2 and Oskn3 identified in a collection of cDNA libraries covering the early stages of rice embryogenesis, Whereas Oskn3 transformants showed the most pronounced phenotypic effects during vegetative development, Oskn2 transformants showed relatively mild alterations in the vegetative phase but a more severely affected flower morphology
- D6~OSH15~Oskn3, OSH71~Oskn2, Characterization of the KNOX class homeobox genes Oskn2 and Oskn3 identified in a collection of cDNA libraries covering the early stages of rice embryogenesis, Characterization of the KNOX class homeobox genes Oskn2 and Oskn3 identified in a collection of cDNA libraries covering the early stages of rice embryogenesis
- D6~OSH15~Oskn3, OSH71~Oskn2, Developmental regulation and downstream effects of the knox class homeobox genes Oskn2 and Oskn3 from rice, Here, the transcriptional control of two rice knox genes, Oskn2 and Oskn3, was addressed, showing that the promoter sequences of both genes mediate the initial down-regulation during lateral organ formation, but are insufficient to keep expression in lateral organs stably off
- D6~OSH15~Oskn3, OSH71~Oskn2, Developmental regulation and downstream effects of the knox class homeobox genes Oskn2 and Oskn3 from rice, Ectopic expression of Oskn2 or Oskn3 induced similar defects in panicle branching
- D6~OSH15~Oskn3, OSH71~Oskn2, Developmental regulation and downstream effects of the knox class homeobox genes Oskn2 and Oskn3 from rice, This was supported by the observation that Oskn3 protein but not Oskn2 could interact with two reported recognition sequences of a KNOX protein from barley
- D6~OSH15~Oskn3, OSH71~Oskn2, Developmental regulation and downstream effects of the knox class homeobox genes Oskn2 and Oskn3 from rice, Finally, protein-protein interactions may contribute to the functioning of KNOX proteins, as the ability of Oskn3 and Oskn2 to form heterodimers could be demonstrated
- D6~OSH15~Oskn3, OSH71~Oskn2, Developmental regulation and downstream effects of the knox class homeobox genes Oskn2 and Oskn3 from rice, Developmental regulation and downstream effects of the knox class homeobox genes Oskn2 and Oskn3 from rice
- D6~OSH15~Oskn3, OSH1~Oskn1, KNOX homeobox genes are sufficient in maintaining cultured cells in an undifferentiated state in rice, We produced transgenic rice calli, which constitutively express each of four KNOX family class 1 homeobox genes of rice, OSH1, OSH16, OSH15, and OSH71, and found that constitutive and ectopic expression of such genes inhibits normal regeneration from transformed calli, which showed continuous growth around their shoot-regenerating stages
- D6~OSH15~Oskn3, OSH71~Oskn2, KNOX homeobox genes are sufficient in maintaining cultured cells in an undifferentiated state in rice, We produced transgenic rice calli, which constitutively express each of four KNOX family class 1 homeobox genes of rice, OSH1, OSH16, OSH15, and OSH71, and found that constitutive and ectopic expression of such genes inhibits normal regeneration from transformed calli, which showed continuous growth around their shoot-regenerating stages
- D6~OSH15~Oskn3, OSH1~Oskn1, Positive autoregulation of a KNOX gene is essential for shoot apical meristem maintenance in rice, Double mutants of osh1 and d6, a loss-of-function mutant of OSH15, fail to establish the SAM both in embryogenesis and regeneration
- D6~OSH15~Oskn3, OSH1~Oskn1, Positive autoregulation of a KNOX gene is essential for shoot apical meristem maintenance in rice, We demonstrate that OSH1 directly binds to five KNOX loci, including OSH1 and OSH15, through evolutionarily conserved cis-elements and that the positive autoregulation of OSH1 is indispensable for its own expression and SAM maintenance
- D6~OSH15~Oskn3, qSH1, KNOX Protein OSH15 Induces Grain Shattering by Repressing Lignin Biosynthesis Genes., Co-immunoprecipitation experiments revealed that OSH15 interacts with SH5 and qSH1, two proteins in the BELL homeobox family
- D6~OSH15~Oskn3, SH5, KNOX Protein OSH15 Induces Grain Shattering by Repressing Lignin Biosynthesis Genes., Co-immunoprecipitation experiments revealed that OSH15 interacts with SH5 and qSH1, two proteins in the BELL homeobox family
- D6~OSH15~Oskn3, SH5, KNOX Protein OSH15 Induces Grain Shattering by Repressing Lignin Biosynthesis Genes., Analyses of osh15 SH5-D double mutants showed that SH5 could not increase the degree of seed shattering when OSH15 was absent, indicating that SH5 functions together with OSH15
- D6~OSH15~Oskn3, SH5, KNOX Protein OSH15 Induces Grain Shattering by Repressing Lignin Biosynthesis Genes., Chromatin immunoprecipitation assays demonstrated that both OSH15 and SH5 directly interact with CAD2 chromatin
- D6~OSH15~Oskn3, SH5, KNOX Protein OSH15 Induces Grain Shattering by Repressing Lignin Biosynthesis Genes., We conclude that OSH15 and SH5 form a dimer that enhances seed shattering by directly inhibiting lignin biosynthesis genes
Prev Next