- Information
- Symbol: DRO1
- MSU: LOC_Os09g26840
- RAPdb: Os09g0439800
- PSP score
- LOC_Os09g26840.1: 0.4394
- PLAAC score
- LOC_Os09g26840.1: 0
- pLDDT score
- 58.95
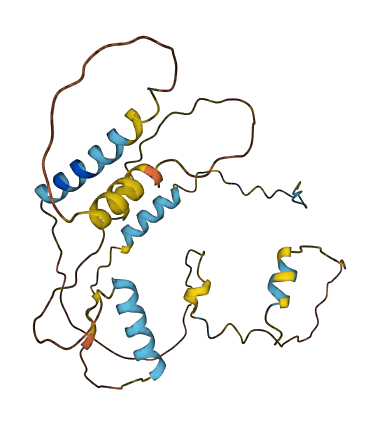
- Protein Structure from AlphaFold and UniProt
- MolPhase score
- LOC_Os09g26840.1: 0.69513934
- MolPhase Result
- Publication
- Genbank accession number
- Key message
- Here we demonstrate that alteration of root system architecture improves drought avoidance through the cloning and characterization of DEEPER ROOTING 1 (DRO1), a rice quantitative trait locus controlling root growth angle
- DRO1 is negatively regulated by auxin and is involved in cell elongation in the root tip that causes asymmetric root growth and downward bending of the root in response to gravity
- Introducing DRO1 into a shallow-rooting rice cultivar by backcrossing enabled the resulting line to avoid drought by increasing deep rooting, which maintained high yield performance under drought conditions relative to the recipient cultivar
- The RDR QTL Dro1 (Deeper rooting 1) was mapped between the markers RM24393 and RM7424, which delimit a 608
- To clarify the influence of Dro1 in an upland field, the root distribution in different soil layers was quantified by means of core sampling
- A line homozygous for the KP allele of Dro1 (Dro1-KP) and IR64 did not differ in root dry weight in the shallow soil layers (0-25 cm), but root dry weight of Dro1-KP in deep soil layers (25-50 cm) was significantly greater than that of IR64, suggesting that Dro1 plays a crucial role in increased deep rooting under upland field conditions
- Dro1, a major QTL involved in deep rooting of rice under upland field conditions
- Higher expression of DRO1 increases the root growth angle, whereby roots grow in a more downward direction
- Connection
Prev Next