- Information
- Symbol: DSM2
- MSU: LOC_Os03g03370
- RAPdb: Os03g0125100
- PSP score
- LOC_Os03g03370.1: 0.0048
- LOC_Os03g03370.2: 0.3063
- PLAAC score
- LOC_Os03g03370.1: 0
- LOC_Os03g03370.2: 0
- pLDDT score
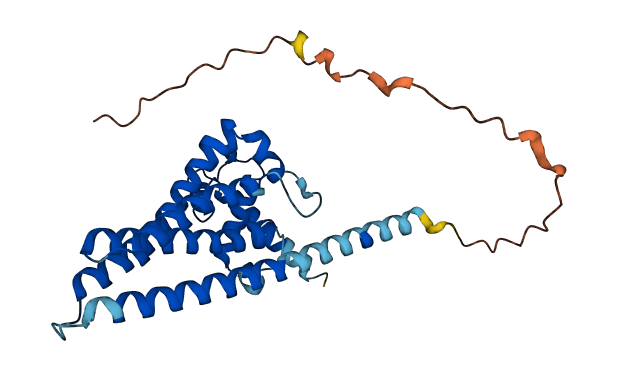
- 83.57
- Protein Structure from AlphaFold and UniProt
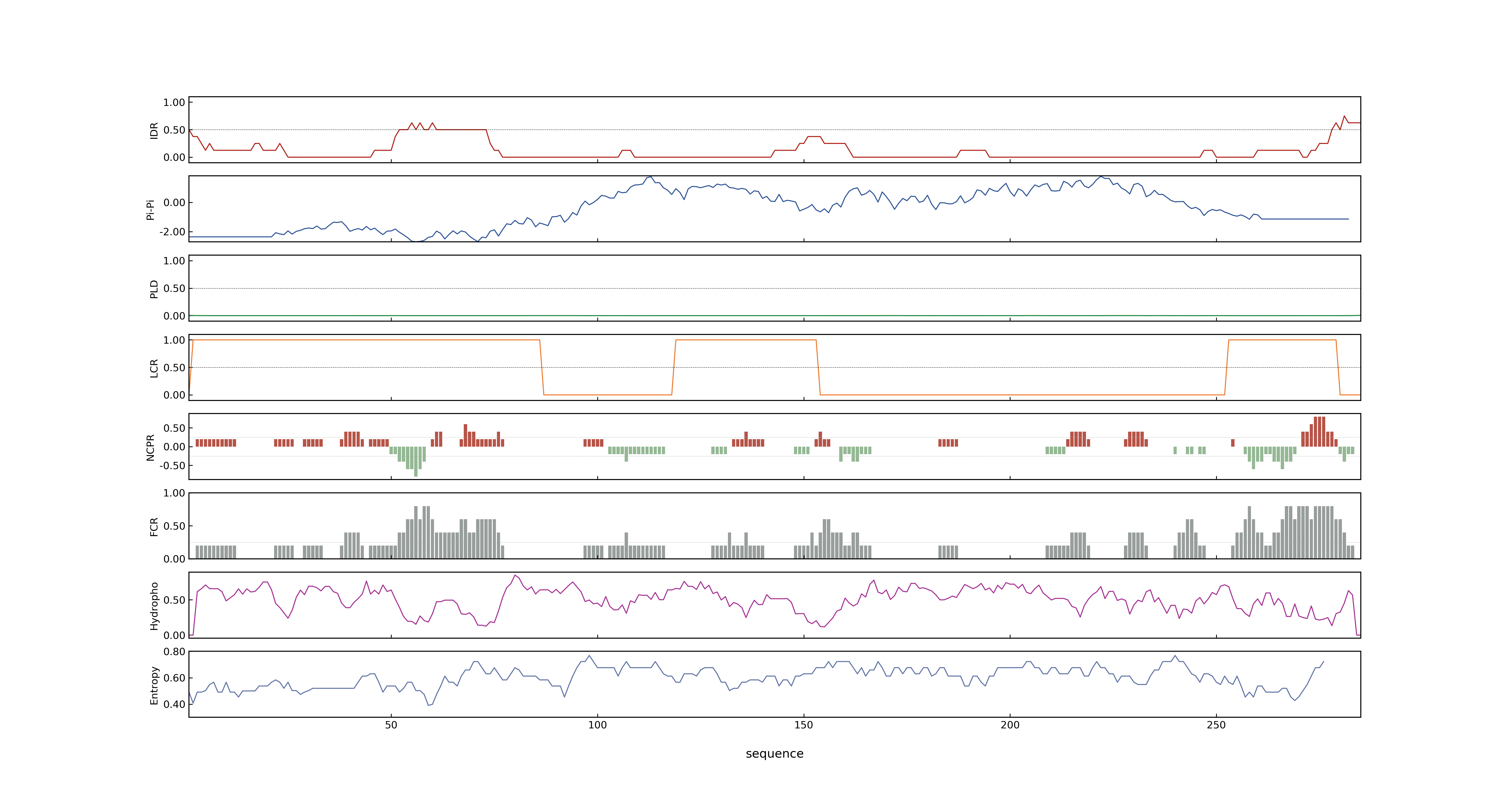
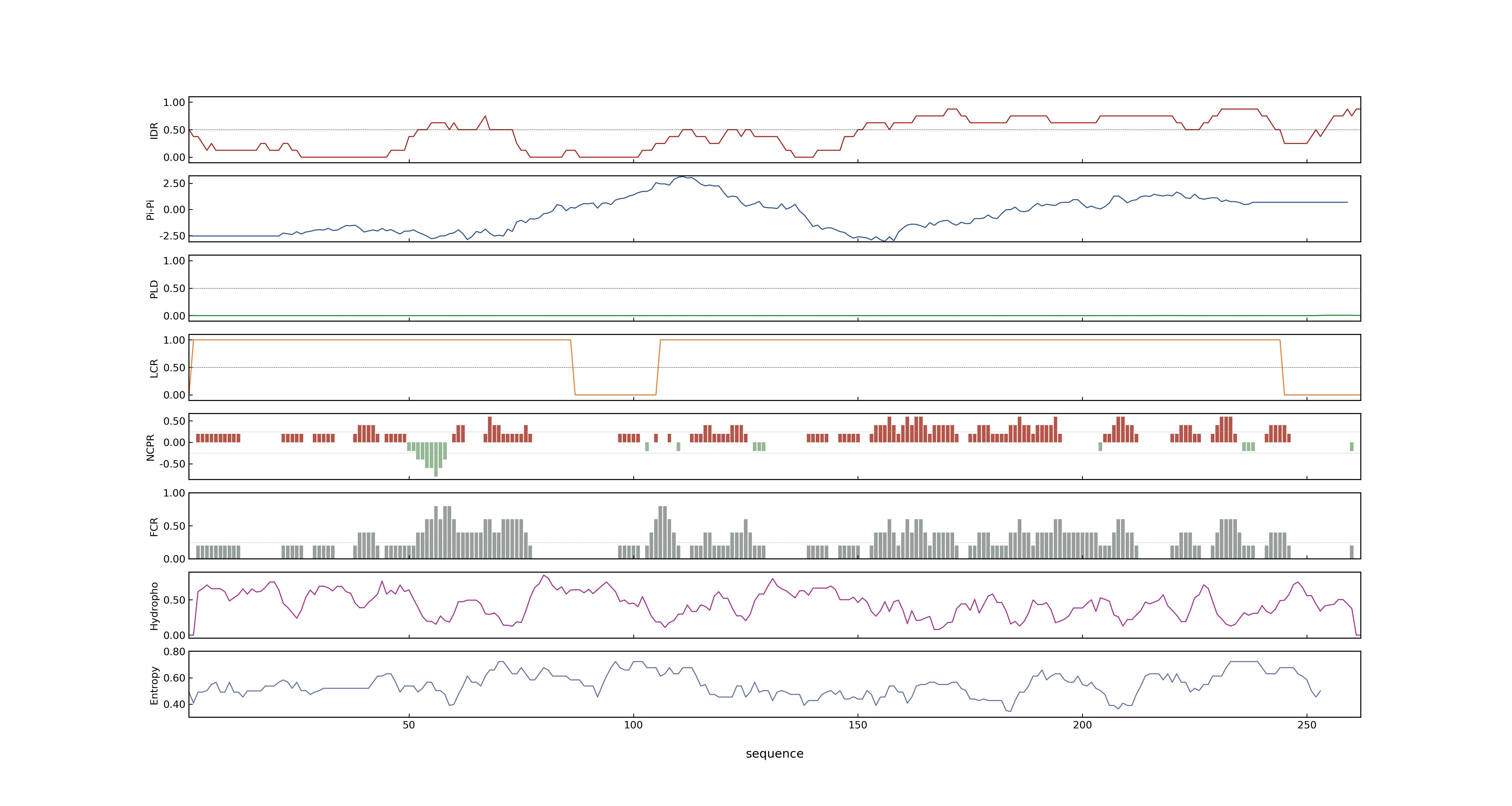
- MolPhase score
- LOC_Os03g03370.1: 0.03697985
- LOC_Os03g03370.2: 0.94223320
- MolPhase Result
- Publication
- Genbank accession number
- Key message
- To identify critical genes for drought resistance in rice (Oryza sativa), we screened T-DNA mutants and identified a drought-hypersensitive mutant, dsm2
- The amounts of zeaxanthin and ABA were significantly reduced in two allelic dsm2 mutants after drought stress compared with the wild type
- Overexpression of DSM2 in rice resulted in significantly increased resistance to drought and oxidative stresses and increases of the xanthophylls and nonphotochemical quenching
- We conclude that the DSM2 gene significantly contributes to control of the xanthophyll cycle and ABA synthesis, both of which play critical roles in the establishment of drought resistance in rice
- Characterization of the beta-carotene hydroxylase gene DSM2 conferring drought and oxidative stress resistance by increasing xanthophylls and abscisic acid synthesis in rice
- DSM2 is a chloroplast protein, and the response of DSM2 to environmental stimuli is distinctive from the other two BCH members in rice
- Connection
Prev Next