- Information
- Symbol: FC1,OsCAD7
- MSU: LOC_Os04g52280
- RAPdb: Os04g0612700
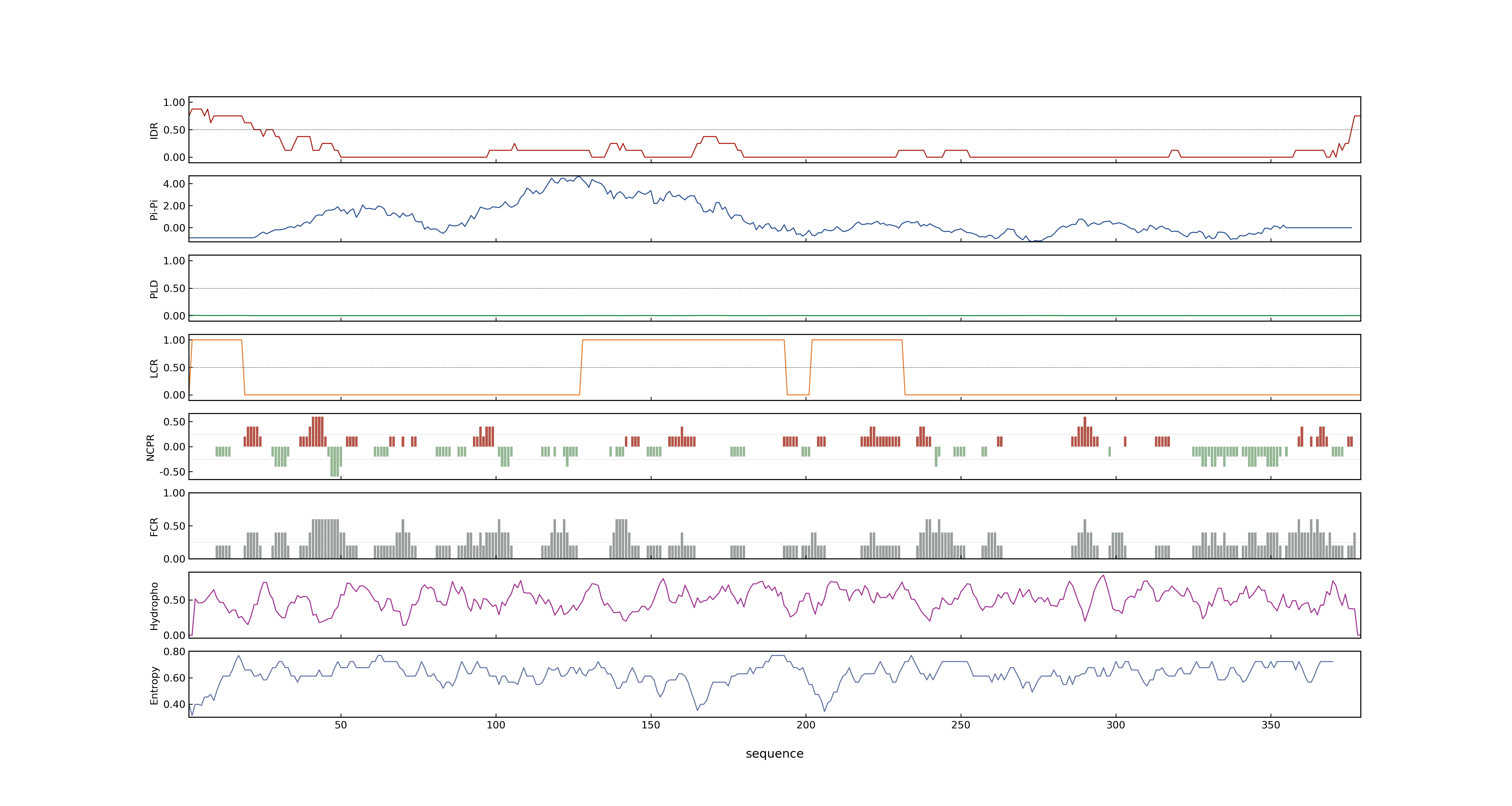
- PSP score
- LOC_Os04g52280.1: 0.1043
- PLAAC score
- LOC_Os04g52280.1: 0
- pLDDT score
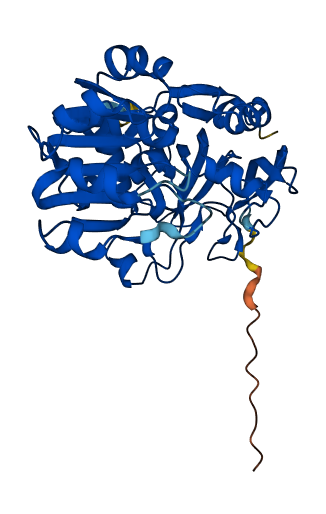
- 93.12
- Protein Structure from AlphaFold and UniProt
- MolPhase score
- LOC_Os04g52280.1: 0.98332190
- MolPhase Result
- Publication
- FLEXIBLE CULM 1 encoding a cinnamyl-alcohol dehydrogenase controls culm mechanical strength in rice, 2009, Plant Mol Biol.
- FINE CULM1 FC1 works downstream of strigolactones to inhibit the outgrowth of axillary buds in rice, 2010, Plant Cell Physiol.
-
Genbank accession number
- Key message
- We found that the increased tillering phenotype of fine culm1 (fc1) mutants of rice is not rescued by the application of 1 microM GR24, a synthetic SL analog
- Treatment with a high concentration of GR24 (10 microM) causes suppression of tiller growth in wild-type plants, but is not effective on fc1 mutants, implying that proper FC1 functioning is required for SLs to inhibit bud growth
- Overexpression of FC1 partially rescued d3-2 defects in the tiller growth and plant height
- An in situ hybridization analysis showed that FC1 mRNA accumulates in axillary buds, the shoot apical meristem, young leaves, vascular tissues and the tips of crown roots
- We propose that FC1 acts as an integrator of multiple signaling pathways and is essential to the fine-tuning of shoot branching in rice
- To understand the molecular mechanisms that control culm mechanical strength, we identified a flexible culm1 (fc1) mutant by screening a rice T-DNA insertion mutant library
- In this study, we cloned the FLEXIBLE CULM1 (FC1) gene in rice using a T-DNA tagging approach
- Our results indicated that FC1 plays an important role in the biosynthesis of lignin and the control of culm strength in rice
- On the other hand, the expression level of FC1 is negatively regulated by cytokinin treatment
- FINE CULM1 (FC1) works downstream of strigolactones to inhibit the outgrowth of axillary buds in rice
- FC1 encodes a cinnamyl-alcohol dehydrogenase and is mainly expressed in the sclerenchyma cells of the secondary cell wall and vascular bundle region
- In these types of cells, a deficiency of FC1 in the fc1 mutant caused a reduction in cell wall thickness, as well as a decrease in lignin
- Further histological and biochemical analyses revealed that the p-hydroxyphenyl and guaiacyl monomers in fc1 cell wall were reduced greatly
- Extracts from the first internodes and panicles of the fc1 plants exhibited drastically reduced cinnamyl-alcohol dehydrogenase activity
- Connection
Prev Next