- Information
- Symbol: FCA,OsFCA
- MSU: LOC_Os09g03610
- RAPdb: Os09g0123200
- PSP score
- LOC_Os09g03610.2: 0.9947
- LOC_Os09g03610.1: 0.9947
- LOC_Os09g03610.4: 0.9939
- LOC_Os09g03610.3: 0.9957
- PLAAC score
- LOC_Os09g03610.2: 63.136
- LOC_Os09g03610.1: 63.136
- LOC_Os09g03610.4: 63.136
- LOC_Os09g03610.3: 63.136
- pLDDT score
- 55.76
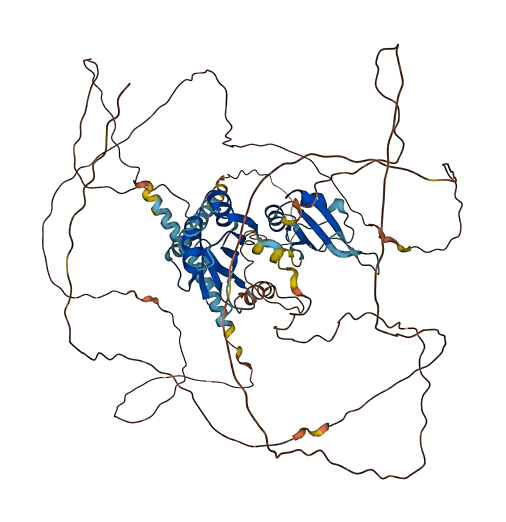
- Protein Structure from AlphaFold and UniProt
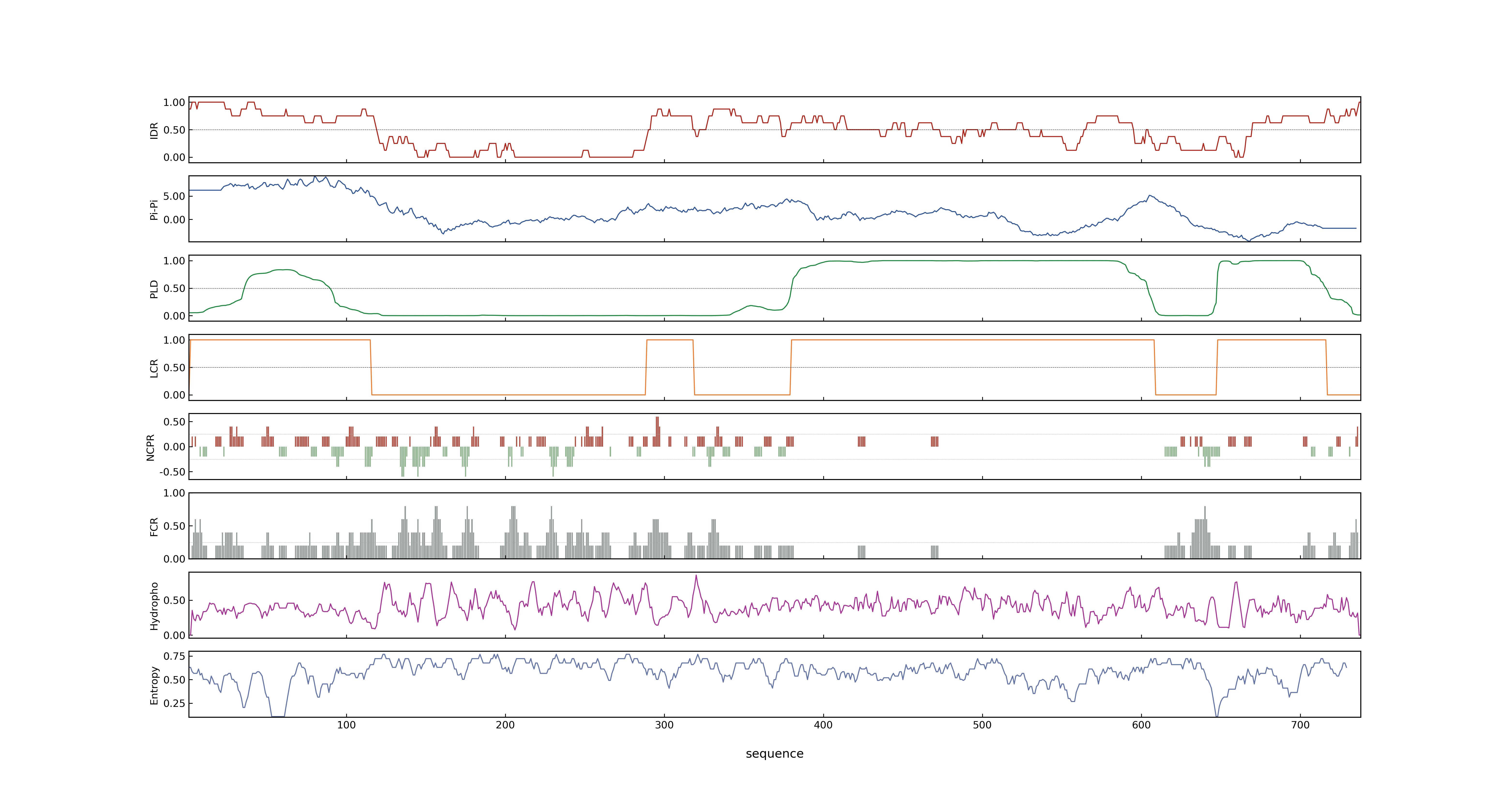
- MolPhase score
- LOC_Os09g03610.1: 0.99995136
- LOC_Os09g03610.2: 0.99995136
- LOC_Os09g03610.3: 0.99994957
- LOC_Os09g03610.4: 0.99995803
- MolPhase Result
- Publication
- Overexpression of the rFCA RNA recognition motif affects morphologies modifications in rice Oryza sativa L., 2007, Biosci Rep.
- Alternative splicing and expression analysis of OsFCA FCA in Oryza sativa L., a gene homologous to FCA in Arabidopsis, 2006, DNA Seq.
- OsFY, a Homolog of AtFY, Encodes a Protein that Can Interact with OsFCA-ÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂó in Rice Oryza sativa L., 2006, Acta Biochimica et Biophysica Sinica.
- Survey of rice proteins interacting with OsFCA and OsFY proteins which are homologous to the Arabidopsis flowering time proteins, FCA and FY, 2009, Plant Cell Physiol.
- Conservation and divergence of FCA function between Arabidopsis and rice, 2005, Plant Mol Biol.
- Genbank accession number
- Key message
- The FCA/FY interaction is also required for the regulation of FLC expression, a major floral repressor in Arabidopsis
- The expression of OsFCA-1 is steady in the leaves of three different stage, but up-regulated in young spikelet of primary branch-differentiating stage and down-regulated in young spikelet of pistil and stamen-differentiating stage
- In order to acquire further insight into the control of heading dates in rice, we isolated and conducted an expression analysis on OsFCA, which exhibited 38% sequence homology with Arabidopsis FCA
- The FCA floral promotion gene in Arabidopsis encodes a protein, containing two RNA recognition motifs (RRM) and a WW protein interaction domain
- Survey of rice proteins interacting with OsFCA and OsFY proteins which are homologous to the Arabidopsis flowering time proteins, FCA and FY
- Recently, alternative RNA processing of OsFCA was observed in rice, which strongly suggested the existence of an autonomous flowering pathway in rice
- The beta and gamma transcripts of the OsFCA gene were detected via Northern analysis in the leaves, roots, and flowers of the plant
- The FCA protein is involved in controlling flowering time and plays more general roles in RNA-mediated chromatin silencing in Arabidopsis
- FCA and FY are flowering time related genes involved in the autonomous flowering pathway in Arabidopsis
- The overexpression of OsFCA cDNA, driven by the 35S promoter, was shown to partially rescue the late flowering phenotype of the fca mutant, suggesting that the functions of the OsFCA and the FCA are partially overlapped, despite the lack of an apparent FLC homologue in the rice genome
- These results indicate that the autonomous flowering pathway is present in monocots, and the regulation through FY and FCA interaction is conserved between monocots and dicots
- Connection
- FCA~OsFCA, OsFY, OsFY, a Homolog of AtFY, Encodes a Protein that Can Interact with OsFCA-ÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂó in Rice Oryza sativa L., FCA and FY are flowering time related genes involved in the autonomous flowering pathway in Arabidopsis
- FCA~OsFCA, OsFY, OsFY, a Homolog of AtFY, Encodes a Protein that Can Interact with OsFCA-ÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂó in Rice Oryza sativa L., FCA interacts with FY to regulate the alternative processing of FCA pre-mRNA
- FCA~OsFCA, OsFY, OsFY, a Homolog of AtFY, Encodes a Protein that Can Interact with OsFCA-ÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂó in Rice Oryza sativa L., The FCA/FY interaction is also required for the regulation of FLC expression, a major floral repressor in Arabidopsis
- FCA~OsFCA, OsFY, OsFY, a Homolog of AtFY, Encodes a Protein that Can Interact with OsFCA-ÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂó in Rice Oryza sativa L., The protein-protein interaction between OsFY and OsFCA-gamma, the key feature of their gene function, was also demonstrated using the yeast two-hybrid system
- FCA~OsFCA, OsFY, OsFY, a Homolog of AtFY, Encodes a Protein that Can Interact with OsFCA-ÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂó in Rice Oryza sativa L., These results indicate that the autonomous flowering pathway is present in monocots, and the regulation through FY and FCA interaction is conserved between monocots and dicots
- FCA~OsFCA, OsFY, OsFY, a Homolog of AtFY, Encodes a Protein that Can Interact with OsFCA-ÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂó in Rice Oryza sativa L., OsFY, a Homolog of AtFY, Encodes a Protein that Can Interact with OsFCA-ÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂó in Rice (Oryza sativa L.)
- FCA~OsFCA, OsFY, Survey of rice proteins interacting with OsFCA and OsFY proteins which are homologous to the Arabidopsis flowering time proteins, FCA and FY, The FCA protein interacts with FY, a polyadenylation factor, via its WW domain
- FCA~OsFCA, OsFY, Survey of rice proteins interacting with OsFCA and OsFY proteins which are homologous to the Arabidopsis flowering time proteins, FCA and FY, Here, we found that the OsFCA protein could interact through its WW domain with the following proteins: OsFY, a protein containing a CID domain present in RNA-processing factors such as Pcf11 and Nrd1; a protein similar to splicing factor SF1; a protein similar to FUSE splicing factor; and OsMADS8
- FCA~OsFCA, OsFY, Survey of rice proteins interacting with OsFCA and OsFY proteins which are homologous to the Arabidopsis flowering time proteins, FCA and FY, Taken together, our data suggest that OsFCA could interact with several proteins other than OsFY through its WW domain and may play several roles in rice
- FCA~OsFCA, OsFY, Survey of rice proteins interacting with OsFCA and OsFY proteins which are homologous to the Arabidopsis flowering time proteins, FCA and FY, Survey of rice proteins interacting with OsFCA and OsFY proteins which are homologous to the Arabidopsis flowering time proteins, FCA and FY
- FCA~OsFCA, OsMADS8~OsMADS24, Survey of rice proteins interacting with OsFCA and OsFY proteins which are homologous to the Arabidopsis flowering time proteins, FCA and FY, Here, we found that the OsFCA protein could interact through its WW domain with the following proteins: OsFY, a protein containing a CID domain present in RNA-processing factors such as Pcf11 and Nrd1; a protein similar to splicing factor SF1; a protein similar to FUSE splicing factor; and OsMADS8
Prev Next