- Information
- Symbol: FLO7
- MSU: LOC_Os10g32680
- RAPdb: Os10g0463800
- pLDDT score
- 88.82
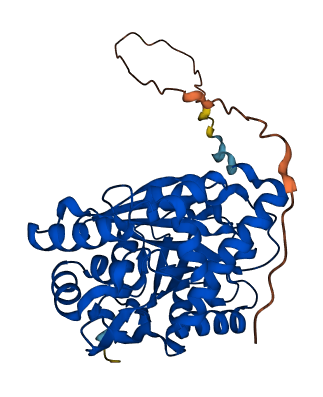
- Protein Structure from AlphaFold and UniProt
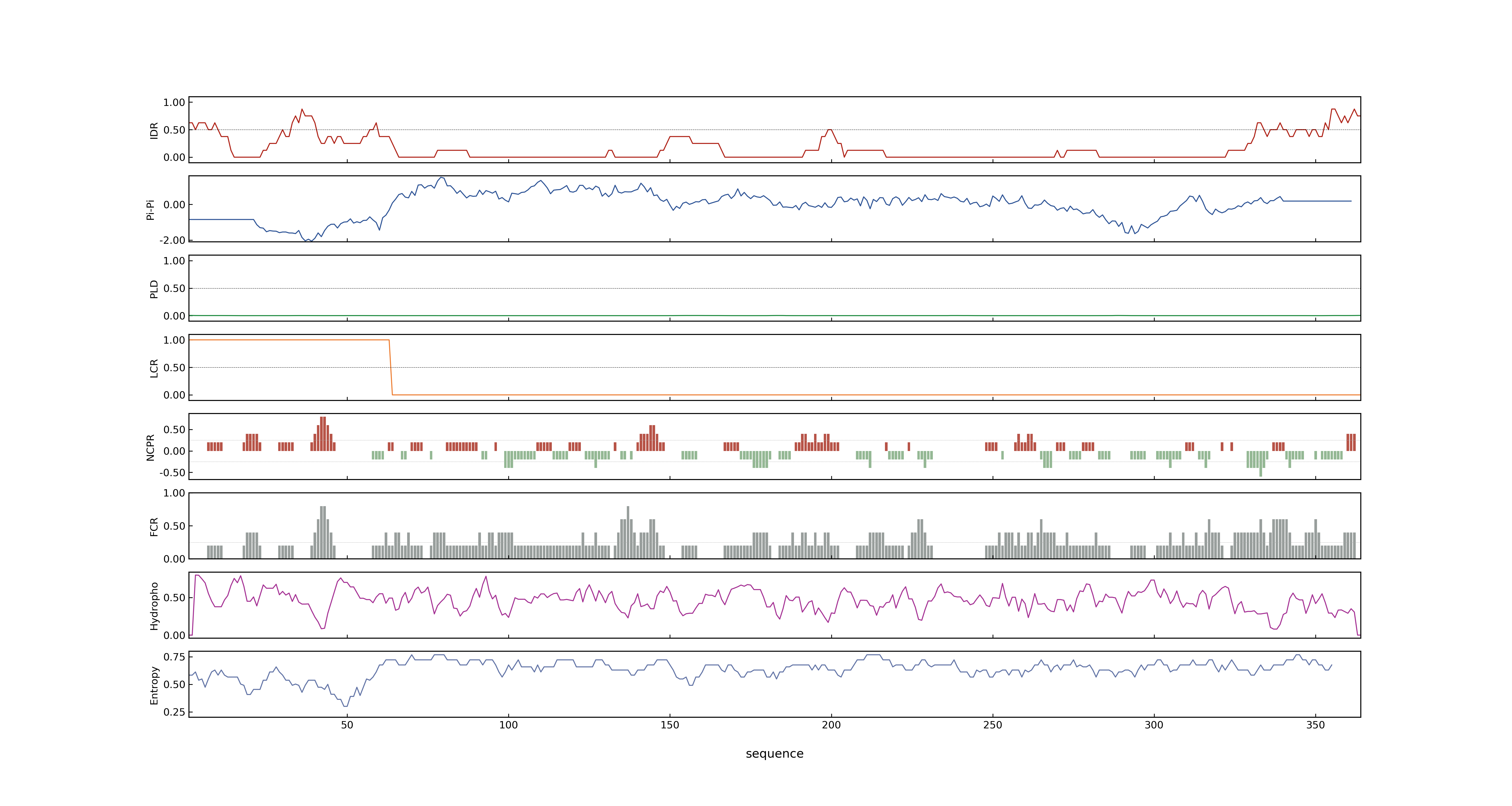
- MolPhase score
- LOC_Os10g32680.1: 0.07539596
- LOC_Os10g32680.2: 0.00178600
- LOC_Os10g32680.3: 0.00167585
- MolPhase Result
- Publication
- PSP score
- LOC_Os10g32680.3: 0.1031
- LOC_Os10g32680.2: 0.0293
- LOC_Os10g32680.1: 0.02
- PLAAC score
- LOC_Os10g32680.3: 0
- LOC_Os10g32680.2: 0
- LOC_Os10g32680.1: 0
-
Genbank accession number
- Key message
- Notably, flo7 peripheral endosperm cells showed obvious defects in compound starch grain development
- Together, our findings identify FLO7 as a unique plant regulator required for starch synthesis and amyloplast development within the peripheral endosperm and provide new insights into the spatial regulation of endosperm development in rice
- Map-based cloning of FLO7 revealed that it encodes a protein of unknown function
- Consistent with the phenotypic alternation in flo7 endosperm, the flo7 mutant had reduced amylose content and seriously disrupted amylopectin structure only in the peripheral endosperm
- FLO7 harbors an N-terminal transit peptide capable of targeting functional FLO7 fused to green fluorescent protein to amyloplast stroma in developing endosperm cells, and a domain of unknown function 1338 (DUF1338) that is highly conserved in green plants
- Furthermore, our combined ÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂò-glucuronidase activity and RNA in situ hybridization assays showed that the FLO7 gene was expressed ubiquitously but exhibited a specific expression in the endosperm periphery
- Moreover, a set of in vivo experiments demonstrated that the missing 32 aa in the flo7 mutant protein are essential for the stable accumulation of FLO7 in the endosperm
- Connection
Prev Next