- Information
- Symbol: GL3.1,qGL3-1,qGL3,OsPPKL1
- MSU: LOC_Os03g44500
- RAPdb: Os03g0646900
- PSP score
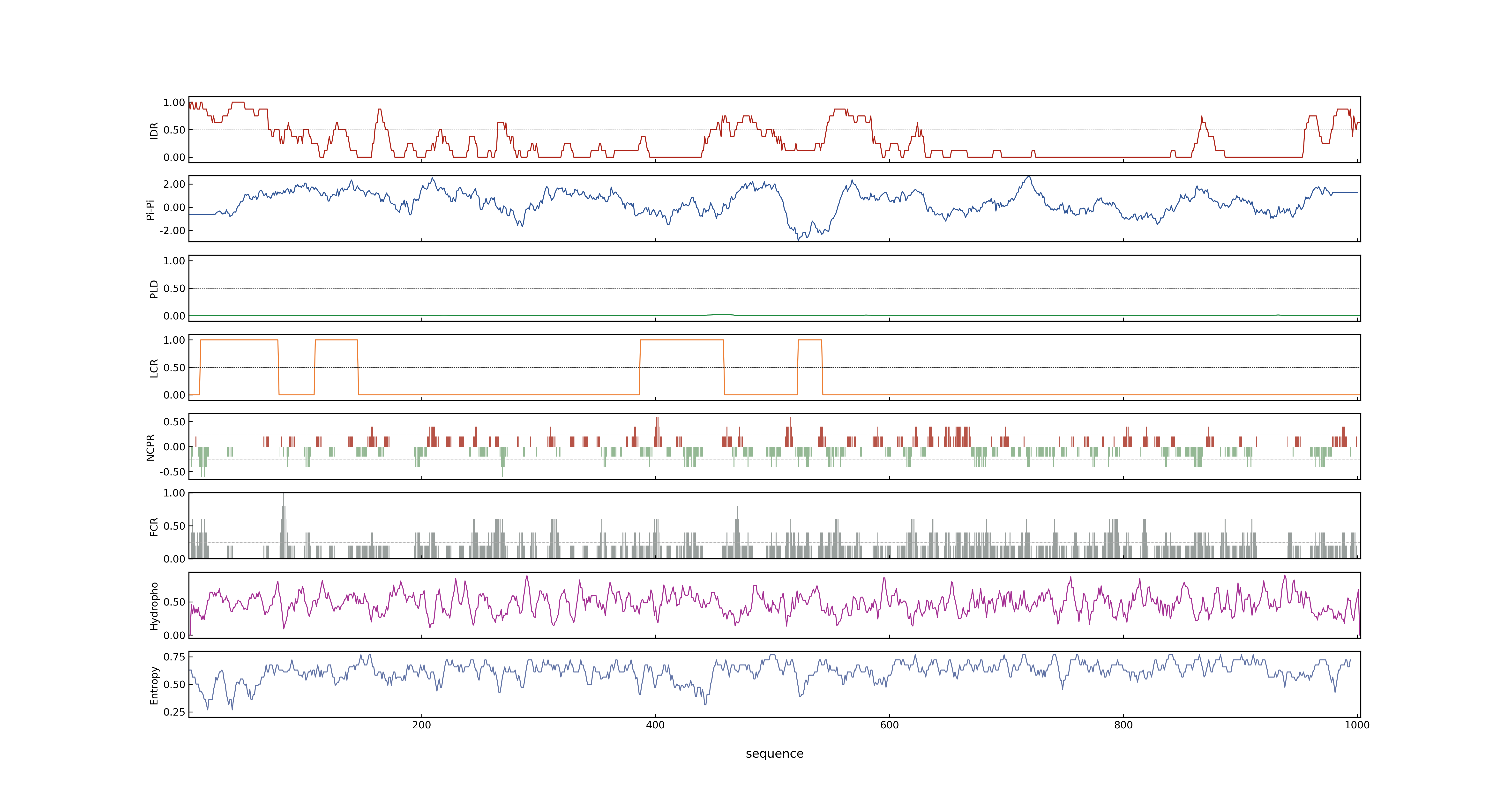
- LOC_Os03g44500.1: 0.7746
- PLAAC score
- LOC_Os03g44500.1: 0
- pLDDT score
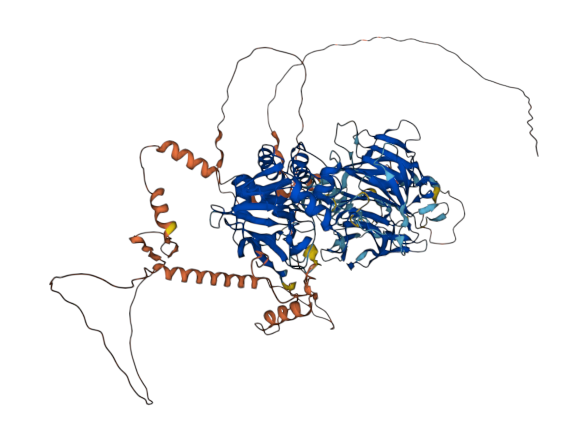
- 70.5
- Protein Structure from AlphaFold and UniProt
- MolPhase score
- LOC_Os03g44500.1: 0.96287715
- MolPhase Result
- Publication
- The novel quantitative trait locus GL3.1 controls rice grain size and yield by regulating Cyclin-T1;3, 2012, Cell Res.
- A Kelch motif-containing serine/threonine protein phosphatase determines the large grain QTL trait in rice, 2012, J Integr Plant Biol.
- Rare allele of OsPPKL1 associated with grain length causes extra-large grain and a significant yield increase in rice, 2012, Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A.
- The additive effects of GS3 and qGL3 on rice grain length regulation revealed by genetic and transcriptome comparisons., 2015, BMC Plant Biol.
- Genbank accession number
- Key message
- Here, we report the cloning and functional characterization of a major grain length QTL, qGL3, which encodes a putative protein phosphatase with Kelch-like repeat domain (OsPPKL1)
- Transgenic studies showed that OsPPKL1 and OsPPKL3 function as negative regulators of grain length, whereas OsPPKL2 as a positive regulator
- Rare allele of OsPPKL1 associated with grain length causes extra-large grain and a significant yield increase in rice
- Field trials showed that the application of the qgl3 allele could significantly increase grain yield in both inbred and hybrid rice varieties, due to its favorable effect on grain length, filling, and weight
- We found a rare allele qgl3 that leads to a long grain phenotype by an aspartate-to-glutamate transition in a conserved AVLDT motif of the second Kelch domain in OsPPKL1
- In particular, qGL3-1, a newly-identified grain length QTL with the highest LOD value and largest phenotypic variation, was fine-mapped to the 17 kb region of chromosome 3
- The novel quantitative trait locus GL3.1 controls rice grain size and yield by regulating Cyclin-T1;3
- Comparative analysis of primary panicle transcriptomes in the four NILs revealed that the genes affected by GS3 and qGL3 partially overlapped, and both loci might be involved in brassinosteroid signaling
- The additive effects of GS3 and qGL3 on rice grain length regulation revealed by genetic and transcriptome comparisons.
- By comparing the grain lengths of 93-11, NIL-GS3, NIL-qgl3 and NIL-GS3/qgl3, we investigated the effects of GS3, qGL3 and GS3ÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂâÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂâÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂqGL3 interaction on grain length based on two-way ANOVA
- We found that GS3 and qGL3 had additive effects on rice grain length regulation
- Connection
- Cyclin-T1;3, GL3.1~qGL3-1~qGL3~OsPPKL1, The novel quantitative trait locus GL3.1 controls rice grain size and yield by regulating Cyclin-T1;3, The novel quantitative trait locus GL3.1 controls rice grain size and yield by regulating Cyclin-T1;3
- GL3.1~qGL3-1~qGL3~OsPPKL1, OsPPKL2, Rare allele of OsPPKL1 associated with grain length causes extra-large grain and a significant yield increase in rice, The rice genome has other two OsPPKL1 homologs, OsPPKL2 and OsPPKL3
- GL3.1~qGL3-1~qGL3~OsPPKL1, OsPPKL2, Rare allele of OsPPKL1 associated with grain length causes extra-large grain and a significant yield increase in rice, Transgenic studies showed that OsPPKL1 and OsPPKL3 function as negative regulators of grain length, whereas OsPPKL2 as a positive regulator
- GL3.1~qGL3-1~qGL3~OsPPKL1, OsPPKL3, Rare allele of OsPPKL1 associated with grain length causes extra-large grain and a significant yield increase in rice, The rice genome has other two OsPPKL1 homologs, OsPPKL2 and OsPPKL3
- GL3.1~qGL3-1~qGL3~OsPPKL1, OsPPKL3, Rare allele of OsPPKL1 associated with grain length causes extra-large grain and a significant yield increase in rice, Transgenic studies showed that OsPPKL1 and OsPPKL3 function as negative regulators of grain length, whereas OsPPKL2 as a positive regulator
- GL3.1~qGL3-1~qGL3~OsPPKL1, GS3, The additive effects of GS3 and qGL3 on rice grain length regulation revealed by genetic and transcriptome comparisons., The additive effects of GS3 and qGL3 on rice grain length regulation revealed by genetic and transcriptome comparisons.
- GL3.1~qGL3-1~qGL3~OsPPKL1, GS3, The additive effects of GS3 and qGL3 on rice grain length regulation revealed by genetic and transcriptome comparisons., To investigate the genetic interaction between two major grain length loci of rice, GS3 and qGL3, we developed two near-isogenic lines (NILs), NIL-GS3 (GS3/qGL3) and NIL-qgl3 (gs3/qgl3), in the genetic background of 93-11 (gs3/qGL3) by conventional backcrossing and marker-assisted selection (MAS)
- GL3.1~qGL3-1~qGL3~OsPPKL1, GS3, The additive effects of GS3 and qGL3 on rice grain length regulation revealed by genetic and transcriptome comparisons., By comparing the grain lengths of 93-11, NIL-GS3, NIL-qgl3 and NIL-GS3/qgl3, we investigated the effects of GS3, qGL3 and GS3ÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂâÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂâÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂqGL3 interaction on grain length based on two-way ANOVA
- GL3.1~qGL3-1~qGL3~OsPPKL1, GS3, The additive effects of GS3 and qGL3 on rice grain length regulation revealed by genetic and transcriptome comparisons., We found that GS3 and qGL3 had additive effects on rice grain length regulation
- GL3.1~qGL3-1~qGL3~OsPPKL1, GS3, The additive effects of GS3 and qGL3 on rice grain length regulation revealed by genetic and transcriptome comparisons., Comparative analysis of primary panicle transcriptomes in the four NILs revealed that the genes affected by GS3 and qGL3 partially overlapped, and both loci might be involved in brassinosteroid signaling
Prev Next