- Information
- Symbol: Gn1a,OsCKX2
- MSU: LOC_Os01g10110
- RAPdb: Os01g0197700
- PSP score
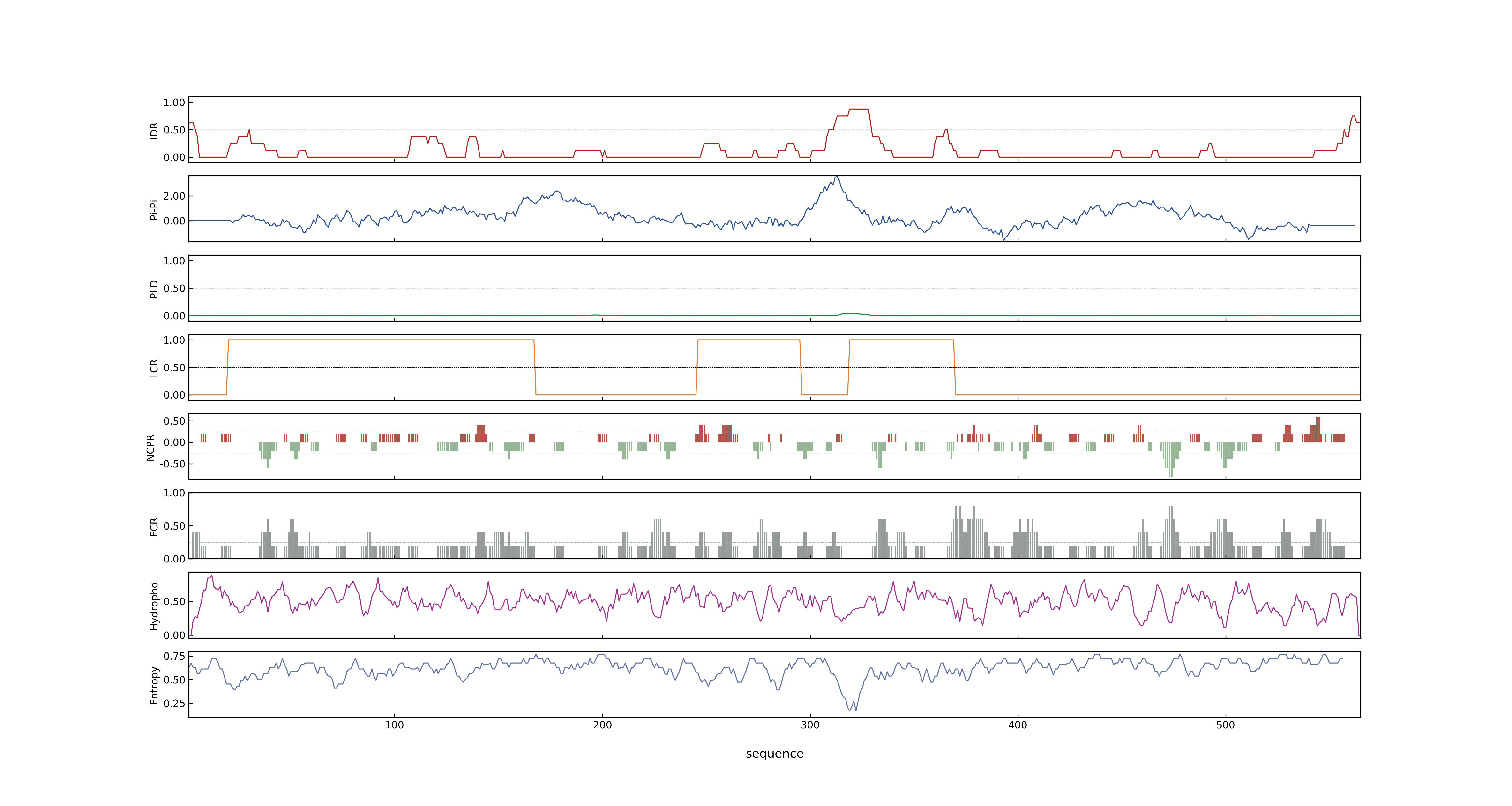
- LOC_Os01g10110.1: 0.3551
- PLAAC score
- LOC_Os01g10110.1: 0
- pLDDT score
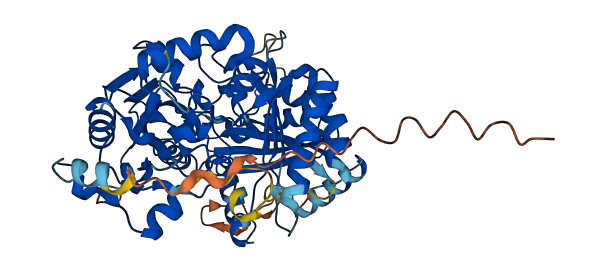
- 87.03
- Protein Structure from AlphaFold and UniProt
- MolPhase score
- LOC_Os01g10110.1: 0.89943522
- MolPhase Result
- Publication
- A loss-of-function mutation of rice DENSE PANICLE 1 causes semi-dwarfness and slightly increased number of spikelets, 2011, Breeding Science.
- Mutations in the F-box gene LARGER PANICLE improve the panicle architecture and enhance the grain yield in rice, 2011, Plant Biotechnol J.
- Rice zinc finger protein DST enhances grain production through controlling Gn1a/OsCKX2 expression, 2013, Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A.
- Cytokinin oxidase regulates rice grain production, 2005, Science.
- Down-Regulation of Cytokinin Oxidase 2 Expression Increases Tiller Number and Improves Rice Yield., 2015, Rice (N Y).
- Artificial Selection of Gn1a Plays an Important role in Improving Rice Yields Across Different Ecological Regions., 2015, Rice (N Y).
- TKnockdown of an inflorescence meristem-specific cytokinin oxidase - OsCKX2 in rice reduces yield penalty under salinity stress condition., 2017, Plant Cell Environ.
- Updating the elite rice variety Kongyu 131 by improving the Gn1a locus., 2017, Rice (N Y).
- Genbank accession number
- Key message
- We here show that a QTL that increases grain productivity in rice, Gn1a, is a gene for cytokinin oxidase/dehydrogenase (OsCKX2), an enzyme that degrades the phytohormone cytokinin
- Quantitative real-time PCR results show that OsCKX2, which encodes cytokinin oxidase/dehydrogenase, is down-regulated evidently in mutants, implying that LP might be involved in modulating cytokinin level in plant tissues
- The expression level of OsCKX2 in the shoot apex of Dn1-1 plants is similar to that in the wild type, indicating that OsCKX2 does not contribute to an increased number of spikelets
- Here, we report that the zinc finger transcription factor DROUGHT AND SALT TOLERANCE (DST) directly regulates OsCKX2 expression in the reproductive meristem
- We identify that DST(reg1), a semidominant allele of the DST gene, perturbs DST-directed regulation of OsCKX2 expression and elevates CK levels in the reproductive SAM, leading to increased meristem activity, enhanced panicle branching, and a consequent increase of grain number
- Reduced expression of OsCKX2 causes cytokinin accumulation in inflorescence meristems and increases the number of reproductive organs, resulting in enhanced grain yield
- ) Gn1a/OsCKX2 (Grain number 1a/Cytokinin oxidase 2) gene, which encodes a cytokinin oxidase, has been identified as a major quantitative trait locus contributing to grain number improvement in rice breeding practice
- Importantly, the DST(reg1) allele provides an approach to pyramid the Gn1a-dependent and Gn1a-independent effects on grain production
- Rice zinc finger protein DST enhances grain production through controlling Gn1a/OsCKX2 expression
- DST-directed expression of OsCKX2 regulates CK accumulation in the SAM and, therefore, controls the number of the reproductive organs
- Southern blot analysis confirmed the integration of the shRNA genes into the rice genome, and quantitative real time RT-PCR and northern blot analyses showed reduced OsCKX2 expression in the young stem of transgenic rice at varying degrees
- Consistently, insertional activation of OsCKX2 led to increased expression of CKX2 and reduced tiller number and growth in a gene-dosage dependant manner
- Taken together, these results demonstrate that specific suppression of OsCKX2 expression through shRNA-mediated gene silencing leads to enhanced growth and productivity in rice by increasing tiller number and grain weight
- Gn1a (OsCKX2), which encodes cytokinin oxidase/dehydrogenase, plays an important role in regulating rice grain yield
- It might be valuable to explore the high-yield-related alleles of Gn1a to develop high-yield rice cultivars in future breeding programs
- Importantly, we found a negative-correlation between OsCKX2 expression and plant productivity as evident by assessment of agronomical parameters such as panicle branching, filled grains per plant, and harvest index both under control and salinity stress conditions
- We utilized an RNAi-based approach to study the function of OsCKX2 in maintaining grain yield under salinity stress condition
- To determine if there exists, a correlation between OsCKX2 levels and yield under salinity stress condition, we assessed the growth, physiology and grain yield of OsCKX2-knockdown plants vis-ÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂ -vis the wild-type
- TKnockdown of an inflorescence meristem-specific cytokinin oxidase - OsCKX2 in rice reduces yield penalty under salinity stress condition.
- Quantitative trait locus (QTL) analysis of the BC3F2 population showed that the introgressed segment carrying the Gn1a allele of GKBR significantly increased the branch number and grain number per panicle
- To achieve the high yield potential of Kongyu 131, a minute chromosome fragment carrying the favorable Gn1a allele from the donor parent was introgressed into the genome of Kongyu 131, which resulted in a larger panicle and subsequent yield increase in the new Kongyu 131
- Connection
- DEP1~DN1~qPE9-1~OsDEP1, Gn1a~OsCKX2, A loss-of-function mutation of rice DENSE PANICLE 1 causes semi-dwarfness and slightly increased number of spikelets, The expression level of OsCKX2 in the shoot apex of Dn1-1 plants is similar to that in the wild type, indicating that OsCKX2 does not contribute to an increased number of spikelets
- EP3~LP, Gn1a~OsCKX2, Mutations in the F-box gene LARGER PANICLE improve the panicle architecture and enhance the grain yield in rice, Quantitative real-time PCR results show that OsCKX2, which encodes cytokinin oxidase/dehydrogenase, is down-regulated evidently in mutants, implying that LP might be involved in modulating cytokinin level in plant tissues
- DST, Gn1a~OsCKX2, Rice zinc finger protein DST enhances grain production through controlling Gn1a/OsCKX2 expression, Here, we report that the zinc finger transcription factor DROUGHT AND SALT TOLERANCE (DST) directly regulates OsCKX2 expression in the reproductive meristem
- DST, Gn1a~OsCKX2, Rice zinc finger protein DST enhances grain production through controlling Gn1a/OsCKX2 expression, DST-directed expression of OsCKX2 regulates CK accumulation in the SAM and, therefore, controls the number of the reproductive organs
- DST, Gn1a~OsCKX2, Rice zinc finger protein DST enhances grain production through controlling Gn1a/OsCKX2 expression, We identify that DST(reg1), a semidominant allele of the DST gene, perturbs DST-directed regulation of OsCKX2 expression and elevates CK levels in the reproductive SAM, leading to increased meristem activity, enhanced panicle branching, and a consequent increase of grain number
- DST, Gn1a~OsCKX2, Rice zinc finger protein DST enhances grain production through controlling Gn1a/OsCKX2 expression, Importantly, the DST(reg1) allele provides an approach to pyramid the Gn1a-dependent and Gn1a-independent effects on grain production
- DST, Gn1a~OsCKX2, Rice zinc finger protein DST enhances grain production through controlling Gn1a/OsCKX2 expression, Rice zinc finger protein DST enhances grain production through controlling Gn1a/OsCKX2 expression
Prev Next