- Information
- Symbol: HSA32
- MSU: LOC_Os06g46900
- RAPdb: Os06g0682900
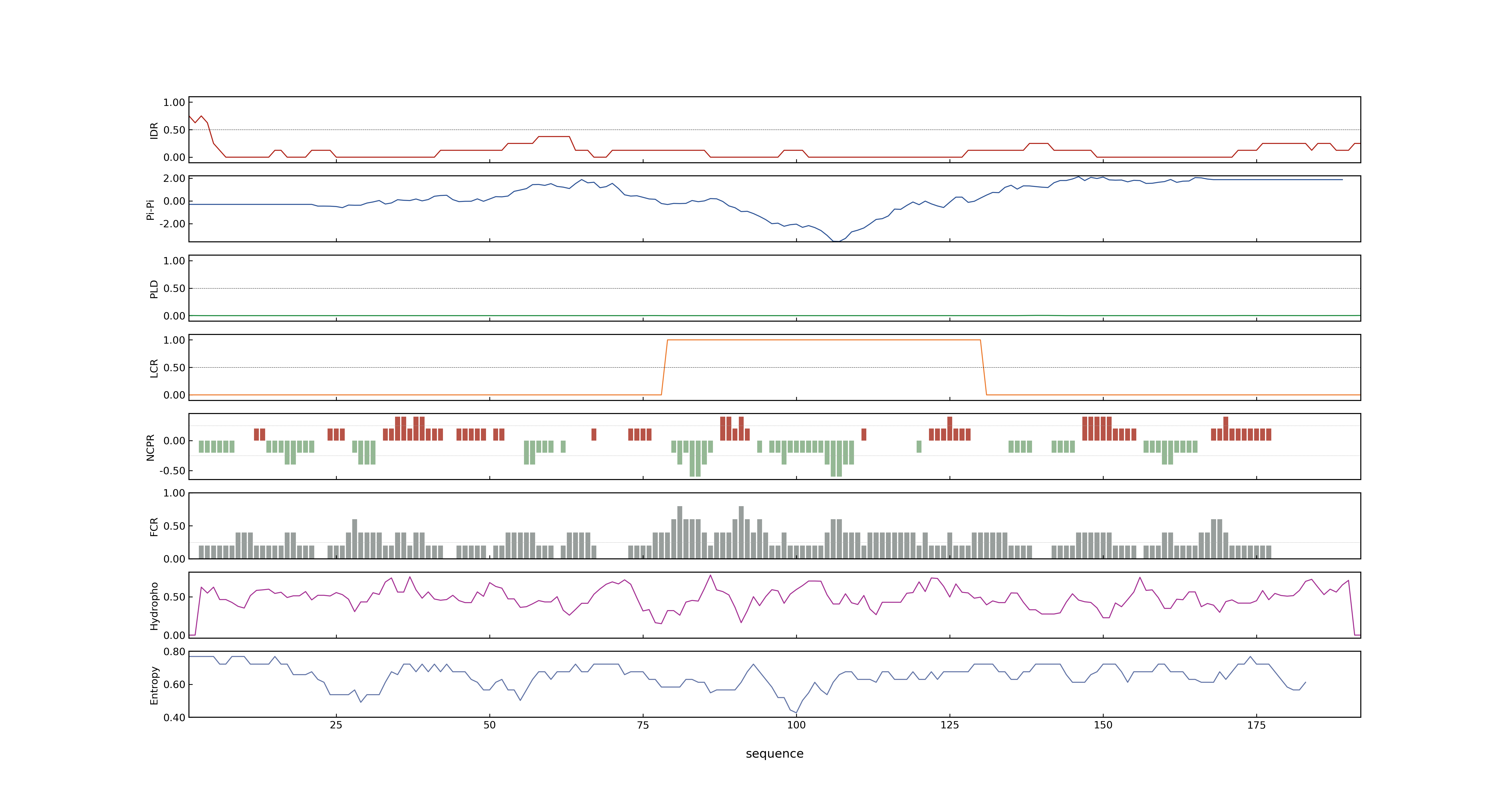
- PSP score
- LOC_Os06g46900.3: 0.0028
- LOC_Os06g46900.4: 0.0034
- LOC_Os06g46900.1: 0.0057
- LOC_Os06g46900.2: 0.0028
- PLAAC score
- LOC_Os06g46900.3: 0
- LOC_Os06g46900.4: 0
- LOC_Os06g46900.1: 0
- LOC_Os06g46900.2: 0
- pLDDT score
- 74.55
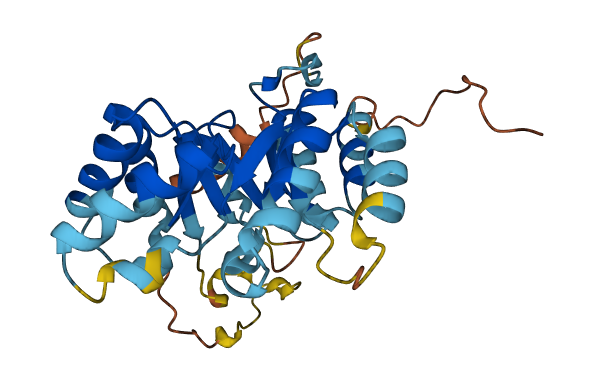
- Protein Structure from AlphaFold and UniProt
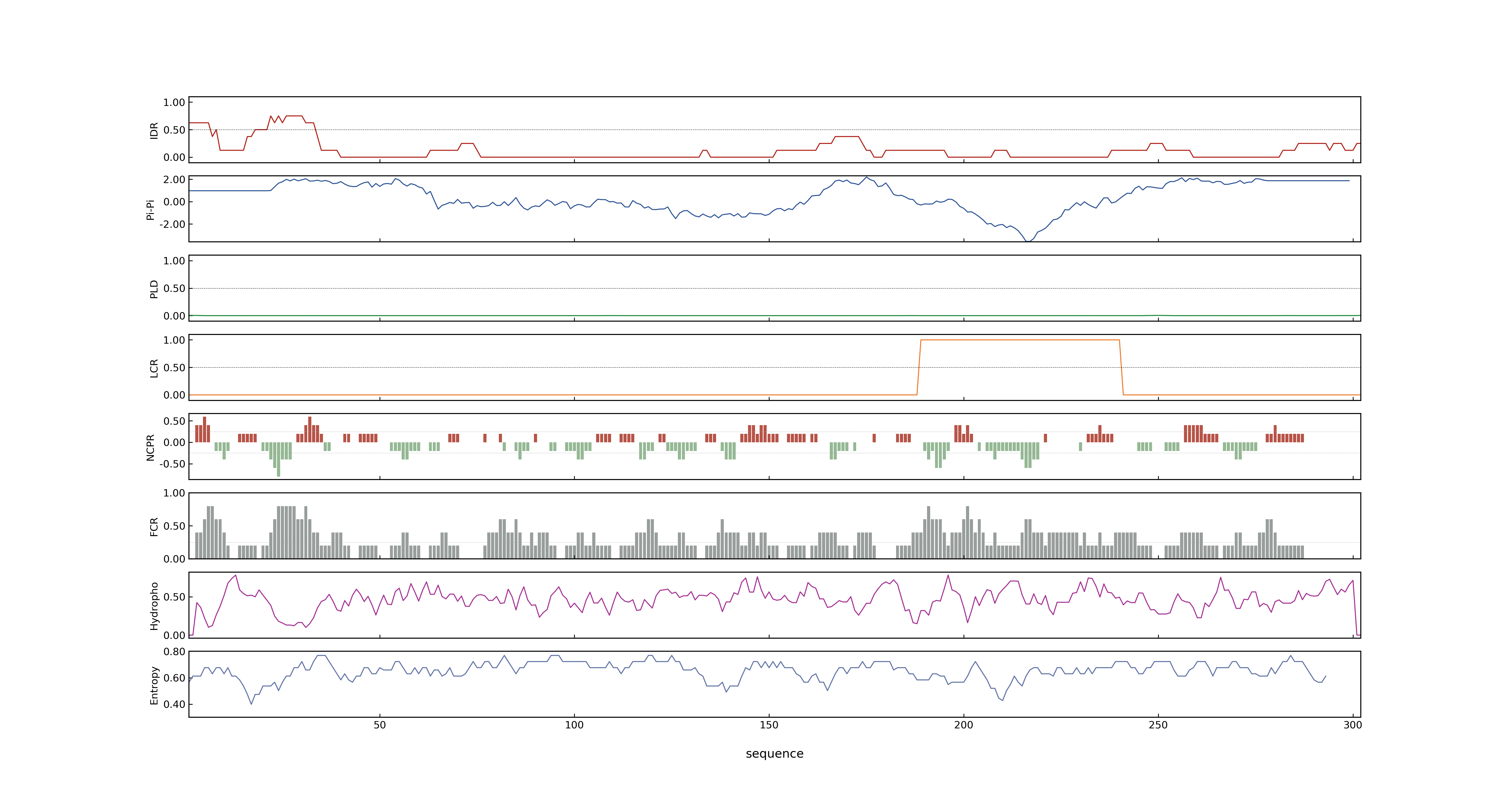
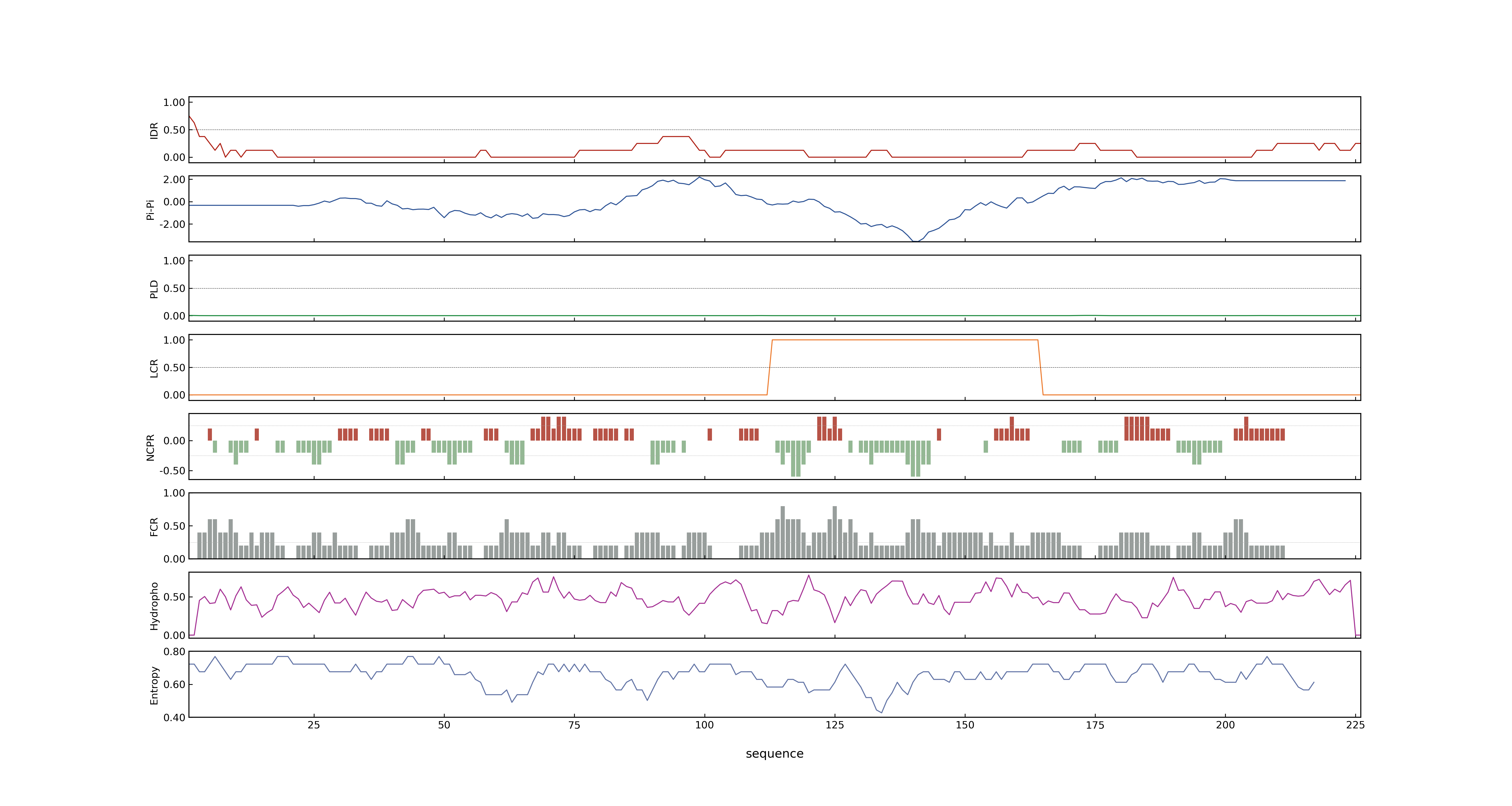
- MolPhase score
- LOC_Os06g46900.1: 0.26191815
- LOC_Os06g46900.2: 0.05108234
- LOC_Os06g46900.3: 0.05108234
- LOC_Os06g46900.4: 0.03900051
- MolPhase Result
- Publication
-
Genbank accession number
- Key message
- Our results showed that a positive feedback loop formed by two heat-inducible genes, HEAT SHOCK PROTEIN101 (HSP101) and HEAT STRESS-ASSOCIATED 32-KD PROTEIN (HSA32), at the posttranscriptional level prolongs the effect of heat acclimation in rice seedlings
- The interplay between HSP101 and HSA32 also affects basal thermotolerance of rice seeds
- Connection
- HSA32, HSP101~OsClpB-cyt~HSP100, A positive feedback loop between HEAT SHOCK PROTEIN101 and HEAT STRESS-ASSOCIATED 32-KD PROTEIN modulates long-term acquired thermotolerance illustrating diverse heat stress responses in rice varieties, Our results showed that a positive feedback loop formed by two heat-inducible genes, HEAT SHOCK PROTEIN101 (HSP101) and HEAT STRESS-ASSOCIATED 32-KD PROTEIN (HSA32), at the posttranscriptional level prolongs the effect of heat acclimation in rice seedlings
- HSA32, HSP101~OsClpB-cyt~HSP100, A positive feedback loop between HEAT SHOCK PROTEIN101 and HEAT STRESS-ASSOCIATED 32-KD PROTEIN modulates long-term acquired thermotolerance illustrating diverse heat stress responses in rice varieties, The interplay between HSP101 and HSA32 also affects basal thermotolerance of rice seeds
- HSA32, HSP101~OsClpB-cyt~HSP100, A positive feedback loop between HEAT SHOCK PROTEIN101 and HEAT STRESS-ASSOCIATED 32-KD PROTEIN modulates long-term acquired thermotolerance illustrating diverse heat stress responses in rice varieties, The HSP101 and HSA32 protein levels were substantially higher in cv Nipponbare than in cv N22 after a long recovery following heat acclimation treatment, at least partly explaining the difference in the LAT phenotype
Prev Next