- Information
- Symbol: LPA1
- MSU: LOC_Os03g13400
- RAPdb: Os03g0237250
- PSP score
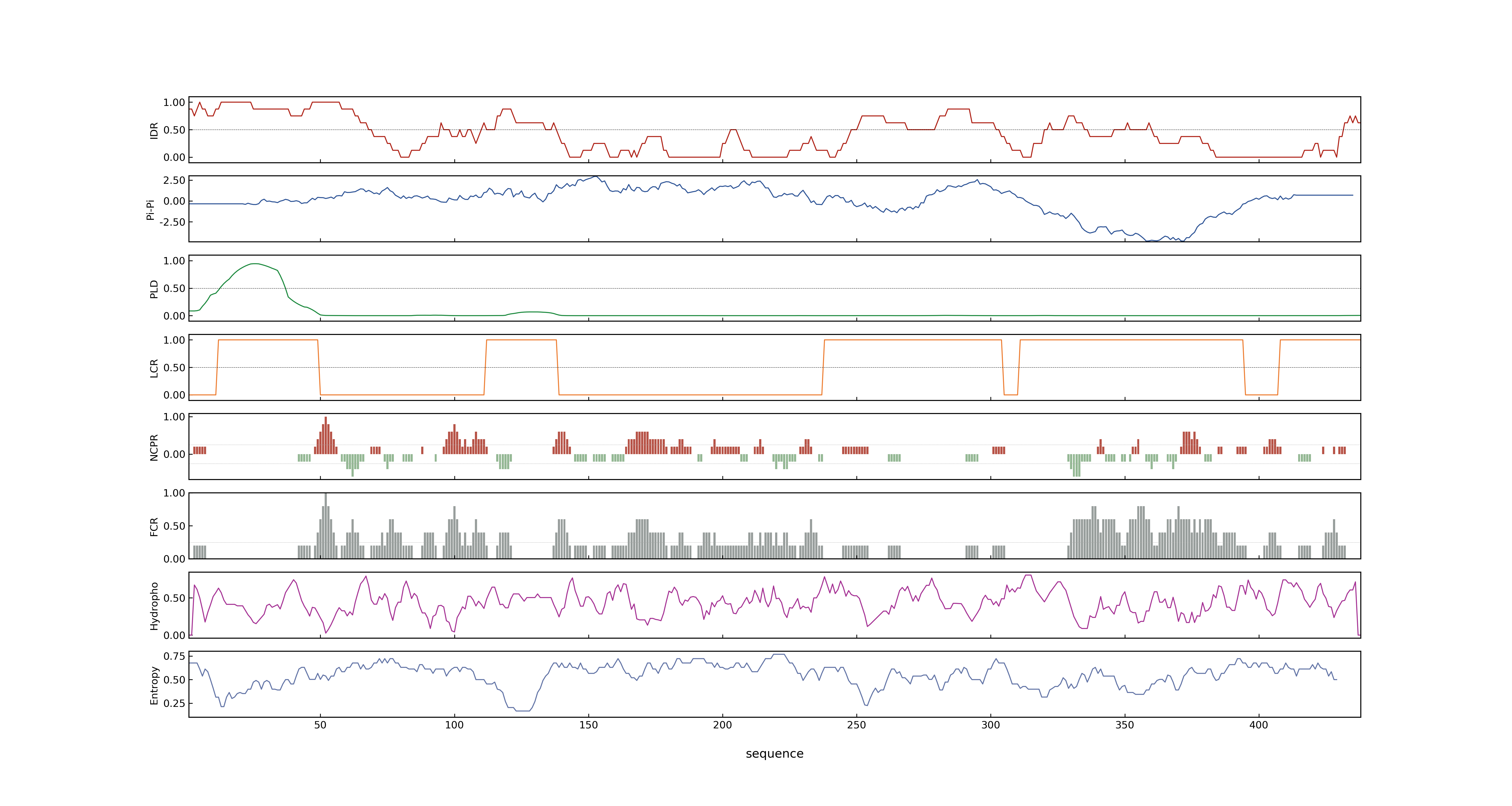
- LOC_Os03g13400.1: 0.7458
- PLAAC score
- LOC_Os03g13400.1: 0
- pLDDT score
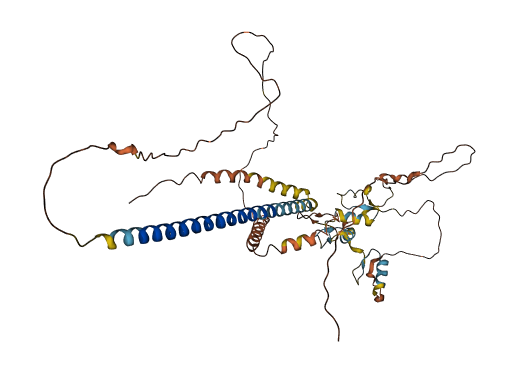
- 53.32
- Protein Structure from AlphaFold and UniProt
- MolPhase score
- LOC_Os03g13400.1: 0.99985933
- MolPhase Result
- Publication
- Loose Plant Architecture1, an INDETERMINATE DOMAIN protein involved in shoot gravitropism, regulates plant architecture in rice, 2013, Plant Physiol.
- Loose Plant Architecture1 LPA1 determines lamina joint bending by suppressing auxin signalling that interacts with C-22-hydroxylated and 6-deoxo brassinosteroids in rice., 2016, J Exp Bot.
- Genbank accession number
- Key message
- LPA1 regulates tiller angle and leaf angle by controlling the adaxial growth of tiller node and lamina joint
- LPA1 is localized in the nucleus and functions as an active transcriptional repressor, an activity mainly conferred by a conserved ethylene response factor-associated amphiphilic repression-like motif
- Expression pattern analysis suggested that LPA1 influences plant architecture by affecting the gravitropism of leaf sheath pulvinus and lamina joint
- Here, we report the cloning and characterization of the Loose Plant Architecture1 (LPA1) gene in rice, the functional ortholog of the AtIDD15/SHOOT GRAVITROPISM5 (SGR5) gene in Arabidopsis (Arabidopsis thaliana)
- LPA1 was also found to affect shoot gravitropism
- Genetic and biochemical data indicate that LPA1 suppresses the auxin signalling that interacts with C-22-hydroxylated and 6-deoxo BRs, which regulates lamina inclination independently of OsBRI1
- RNA sequencing analysis and qRT-PCR indicate that LPA1 influences the expression of three OsPIN genes (OsPIN1a, OsPIN1c and OsPIN3a), which suggests that auxin flux might be an important factor in LPA1-mediated lamina inclination in rice
- Mutant lpa1 plants are hypersensitive to indole-3-acetic acid (IAA) during the lamina inclination response, which is suppressed by the brassinazole (Brz) inhibitor of C-22 hydroxylase involved in BR synthesis
- This study explores the role of LPA1 in determining lamina inclination in rice
- LPA1 acts as a positive regulator to suppress lamina bending
- A strong synergic effect is detected between lpa1 and d2 (the defective mutant for catalysis of C-23-hydroxylated BRs) during IAA-mediated lamina inclination
- Connection
- LPA1, ONAC106, Rice ONAC106 inhibits leaf senescence and increases salt tolerance and tiller angle., Using yeast one-hybrid assays, we found that ONAC106 binds to the promoter regions of SGR, NYC1, OsNAC5, and LPA1
- D2~CYP90D2~SMG11, LPA1, Loose Plant Architecture1 LPA1 determines lamina joint bending by suppressing auxin signalling that interacts with C-22-hydroxylated and 6-deoxo brassinosteroids in rice., A strong synergic effect is detected between lpa1 and d2 (the defective mutant for catalysis of C-23-hydroxylated BRs) during IAA-mediated lamina inclination
- D61~OsBRI1, LPA1, Loose Plant Architecture1 LPA1 determines lamina joint bending by suppressing auxin signalling that interacts with C-22-hydroxylated and 6-deoxo brassinosteroids in rice., Genetic and biochemical data indicate that LPA1 suppresses the auxin signalling that interacts with C-22-hydroxylated and 6-deoxo BRs, which regulates lamina inclination independently of OsBRI1
- D61~OsBRI1, LPA1, Loose Plant Architecture1 LPA1 determines lamina joint bending by suppressing auxin signalling that interacts with C-22-hydroxylated and 6-deoxo brassinosteroids in rice., No significant interaction between LPA1 and OsBRI1 was identified
- LPA1, OsMRP5, Mutations of the multi-drug resistance-associated protein ABC transporter gene 5 result in reduction of phytic acid in rice seeds., In this study, we mapped the XS-lpa2-1 gene to a region on chromosome 3 between microsatellite markers RM14360 and RM1332, where the rice orthologue (OsMRP5) of the maize lpa1 gene is located
Prev Next