- Information
- Symbol: NAL1,qFLW4
- MSU: LOC_Os04g52479
- RAPdb: Os04g0615000
- PSP score
- LOC_Os04g52479.1: 0.3696
- LOC_Os04g52479.2: 0.3696
- LOC_Os04g52479.3: 0.3696
- PLAAC score
- LOC_Os04g52479.1: 0
- LOC_Os04g52479.2: 0
- LOC_Os04g52479.3: 0
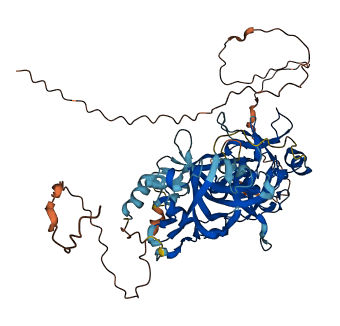
- pLDDT score
- 71.39
- Protein Structure from AlphaFold and UniProt
- MolPhase score
- LOC_Os04g52479.1: 0.99418550
- LOC_Os04g52479.2: 0.99418550
- LOC_Os04g52479.3: 0.99418550
- MolPhase Result
- Publication
- Fine mapping of a major QTL for flag leaf width in rice, qFLW4, which might be caused by alternative splicing of NAL1, 2012, Plant Cell Rep.
- Mutation of the rice Narrow leaf1 gene, which encodes a novel protein, affects vein patterning and polar auxin transport, 2008, Plant Physiol.
- NAL1 allele from a rice landrace greatly increases yield in modern indica cultivars, 2013, Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A.
- Characterization of a Null Allelic Mutant of the Rice NAL1 Gene Reveals Its Role in Regulating Cell Division., 2015, PLoS One.
- Natural Variation in the Flag Leaf Morphology of Rice Due to a Mutation of the NARROW LEAF 1 Gene in Oryza sativa L., 2015, Genetics.
- Genbank accession number
- Key message
- Anatomical investigations revealed that the culms of nal1 also show a defective vascular system, in which the number and distribution pattern of vascular bundles are altered
- These results indicate that Nal1 affects polar auxin transport as well as the vascular patterns of rice plants and plays an important role in the control of lateral leaf growth
- To understand the molecular mechanism governing plant leaf shape, we characterized a classic rice (Oryza sativa) dwarf mutant named narrow leaf1 (nal1), which exhibits a characteristic phenotype of narrow leaves
- In accordance with reduced leaf blade width, leaves of nal1 contain a decreased number of longitudinal veins
- NAL1 allele from a rice landrace greatly increases yield in modern indica cultivars
- We provide evidence showing that Nal1 is richly expressed in vascular tissues and that mutation of this gene leads to significantly reduced polar auxin transport capacity
- 8 kb interval between the SSR loci RM17483 and RM17486, a region which also contains the gene NAL1 (Narrow leaf 1)
- The analysis of expression of other known genes involved in the determination of leaf width provided no evidence of their having any clear functional association with qFLW4/NAL1
- Fine mapping of a major QTL for flag leaf width in rice, qFLW4, which might be caused by alternative splicing of NAL1
- Map-based cloning revealed that SPIKE was identical to NARROW LEAF1 (NAL1), which has been reported to control vein pattern in leaf
- Previous studies have shown that NAL1 plays a role in regulating vein patterning and increasing grain yield in indica cultivars, but its role in leaf growth and development remains unknown
- We demonstrated that NAL1 functions in the regulation of cell division as early as during leaf primordia initiation
- These results suggest that NAL1 controls leaf width and plant height through its effects on cell division
- Map-based cloning revealed that nal1-2 is a null allelic mutant of NAL1 since both the whole promoter and a 404-bp fragment in the first exon of NAL1 were deleted, and that a 6-bp fragment was deleted in the mutant nal1-3
- Characterization of a Null Allelic Mutant of the Rice NAL1 Gene Reveals Its Role in Regulating Cell Division.
- Heterogenous expression of NAL1 in fission yeast (Schizosaccharomyces pombe) further supported that NAL1 affects cell division
- The altered transcript level of G1- and S-phase-specific genes suggested that NAL1 affects cell cycle regulation
- Connection
- NAL1~qFLW4, OsFMO~OsCOW1~NAL7, Genetic analysis of rice mutants responsible for narrow leaf phenotype and reduced vein number., In this paper, we examined the function of four genes that regulate the width of the leaf blade and the vein number: NARROW LEAF1 (NAL1), NAL2, NAL3 and NAL7
- NAL1~qFLW4, OsFMO~OsCOW1~NAL7, Genetic analysis of rice mutants responsible for narrow leaf phenotype and reduced vein number., The nal7 mutation showed additive effects on both leaf width and vein number, when combined with the nal1 single or the nal2 nal3 double mutation
Prev Next