- Information
- Symbol: OSHB3,OsHox33
- MSU: LOC_Os12g41860
- RAPdb: Os12g0612700
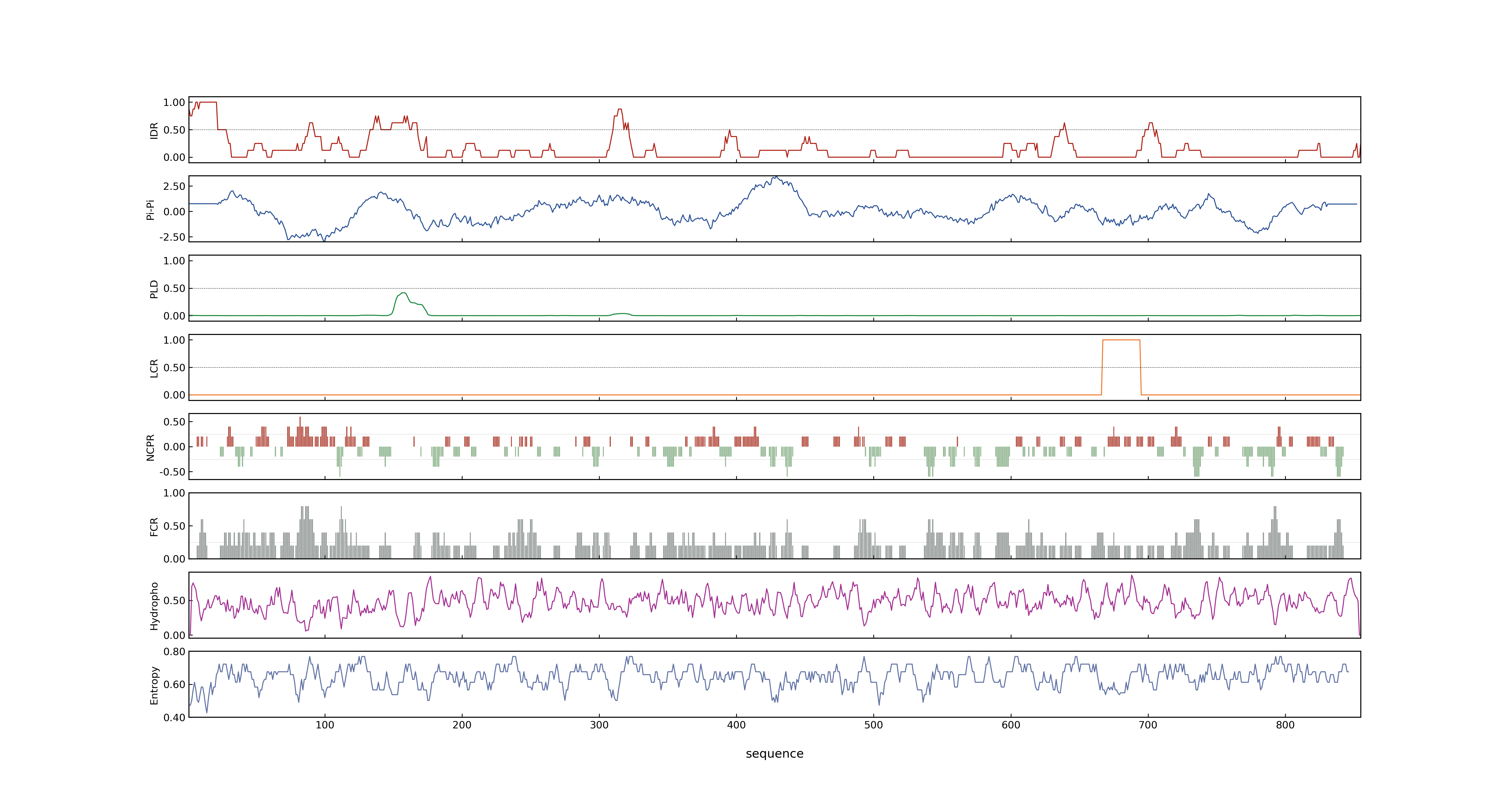
- PSP score
- LOC_Os12g41860.1: 0.7684
- PLAAC score
- LOC_Os12g41860.1: 0
- pLDDT score
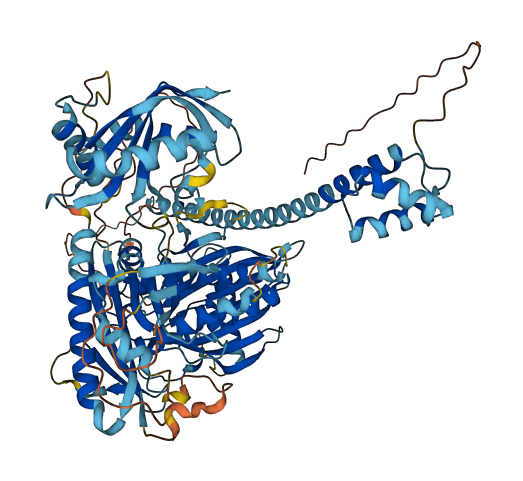
- 77.35
- Protein Structure from AlphaFold and UniProt
- MolPhase score
- LOC_Os12g41860.1: 0.95552253
- MolPhase Result
- Publication
- Genbank accession number
- Key message
- pOsHox33::GUS fusion expression and RT-PCR revealed that OsHox33 is highly expressed in young organs, especially in young meristems such as shoot apical meristems, intercalary meristems, and young callus
- In this study, we analyzed a HD-Zip III member, OsHox33, and demonstrated that it plays an important role in age-dependent leaf senescence in rice
- Transgenic plants harboring either RNAi construct displayed similar phenotypes of precocious leaf senescence symptoms, suggesting that knockdown of OsHox33 accelerates leaf senescence in rice
- Finally, real-time PCR studies showed that OsHox33 can regulate the expression of GS1 and GS2, two senescence-associated genes
- Knockdown of OsHox33, a member of the class III homeodomain-leucine zipper gene family, accelerates leaf senescence in rice
- Plants ectopically expressing microRNA166-resistant versions of the OSHB3 gene exhibited severe defects, including the ectopic production of leaf margins, shoots, and radialized leaves
- To further investigate OsHox33 function, we analyzed chloroplast ultrastructure in different-aged leaves of RNAi plants, and found that OsHox33 knockdown accelerated chloroplast degradation, which is consistent with RNAi phenotypes
- Furthermore, this ectopic expression of OSHB3 was correlated with leaf initiation defects
- The treatment of seedlings with auxin quickly induced ectopic OSHB3 expression in the entire region of the SAM, but not in other tissues
- Connection
Prev Next