- Information
- Symbol: OZT1,OsMTP1
- MSU: LOC_Os05g03780
- RAPdb: Os05g0128400
- PSP score
- LOC_Os05g03780.1: 0.1748
- PLAAC score
- LOC_Os05g03780.1: 0
- pLDDT score
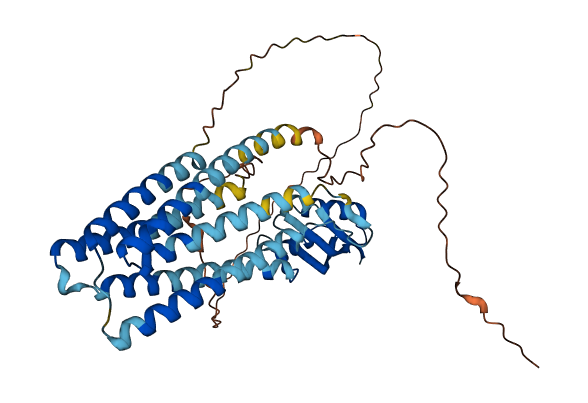
- 70.97
- Protein Structure from AlphaFold and UniProt
- MolPhase score
- LOC_Os05g03780.1: 0.89485508
- MolPhase Result
- Publication
- Molecular characterization of a rice metal tolerance protein, OsMTP1, 2012, Plant Cell Rep.
- Functional analysis of the rice vacuolar zinc transporter OsMTP1, 2013, J Exp Bot.
- Characterization of a vacuolar zinc transporter OZT1 in rice Oryza sativa L., 2013, Mol Biol Rep.
- Enhanced cadmium accumulation and tolerance in transgenic tobacco overexpressing rice metal tolerance protein gene OsMTP1 is promising for phytoremediation, 2016, Plant Physiology and Biochemistry.
- Genbank accession number
- Key message
- Together, OZT1 is a CDF family vacuolar zinc transporter conferring tolerance to Zn(2+) and Cd(2+) stress, which is important to transporting and homeostasis of Zn, Cd or other heavy metals in plants
- Taken together, our results show that OsMTP1 is a bivalent cation transporter localized in the cell membrane, which is necessary for efficient translocation of Zn, Cd and other heavy metals, and maintain ion homeostasis in plant
- OsMTP1 is a member of the cation diffusion facilitator (CDF)/metal tolerance protein (MTP) family of metal cation transporters in Oryza sativa, which is closely related to Arabidopsis thaliana MTP1
- OsMTP1 alleviated, to some extent, the Co sensitivity of this mutant, rescued the Fe hypersensitivity of the ccc1 mutant at low Fe concentrations, and restored growth of the Cd-hypersensitive mutant ycf1 at low Cd concentrations
- The OZT1 expression was significantly induced both in the seedlings of japonica rice Nipponbare and indica rice IR26 in response to Zn(2+) and Cd(2+) treatments
- OsMTP1 expression increased tolerance to Zn, Cd, and Ni in wild-type yeast BY4741 during the exponential growth phase
- OsMTP1 dsRNAi mediated by transgenic assay in rice seedlings resulted in heavy metal sensitivity and changed the heavy metal accumulation in different organs of mature rice under low-concentration heavy metal stress
- In this research, a full length cDNA named Oryza sativa Zn Transporter 1 (OZT1) that closely related to rat ZnT-2 (Zn Transporter 2) gene was isolated from rice
- Characterization of a vacuolar zinc transporter OZT1 in rice (Oryza sativa L.)
- Functional analysis of the rice vacuolar zinc transporter OsMTP1
- A cDNA clone, encoding the rice homolog of Metal Tolerance Protein (OsMTP1), was induced by Cd treatment
- Molecular characterization of a rice metal tolerance protein, OsMTP1
- Heterologous expression of OsMTP1 in tobacco resulted in the reduction of Cd stress-induced phytotoxic effects, including growth inhibition, lipid peroxidation, and cell death
- Together, findings of our research suggest that the transgenic tobacco plants overexpressing OsMTP1 with its hyperaccumulating activity and increased growth rate could be useful for future phytoremediation applications to clean up the Cd-contaminated soil
- Enhanced cadmium accumulation and tolerance in transgenic tobacco overexpressing rice metal tolerance protein gene OsMTP1 is promising for phytoremediation
- The transgenic plants also showed moderate tolerance and accumulation of arsenic (As) upon exogenous As stress, signifying broad substrate specificity of OsMTP1
- The 1257 bp coding DNA sequence (CDS) of OsMTP1 encodes a 46 kDa protein belonging to the cation diffusion facilitator (CDF) or metal tolerance/transport protein (MTP) family
- The OsMTP1 transcript in rice plant was found to respond during external Cd stress
- Connection
Prev Next