- Information
- Symbol: OsAKT1
- MSU: LOC_Os01g45990
- RAPdb: Os01g0648000
- PSP score
- LOC_Os01g45990.1: 0.0934
- PLAAC score
- LOC_Os01g45990.1: 0
- pLDDT score
- 75.89
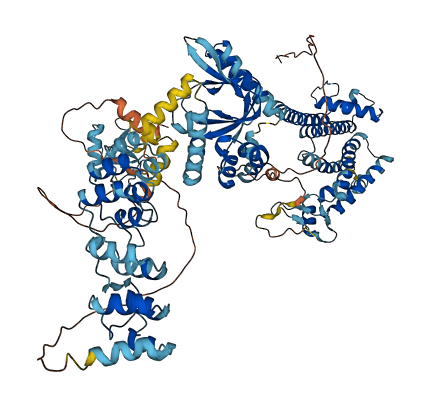
- Protein Structure from AlphaFold and UniProt
- MolPhase score
- LOC_Os01g45990.1: 0.97664046
- MolPhase Result
- Publication
- Rice K+ uptake channel OsAKT1 is sensitive to salt stress, 2005, Planta.
- The Os-AKT1 Channel Is Critical for K+ Uptake in Rice Roots and Is Modulated by the Rice CBL1-CIPK23 Complex, 2014, Plant Cell.
- Overexpression of the rice AKT1 potassium channel affects potassium nutrition and rice drought tolerance., 2016, J Exp Bot.
- Genbank accession number
- Key message
- To unravel the mechanisms of K+ uptake and its sensitivity to salt stress in the model plant rice, we isolated and functionally characterized OsAKT1, a potassium channel homologous to the Arabidopsis root inward rectifier AKT1
- OsAKT1 transcripts were predominantly found in the coleoptile and in the roots of young rice seedlings
- Patch-clamp studies on rice root protoplasts identified a K+ inward rectifier with similar channel properties as heterologously expressed OsAKT1
- In line with the transcriptional downregulation of OsAKT1 in response to salt stress, inward K+ currents were significantly reduced in root protoplasts
- Thus, OsAKT1 seems to represent the dominant salt-sensitive K+ uptake channel in rice roots
- Rice K+ uptake channel OsAKT1 is sensitive to salt stress
- The Os-AKT1 Channel Is Critical for K+ Uptake in Rice Roots and Is Modulated by the Rice CBL1-CIPK23 Complex
- Disruption of Os-AKT1 significantly reduced the K+ content, which resulted in inhibition of plant growth and development.
- The most prominent result of OsAKT1 overexpression was a reduction in sensitivity to osmotic/drought stress in transgenic plants: the data suggest that AKT1 overexpression improved rice osmotic and drought stress tolerance by increasing tissue levels of K(+), especially in the root
- Connection
- OsAKT1, OsCBL1, The Os-AKT1 Channel Is Critical for K+ Uptake in Rice Roots and Is Modulated by the Rice CBL1-CIPK23 Complex, The Os-AKT1 Channel Is Critical for K+ Uptake in Rice Roots and Is Modulated by the Rice CBL1-CIPK23 Complex
- OsAKT1, OsCBL1, The Os-AKT1 Channel Is Critical for K+ Uptake in Rice Roots and Is Modulated by the Rice CBL1-CIPK23 Complex, Similar to the AKT1 regulation in Arabidopsis, Os-CBL1 and Os-CIPK23 were identified as the upstream regulators of Os-AKT1 in rice
- OsAKT1, OsCBL1, The Os-AKT1 Channel Is Critical for K+ Uptake in Rice Roots and Is Modulated by the Rice CBL1-CIPK23 Complex, The Os-CBL1-Os-CIPK23 complex could enhance Os-AKT1-mediated K+ uptake.
- OsAKT1, OsCBL1, The Os-AKT1 Channel Is Critical for K+ Uptake in Rice Roots and Is Modulated by the Rice CBL1-CIPK23 Complex, These findings demonstrate that Os-AKT1-mediated K+ uptake in rice roots is modulated by the Os-CBL1-Os-CIPK23 complex.
- OsAKT1, OsCIPK23, The Os-AKT1 Channel Is Critical for K+ Uptake in Rice Roots and Is Modulated by the Rice CBL1-CIPK23 Complex, Similar to the AKT1 regulation in Arabidopsis, Os-CBL1 and Os-CIPK23 were identified as the upstream regulators of Os-AKT1 in rice.
- OsAKT1, OsCIPK23, The Os-AKT1 Channel Is Critical for K+ Uptake in Rice Roots and Is Modulated by the Rice CBL1-CIPK23 Complex, The Os-CBL1-Os-CIPK23 complex could enhance Os-AKT1-mediated K+ uptake.
- OsAKT1, OsCIPK23, The Os-AKT1 Channel Is Critical for K+ Uptake in Rice Roots and Is Modulated by the Rice CBL1-CIPK23 Complex, These findings demonstrate that Os-AKT1-mediated K+ uptake in rice roots is modulated by the Os-CBL1-Os-CIPK23 complex.
- OsAKT1, OsPEX11, OsPEX11, a Peroxisomal Biogenesis Factor 11, Contributes to Salt Stress Tolerance in Oryza sativa., Furthermore, qPCR data suggested that OsPEX11 acted as a positive regulator of salt tolerance by reinforcing the expression of several well-known rice transporters (OsHKT2;1, OsHKT1;5, OsLti6a, OsLti6b, OsSOS1, OsNHX1, and OsAKT1) involved in Na(+)/K(+) homeostasis in transgenic plants under salinity
Prev Next