- Information
- Symbol: OsAPL4,OsAGPL4
- MSU: LOC_Os07g13980
- RAPdb: Os07g0243200
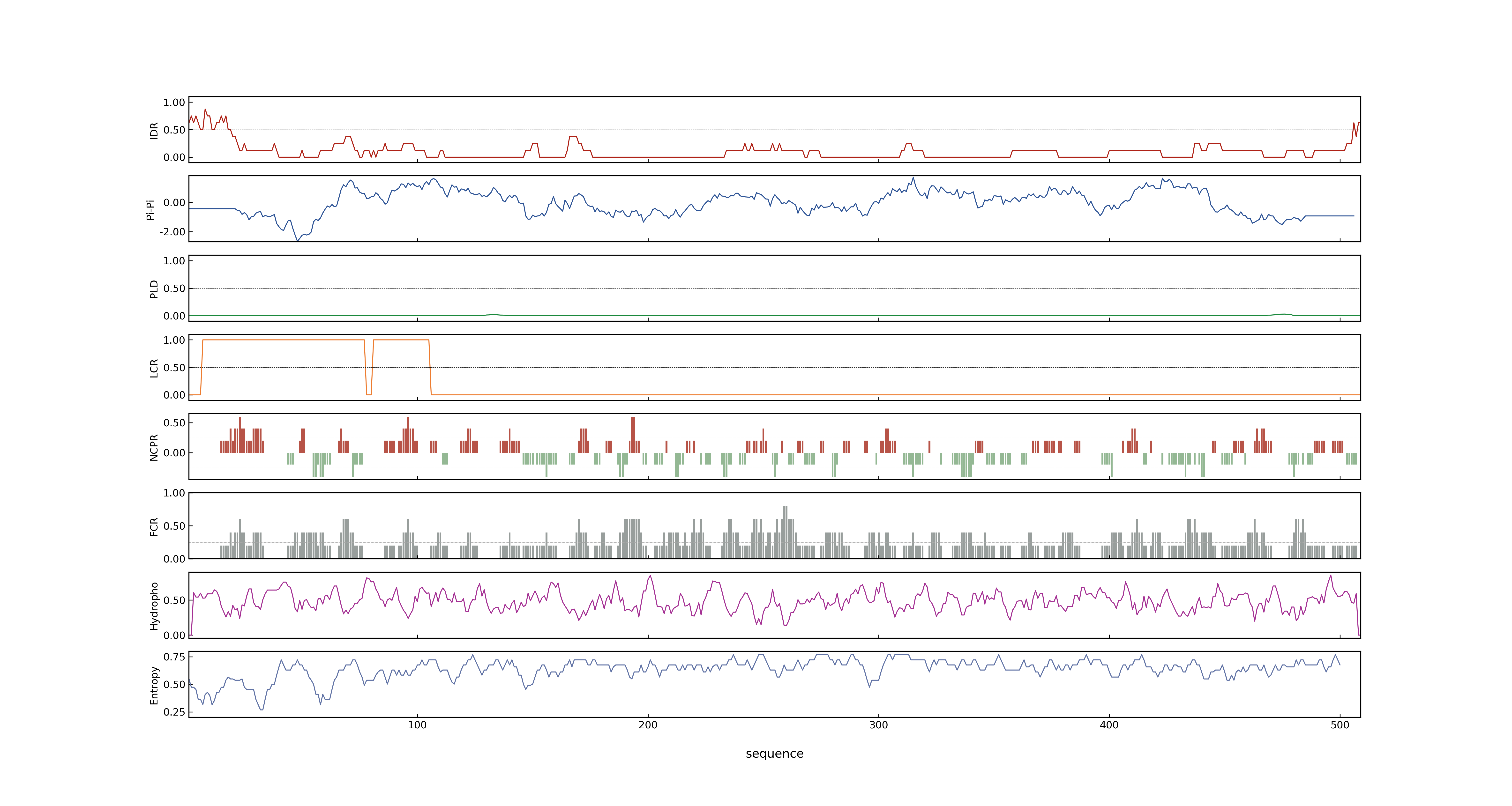
- PSP score
- LOC_Os07g13980.1: 0.0068
- PLAAC score
- LOC_Os07g13960.1: 0
- LOC_Os07g13980.1: 0
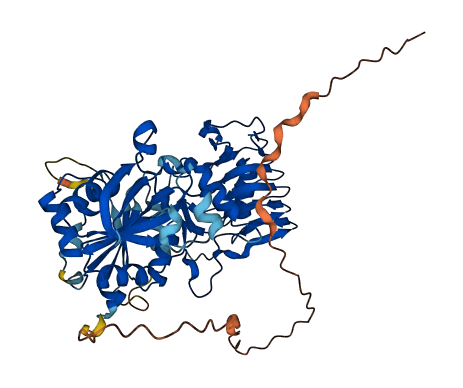
- pLDDT score
- 83.96
- Protein Structure from AlphaFold and UniProt
- MolPhase score
- LOC_Os07g13960.1:
- LOC_Os07g13980.1: 0.29965347
- MolPhase Result
- Publication
- Identification of the ADP-glucose pyrophosphorylase isoforms essential for starch synthesis in the leaf and seed endosperm of rice Oryza sativa L., 2007, Plant Mol Biol.
- Gene expression of ADP-glucose pyrophosphorylase and starch contents in rice cultured cells are cooperatively regulated by sucrose and ABA, 2005, Plant Cell Physiol.
- Genbank accession number
- Key message
- Subcellular localization studies using green fluorescent protein (GFP) fusion constructs indicate that OsAGPS2a, the product of the leaf-preferential transcript of OsAGPS2, and OsAGPS1, OsAGPL1, OsAGPL3, and OsAGPL4 are plastid-targeted isoforms
- OsAPS2 and OsAPL4 were constitutively expressed and these isoforms were coordinated with starch accumulation in the developing rice seed
- Connection
- OsAPL1~OsAGPL3~OsAGPL1, OsAPL4~OsAGPL4, Identification of the ADP-glucose pyrophosphorylase isoforms essential for starch synthesis in the leaf and seed endosperm of rice Oryza sativa L., To identify AGP isoforms essential for this biosynthetic process in sink and source tissues of rice plants, we analyzed the rice AGP gene family which consists of two genes, OsAGPS1 and OsAGPS2, encoding small subunits (SSU) and four genes, OsAGPL1, OsAGPL2, OsAGPL3 and OsAGPL4, encoding large subunits (LSU) of this enzyme heterotetrameric complex
- OsAPL1~OsAGPL3~OsAGPL1, OsAPL4~OsAGPL4, Identification of the ADP-glucose pyrophosphorylase isoforms essential for starch synthesis in the leaf and seed endosperm of rice Oryza sativa L., Subcellular localization studies using green fluorescent protein (GFP) fusion constructs indicate that OsAGPS2a, the product of the leaf-preferential transcript of OsAGPS2, and OsAGPS1, OsAGPL1, OsAGPL3, and OsAGPL4 are plastid-targeted isoforms
- OsAPL4~OsAGPL4, OsAPS1~OsAGPS1, Identification of the ADP-glucose pyrophosphorylase isoforms essential for starch synthesis in the leaf and seed endosperm of rice Oryza sativa L., To identify AGP isoforms essential for this biosynthetic process in sink and source tissues of rice plants, we analyzed the rice AGP gene family which consists of two genes, OsAGPS1 and OsAGPS2, encoding small subunits (SSU) and four genes, OsAGPL1, OsAGPL2, OsAGPL3 and OsAGPL4, encoding large subunits (LSU) of this enzyme heterotetrameric complex
- OsAPL4~OsAGPL4, OsAPS1~OsAGPS1, Identification of the ADP-glucose pyrophosphorylase isoforms essential for starch synthesis in the leaf and seed endosperm of rice Oryza sativa L., Subcellular localization studies using green fluorescent protein (GFP) fusion constructs indicate that OsAGPS2a, the product of the leaf-preferential transcript of OsAGPS2, and OsAGPS1, OsAGPL1, OsAGPL3, and OsAGPL4 are plastid-targeted isoforms
- OsAPL1~OsAGPL3~OsAGPL1, OsAPL4~OsAGPL4, Gene expression of ADP-glucose pyrophosphorylase and starch contents in rice cultured cells are cooperatively regulated by sucrose and ABA, Six cDNA clones encoding two small subunits and four large subunits of ADP-glucose pyrophosphorylase (AGPase) were mined from the database of rice full-length cDNAs, cloned and subsequently named: OsAPS1, OsAPS2, OsAPL1, OsAPL2, OsAPL3 and OsAPL4
- OsAPL2~osagpl2-3~OsAGPL2~GIF2, OsAPL4~OsAGPL4, Gene expression of ADP-glucose pyrophosphorylase and starch contents in rice cultured cells are cooperatively regulated by sucrose and ABA, Six cDNA clones encoding two small subunits and four large subunits of ADP-glucose pyrophosphorylase (AGPase) were mined from the database of rice full-length cDNAs, cloned and subsequently named: OsAPS1, OsAPS2, OsAPL1, OsAPL2, OsAPL3 and OsAPL4
- OsAPL3, OsAPL4~OsAGPL4, Gene expression of ADP-glucose pyrophosphorylase and starch contents in rice cultured cells are cooperatively regulated by sucrose and ABA, Six cDNA clones encoding two small subunits and four large subunits of ADP-glucose pyrophosphorylase (AGPase) were mined from the database of rice full-length cDNAs, cloned and subsequently named: OsAPS1, OsAPS2, OsAPL1, OsAPL2, OsAPL3 and OsAPL4
- OsAPL4~OsAGPL4, OsAPS1~OsAGPS1, Gene expression of ADP-glucose pyrophosphorylase and starch contents in rice cultured cells are cooperatively regulated by sucrose and ABA, Six cDNA clones encoding two small subunits and four large subunits of ADP-glucose pyrophosphorylase (AGPase) were mined from the database of rice full-length cDNAs, cloned and subsequently named: OsAPS1, OsAPS2, OsAPL1, OsAPL2, OsAPL3 and OsAPL4
- OsAPL4~OsAGPL4, OsAPS2~OsAGPS2b, Gene expression of ADP-glucose pyrophosphorylase and starch contents in rice cultured cells are cooperatively regulated by sucrose and ABA, Six cDNA clones encoding two small subunits and four large subunits of ADP-glucose pyrophosphorylase (AGPase) were mined from the database of rice full-length cDNAs, cloned and subsequently named: OsAPS1, OsAPS2, OsAPL1, OsAPL2, OsAPL3 and OsAPL4
- OsAPL4~OsAGPL4, OsAPS2~OsAGPS2b, Gene expression of ADP-glucose pyrophosphorylase and starch contents in rice cultured cells are cooperatively regulated by sucrose and ABA, OsAPS2 and OsAPL4 were constitutively expressed and these isoforms were coordinated with starch accumulation in the developing rice seed
- OsAPL4~OsAGPL4, OspPGM, Plastidic phosphoglucomutase and ADP-glucose pyrophosphorylase mutants impair starch synthesis in rice pollen grains and cause male sterility., To elucidate the starch synthesis pathway and the role of this reserve in rice pollen, we characterized mutations in the plastidic phosphoglucomutase, OspPGM, and the plastidic large subunit of ADP-glucose (ADP-Glc) pyrophosphorylase, OsAGPL4 Both genes were up-regulated in maturing pollen, a stage when starch begins to accumulate
- OsAPL4~OsAGPL4, OspPGM, Plastidic phosphoglucomutase and ADP-glucose pyrophosphorylase mutants impair starch synthesis in rice pollen grains and cause male sterility., Progeny analysis of self-pollinated heterozygous lines carrying the OspPGM mutant alleles, osppgm-1 and osppgm-2, or the OsAGPL4 mutant allele, osagpl4-1, as well as reciprocal crosses between the wild type (WT) and heterozygotes revealed that loss of OspPGM or OsAGPL4 caused male sterility, with the former condition rescued by the introduction of the WT OspPGM gene
Prev Next