- Information
- Symbol: OsBIHD1
- MSU: LOC_Os03g47740
- RAPdb: Os03g0680800
- PSP score
- LOC_Os03g47740.1: 0.9298
- LOC_Os03g47740.3: 0.9801
- LOC_Os03g47740.2: 0.9801
- PLAAC score
- LOC_Os03g47740.1: 0
- LOC_Os03g47740.3: 0
- LOC_Os03g47740.2: 0
- pLDDT score
- 53.08
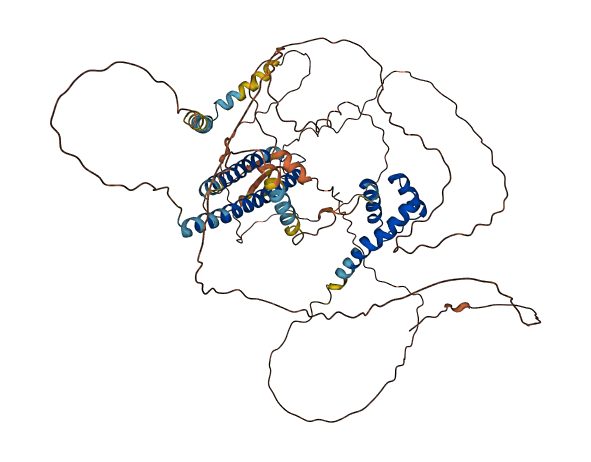
- Protein Structure from AlphaFold and UniProt
- MolPhase score
- LOC_Os03g47740.1: 0.99944037
- LOC_Os03g47740.2: 0.99970537
- LOC_Os03g47740.3: 0.99970537
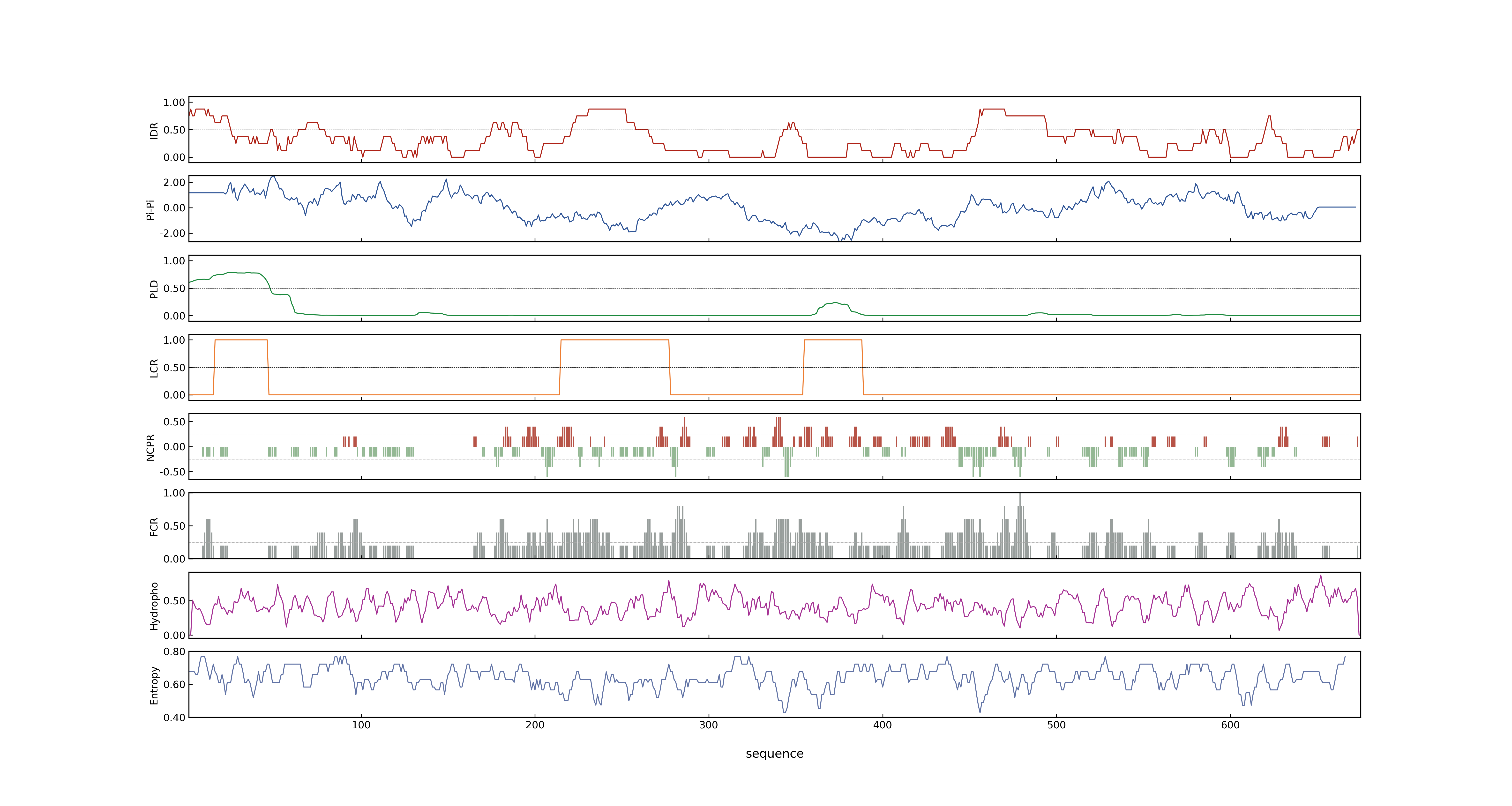
- MolPhase Result
- Publication
- Up-regulation of OsBIHD1, a rice gene encoding BELL homeodomain transcriptional factor, in disease resistance responses, 2005, Plant Biol (Stuttg).
- Overexpression in transgenic tobacco reveals different roles for the rice homeodomain gene OsBIHD1 in biotic and abiotic stress responses, 2005, J Exp Bot.
- NBS-LRR Protein Pik-H4 Interacts with OsBIHD1 to Balance Rice Blast Resistance and Growth by Coordinating Ethylene-Brassinosteroid Pathway., 2017, Front Plant Sci.
- Genbank accession number
- Key message
- To allow a better understanding of the function of OsBIHD1 in plant disease resistance response, the OsBIHD1 gene in tobacco was overexpressed by Agrobacterium-mediated leaf disc transformation with a construct containing the OsBIHD1 ORF under control of the 35S promoter
- The results suggested that the OsBIHD1 protein may be positively involved in activating expression of the defence-related genes in disease resistance responses, and is also important in rice development and abiotic stress tolerance
- Northern blot analysis showed that expression of OsBIHD1 was activated upon treatment with benzothiadiazole (BTH), which is capable of inducing disease resistance
- Up-regulation of OsBIHD1, a rice gene encoding BELL homeodomain transcriptional factor, in disease resistance responses
- These results suggest that OsBIHD1 is a BELL type of homeodomain transcription factor present in the nucleus, whose induction is associated with resistance response in rice
- Expression of OsBIHD1 was also up-regulated rapidly during the first 6 h after inoculation with Magnaporthe grisea in BTH-treated rice seedlings and during the incompatible interaction between M
- Overexpression of the rice OsBIHD1 gene in some of the transgenic tobacco lines led to some morphological abnormalities in the top buds and roots
- However, the transgenic tobacco plants overexpressing OsBIHD1 showed enhanced sensitivity to salt and oxidative stress as compared with the wild-type plants
- Overexpression in transgenic tobacco reveals different roles for the rice homeodomain gene OsBIHD1 in biotic and abiotic stress responses
- In a large-scale yeast two-hybrid screening for Pik-H4-interacting proteins, a homeodomain transcription factor OsBIHD1 was identified, which is previously known to function in biotic and abiotic stress responses
- NBS-LRR Protein Pik-H4 Interacts with OsBIHD1 to Balance Rice Blast Resistance and Growth by Coordinating Ethylene-Brassinosteroid Pathway.
- Furthermore, OsBIHD1 was found to be capable of binding to the sequence-specific cis-elements on the promoters of CYP734A2 to suppress the plant growth under fungal invasion
- Our results collectively suggest a model that OsBIHD1 is required for Pik-H4-mediated blast resistance through modulating the trade-off between resistance and growth by coordinating brassinosteroid-ethylene pathway
- The knockout of OsBIHD1 in rice lines carrying Pik-H4 largely compromised the resistance of the rice lines to Magnaporthe oryzae, the fungus that causes rice blast
- While overexpression of OsBIHD1 resulted in enhanced expression of the pathogenesis-related (PR) and ethylene (ET) synthesis genes
- In addition, OsBIHD1 overexpression or deficiency provoked dwarfism and reduced brassinosteroid (BR) insensitivity through repressing the expression of several critical genes involved in BR biosynthesis and BR signaling
- Connection
- CYP734A2, OsBIHD1, NBS-LRR Protein Pik-H4 Interacts with OsBIHD1 to Balance Rice Blast Resistance and Growth by Coordinating Ethylene-Brassinosteroid Pathway., Furthermore, OsBIHD1 was found to be capable of binding to the sequence-specific cis-elements on the promoters of CYP734A2 to suppress the plant growth under fungal invasion
- OsACO3, OsBIHD1, NBS-LRR Protein Pik-H4 Interacts with OsBIHD1 to Balance Rice Blast Resistance and Growth by Coordinating Ethylene-Brassinosteroid Pathway., Moreover, OsBIHD1 was also found to directly bind to the promoter region of ethylene-synthesis enzyme OsACO3
Prev Next