- Information
- Symbol: OsBISERK1,OsSERK1,OsBAK1,TBP1
- MSU: LOC_Os08g07760
- RAPdb: Os08g0174700
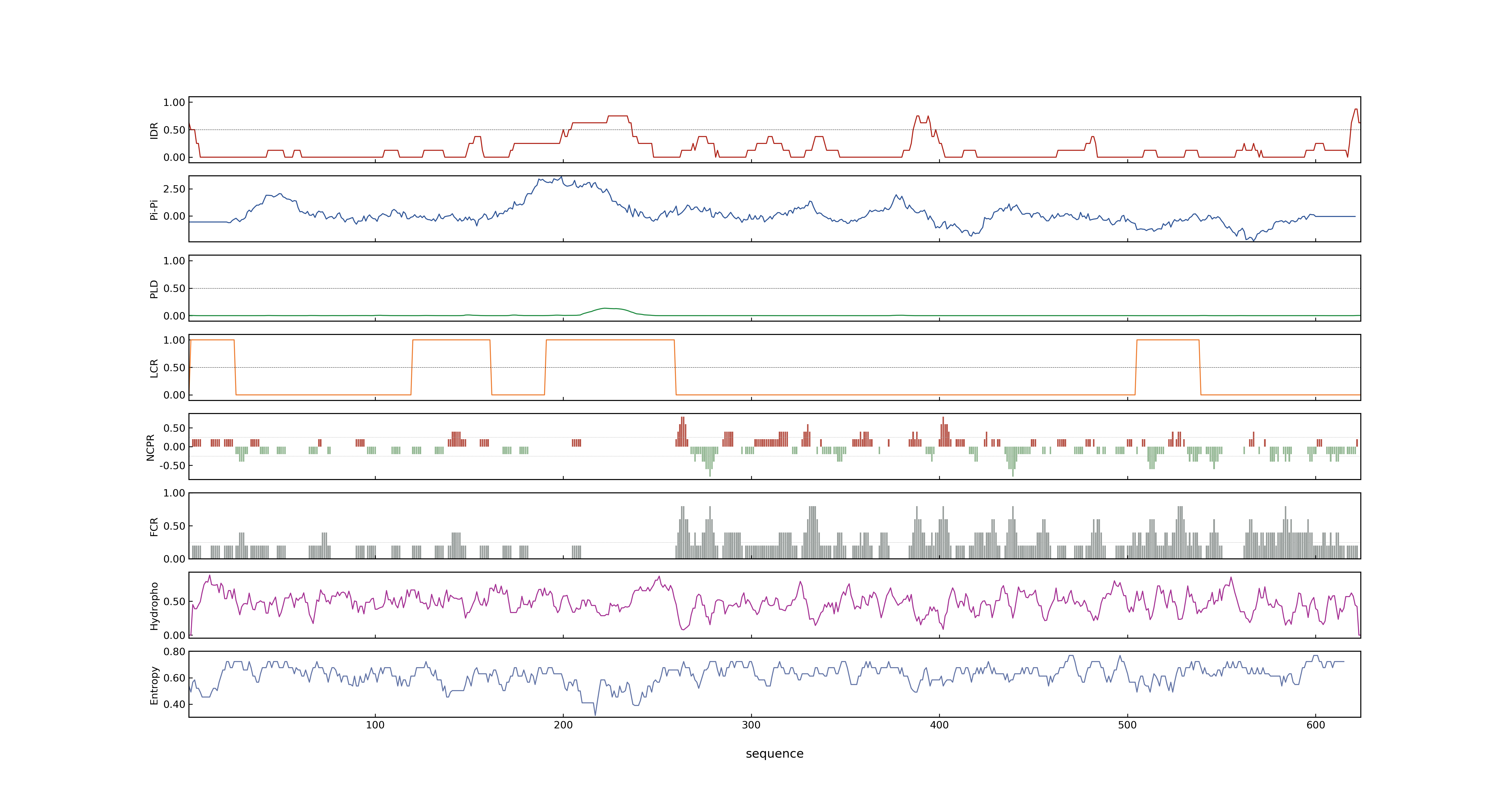
- PSP score
- LOC_Os08g07760.1: 0.0789
- PLAAC score
- LOC_Os08g07760.1: 0
- pLDDT score
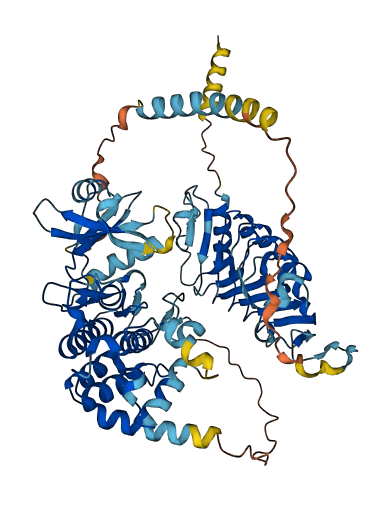
- 81.37
- Protein Structure from AlphaFold and UniProt
- MolPhase score
- LOC_Os08g07760.1: 0.99690407
- MolPhase Result
- Publication
- Expression of SERK family receptor-like protein kinase genes in rice, 2005, Biochim Biophys Acta.
- Rice SERK1 gene positively regulates somatic embryogenesis of cultured cell and host defense response against fungal infection, 2005, Planta.
- COE1, an LRR-RLK responsible for commissural vein pattern formation in rice, 2010, Plant J.
- Engineering OsBAK1 gene as a molecular tool to improve rice architecture for high yield, 2009, Plant Biotechnol J.
- A subset of OsSERK genes, including OsBAK1, affects normal growth and leaf development of rice, 2011, Mol Cells.
- Molecular characterization and expression analysis of OsBISERK1, a gene encoding a leucine-rich repeat receptor-like kinase, during disease resistance responses in rice, 2008, Mol Biol Rep.
- OsSERK1 regulates rice development but not immunity to Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae or Magnaporthe oryzae, 2014, J Integr Plant Biol.
- 08SG2/OsBAK1 regulates grain size and number, and functions differently in Indica and Japonica backgrounds in rice., 2017, Rice (N Y).
- Top Bending Panicle1 is involved in brassinosteroid signaling and regulates the plant architecture in rice, 2017, Plant Physiology and Biochemistry.
- Genbank accession number
- Key message
- OsBISERK1 has a low level of basal expression in leaf tissue
- Suppression of OsSERK1 expression in transgenic calli by RNA interference resulted in a significant reduction of shoot regeneration rate (from 72% to 14% in the japonica rice Zhonghua11)
- Overexpression of OsSERK1, however, increased the shoot regeneration rate (from 72% to 86%)
- Interestingly, OsSERK1 is significantly activated by the rice blast fungus, particularly during the incompatible interaction, and is associated with host cell death in Sekigushi lesion mimic mutants
- However, expression of OsBISERK1 was induced by treatment with benzothiadiazole (BTH), which is capable of inducing disease resistance in rice, and also up-regulated after inoculation with Magnaporthe grisea in BTH-treated rice seedlings and during incompatible interaction between a blast-resistant rice genotype and M
- The results suggest that OsBISERK1 may be involved in disease resistance responses in rice
- Molecular characterization and expression analysis of OsBISERK1, a gene encoding a leucine-rich repeat receptor-like kinase, during disease resistance responses in rice
- Most of the OsBAK1RNAi transgenic rice plants were defective in the development of bulliform cells in the leaf epidermal layer
- A subset of OsSERK genes, including OsBAK1, affects normal growth and leaf development of rice
- Here, we identified OsBAK1 as a potential gene to alter rice architecture
- Therefore, OsBAK1 is a potential molecular breeding tool for improving rice grain yield by modifying rice architecture
- Engineering OsBAK1 gene as a molecular tool to improve rice architecture for high yield
- Our data suggest that OsSERK1 may partially mediate defense signal transduction in addition to its basic role in somatic embryogenesis
- Furthermore, constitutive overexpression of OsSERK1 in two rice cultivars led to an increase in host resistance to the blast fungus
- The OsSERK1 promoter showed reporter gene activities in some specific tissues in a germinating seed, leaf and root, but not in a developing embryo
- The expression of OsBAK1 changed important agricultural traits of rice such as plant height, leaf erectness, grain morphologic features, and disease resistance responses
- Our results suggested that a new rice variety with erect-leaf and normal reproduction can be generated simply by suppressing the expression level of OsBAK1
- These results indicate that OsSERK genes, such as OsBAK1, play versatile roles in rice growth and development
- Overexpression of a truncated intracellular domain of OsBAK1, but not the extracellular domain of OsBAK1, resulted in a dwarfed phenotype, similar to the rice BR-insensitive mutant plants
- OsSERK1 regulates rice development but not immunity to Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae or Magnaporthe oryzae
- Overexpression of OsSerk1 results in a semi-dwarf phenotype whereas silencing of OsSerk1 results in a reduced angle of the lamina joint.
- The grain size and number of knockout mutants of OsBAK1 in the japonica background were significantly decreased, but less so than in 08sg2, supporting the idea that the SNP in OsBAK1 was responsible for the 08sg2 phenotype, but that 08SG2/OsBAK1 function differently in indica and japonica backgrounds
- Map-based cloning, together with transgenic complementation and RNA-interference tests, revealed that TBP1 is a member of the somatic embryogenesis receptor kinases (SERKs) family involved in BR signaling
- Taken together, our results demonstrate that TBP1 plays a significant role in regulating plant architecture via the brassinosteroid signaling pathway
- Compared to wild type, tbp1 mutant plants displayed semi-dwarf stature, erect leaves, small and round grains, as well as more tillers
- Connection
- OsBISERK1~OsSERK1~OsBAK1~TBP1, OsSERK2, Expression of SERK family receptor-like protein kinase genes in rice, In this study, we isolated two novel rice genes, OsSERK1 and OsSERK2, belonging to the SERK-family
- COE1, OsBISERK1~OsSERK1~OsBAK1~TBP1, COE1, an LRR-RLK responsible for commissural vein pattern formation in rice, COE1 encodes a leucine-rich repeat receptor-like kinase, whose amino acid sequence is similar to that of brassinosteroid-insensitive 1-associated receptor kinase 1 (BAK1), and which is localized at the plasma membrane
- COE1, OsBISERK1~OsSERK1~OsBAK1~TBP1, COE1, an LRR-RLK responsible for commissural vein pattern formation in rice, Because of the sequence similarity of COE1 to BAK1, we also examined the involvement of brassinosteroids in CV formation
- OsBISERK1~OsSERK1~OsBAK1~TBP1, OsSERK2, OsSERK1 regulates rice development but not immunity to Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae or Magnaporthe oryzae, In yeast, OsSERK1 interacts with itself forming homodimers, and also interacts with the kinase domains of OsSERK2 and BRI1, respectively.
- D61~OsBRI1, OsBISERK1~OsSERK1~OsBAK1~TBP1, OsSERK1 regulates rice development but not immunity to Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae or Magnaporthe oryzae, In yeast, OsSERK1 interacts with itself forming homodimers, and also interacts with the kinase domains of OsSERK2 and BRI1, respectively.
- OsBISERK1~OsSERK1~OsBAK1~TBP1, OsI-BAK1, Brassinosteroid insensitive 1-associated kinase 1 OsI-BAK1 is associated with grain filling and leaf development in rice., The aim of this study is to investigate the functions of a rice OsBAK1 homologue, designated as OsI-BAK1, which is highly expressed after heading
- OsBISERK1~OsSERK1~OsBAK1~TBP1, OsREM4.1, OsREM4.1 Interacts with OsSERK1 to Coordinate the Interlinking between Abscisic Acid and Brassinosteroid Signaling in Rice., OsREM4.1 Interacts with OsSERK1 to Coordinate the Interlinking between Abscisic Acid and Brassinosteroid Signaling in Rice.
- OsBISERK1~OsSERK1~OsBAK1~TBP1, OsPRA2, OsPRA2 fine-tunes rice brassinosteroid receptor., Recently we have reported that a rice small G protein, OsPRA2, bound to the BR receptor OsBRI1 at the plasma membrane (PM) and inhibited its kinase activity and its interaction with the co-receptor OsBAK1, leading to a lower sensitivity to BR treatment and dephosphorylation of OsBZR1
- D61~OsBRI1, OsBISERK1~OsSERK1~OsBAK1~TBP1, Top Bending Panicle1 is involved in brassinosteroid signaling and regulates the plant architecture in rice, Furthermore, bimolecular fluorescence complementation and co-immunoprecipitation analysis demonstrated that a substitution at 61st amino acid (His61Leu) in the tbp1 mutant may result in a reduction of the interaction between TBP1 and OsBRI1 (BR receptor in rice)
Prev Next