- Information
- Symbol: OsCCS52A,TAD,TE
- MSU: LOC_Os03g03150
- RAPdb: Os03g0123300
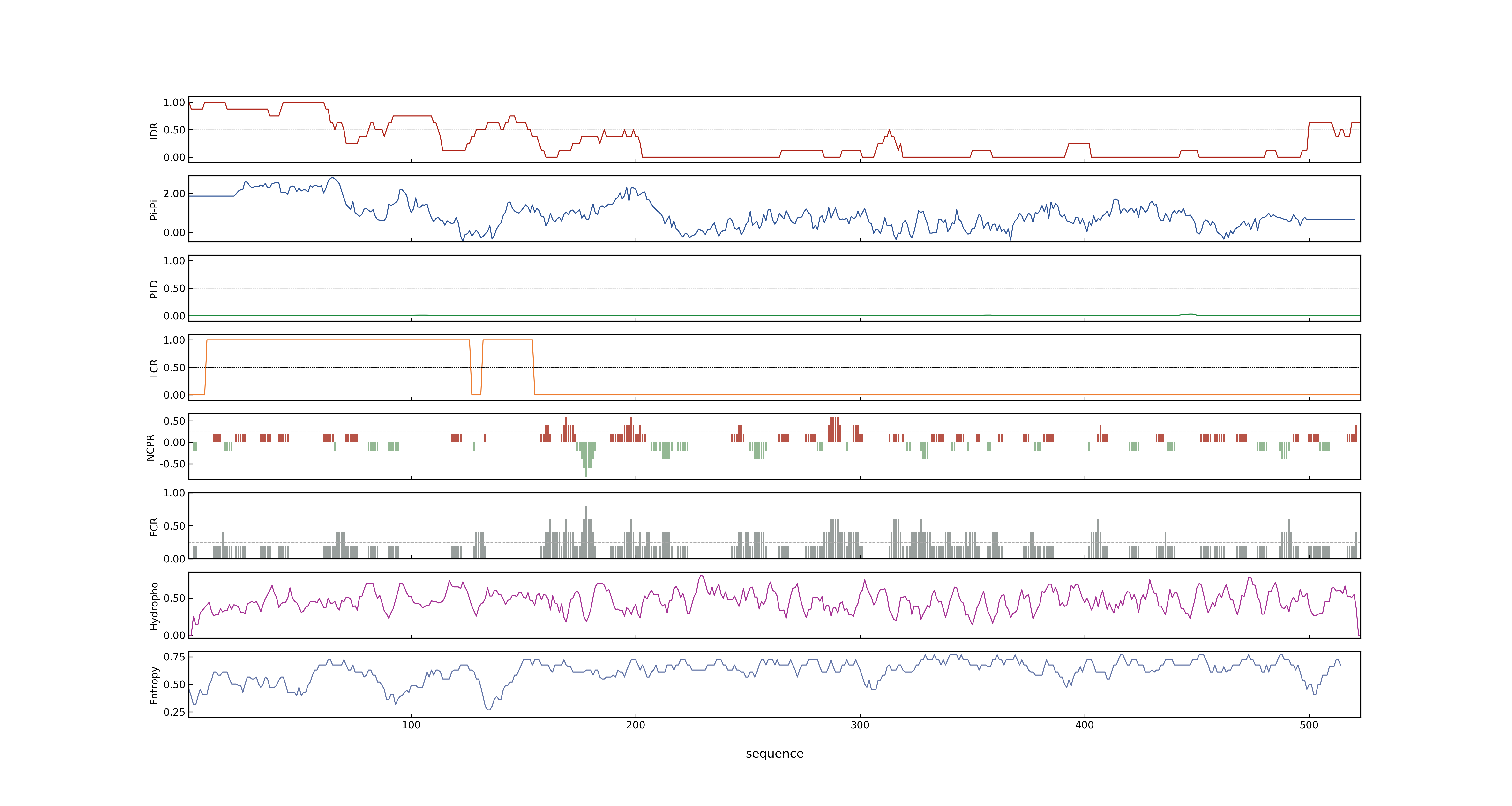
- PSP score
- LOC_Os03g03150.2: 0.9778
- LOC_Os03g03150.1: 0.9778
- PLAAC score
- LOC_Os03g03150.2: 0
- LOC_Os03g03150.1: 0
- pLDDT score
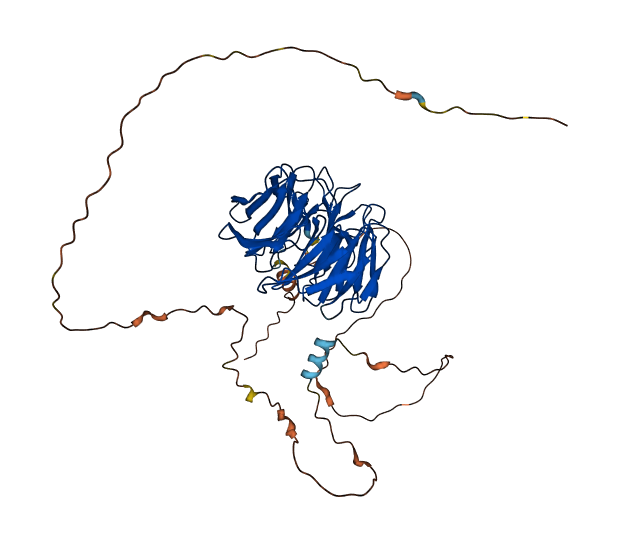
- 75.81
- Protein Structure from AlphaFold and UniProt
- MolPhase score
- LOC_Os03g03150.1: 0.99976557
- LOC_Os03g03150.2: 0.99976557
- MolPhase Result
- Publication
- Potential role of the rice OsCCS52A gene in endoreduplication, 2012, Planta.
- Rice APC/CTE controls tillering by mediating the degradation of MONOCULM 1, 2012, Nat Commun.
- Degradation of MONOCULM 1 by APC/CTAD1 regulates rice tillering, 2012, Nat Commun.
- The SnRK2-APC/CTE regulatory module mediates the antagonistic action of gibberellic acid and abscisic acid pathways., 2015, Nat Commun.
- Genbank accession number
- Key message
- In rice, OsCCS52A is highly expressed in seedlings, flowers, immature panicles and 15 DAP kernels
- We conclude that besides having a conserved role in regulating cell cycle, APC/C(TE) has a unique function in regulating the plant-specific postembryonic shoot branching and tillering, which are major determinants of plant architecture and grain yield
- In this study, rice cell cycle switch 52 A (OsCCS52A), an APC activator, is functionally characterized using the reverse genetic approach
- In addition, overexpression of OsCCS52A inhibits mitotic cell division and induces endoreduplication and cell elongation in fission yeast
- A cycle of endoreduplication is common in most of the differentiated cells of plant vegetative tissues and it occurs extensively in cereal endosperm cells
- Taken together, these results suggest that OsCCS52A is involved in maintaining normal seed size formation by mediating the exit from mitotic cell division to enter the endoreduplication cycles in rice endosperm
- A rice tiller is a specialized grain-bearing branch that contributes greatly to grain yield
- We find that TE physically interacts with ABA receptor OsPYL/RCARs and promotes their degradation by the proteasome
- Genetic analysis also shows OsPYL/RCARs act downstream of TE in mediating ABA responses
- Conversely, ABA inhibits APC/C(TE) activity by phosphorylating TE through activating the SNF1-related protein kinases (SnRK2s), which may interrupt the interaction between TE and OsPYL/RCARs and subsequently stabilize OsPYL/RCARs
- Connection
- OsCCS52A~TAD~TE, OsCDC27, The SnRK2-APC/CTE regulatory module mediates the antagonistic action of gibberellic acid and abscisic acid pathways, Yeast two-hybrid assay showing that TE interacts with MOC1 and OsCDC27, but not with MOC1d and MOC1-m
- MOC1, OsCCS52A~TAD~TE, Rice APC/CTE controls tillering by mediating the degradation of MONOCULM 1, TE physically interacts with MOC1 and OsCDC27
Prev Next