- Information
- Symbol: OsCDPK7
- MSU: LOC_Os04g49510
- RAPdb: Os04g0584600
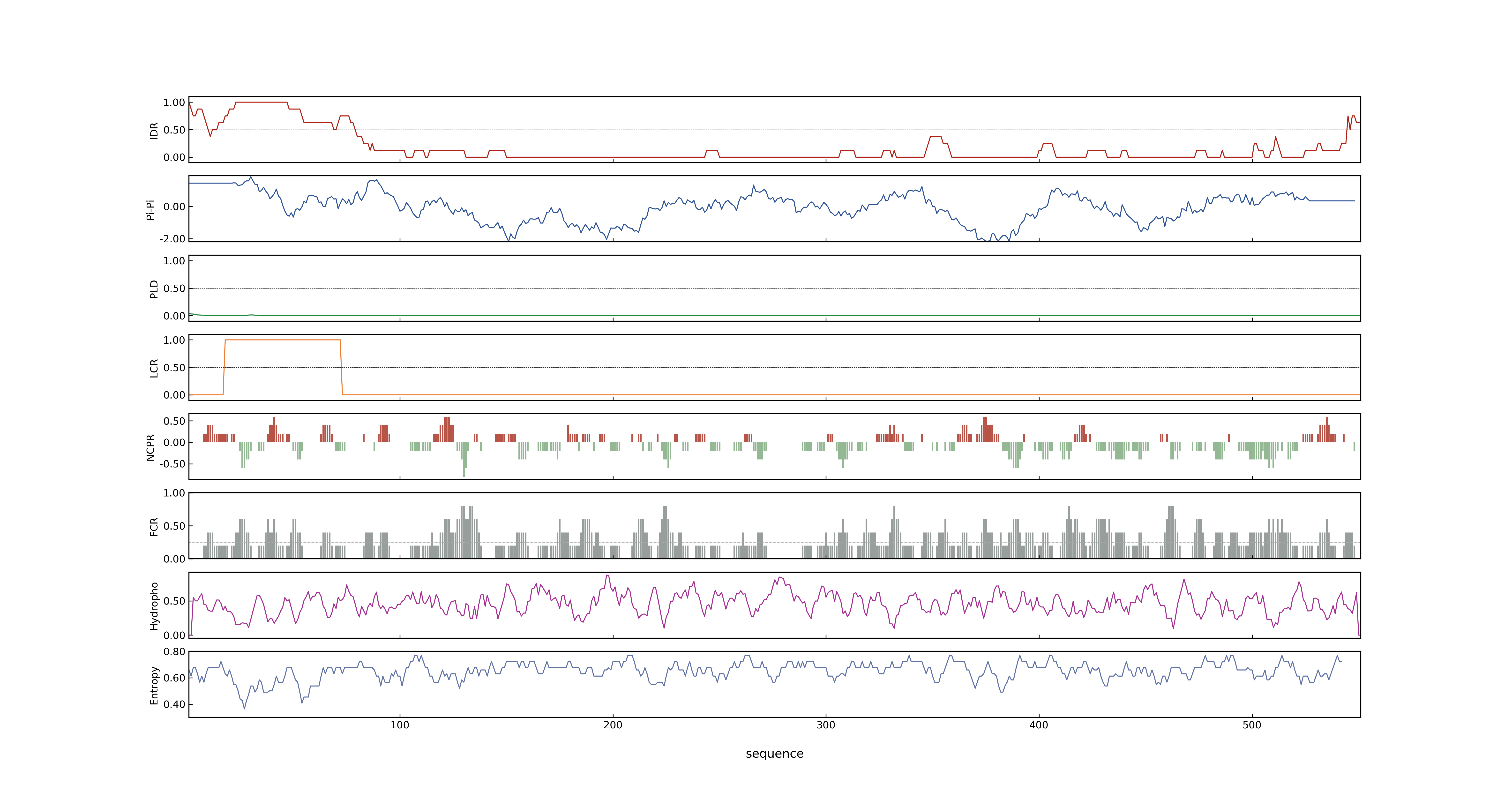
- PSP score
- LOC_Os04g49510.3: 0.0241
- LOC_Os04g49510.1: 0.003
- LOC_Os04g49510.4: 0.0129
- LOC_Os04g49510.2: 0.0047
- PLAAC score
- LOC_Os04g49510.3: 0
- LOC_Os04g49510.1: 0
- LOC_Os04g49510.4: 0
- LOC_Os04g49510.2: 0
- pLDDT score
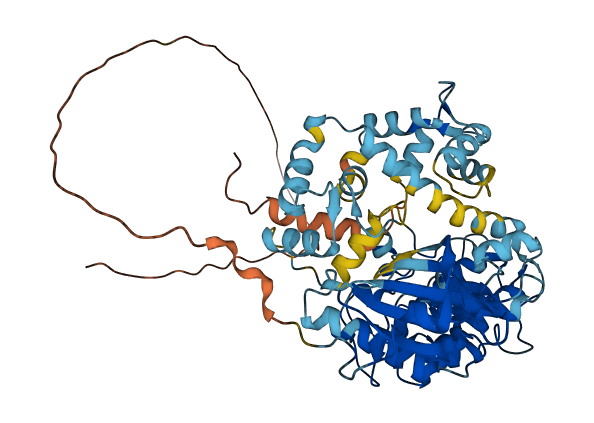
- 76.84
- Protein Structure from AlphaFold and UniProt
- MolPhase score
- LOC_Os04g49510.1: 0.88097494
- LOC_Os04g49510.2: 0.98408448
- LOC_Os04g49510.3: 0.24582915
- LOC_Os04g49510.4: 0.84322136
- MolPhase Result
- Publication
- Over-expression of a single Ca2+-dependent protein kinase confers both cold and salt/drought tolerance on rice plants, 2000, The Plant Journal.
- A Ca2+-Dependent Protein Kinase that Endows Rice Plants with Cold- and Salt-Stress Tolerance Functions in Vascular Bundles, 2001, Plant and Cell Physiology.
- Genbank accession number
- Key message
- Over-expression of OsCDPK7 enhanced induction of some stress-responsive genes in response to salinity/drought, but not to cold
- A rice Ca2+-dependent protein kinase, OsCDPK7, is a positive regulator commonly involved in the tolerance to cold and salt/drought
- The transcript of a putative target gene of the OsCDPK7 signaling pathway, rab16A, was also detected essentially in the same tissues upon salt stress, suggesting that the OsCDPK7 pathway operates predominantly in these regions
- In the wild-type rice plants under both stress conditions, OsCDPK7 was expressed predominantly in vascular tissues of crowns and roots, vascular bundles and central cylinder, respectively, where water stress occurs most severely
- Similar localization patterns with stronger signals were observed in stress-tolerant OsCDPK7 over-expressing transformants with the cauliflower mosaic virus 35S promoter
- A rice gene encoding a calcium-dependent protein kinase (CDPK), OsCDPK7, was induced by cold and salt stresses
- The extent of tolerance to cold and salt/drought stresses of these plants correlated well with the level of OsCDPK7 expression
- Connection
Prev Next