- Information
- Symbol: OsCIN1
- MSU: LOC_Os02g33110
- RAPdb: Os02g0534400
- PSP score
- LOC_Os02g33110.1: 0.0068
- LOC_Os02g33110.3: 0.0118
- LOC_Os02g33110.2: 0.0311
- PLAAC score
- LOC_Os02g33110.1: 0
- LOC_Os02g33110.3: 0
- LOC_Os02g33110.2: 0
- pLDDT score
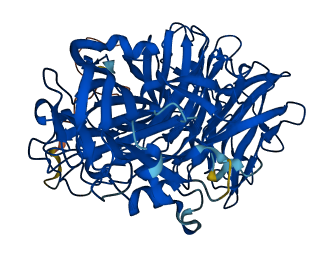
- 92.36
- Protein Structure from AlphaFold and UniProt
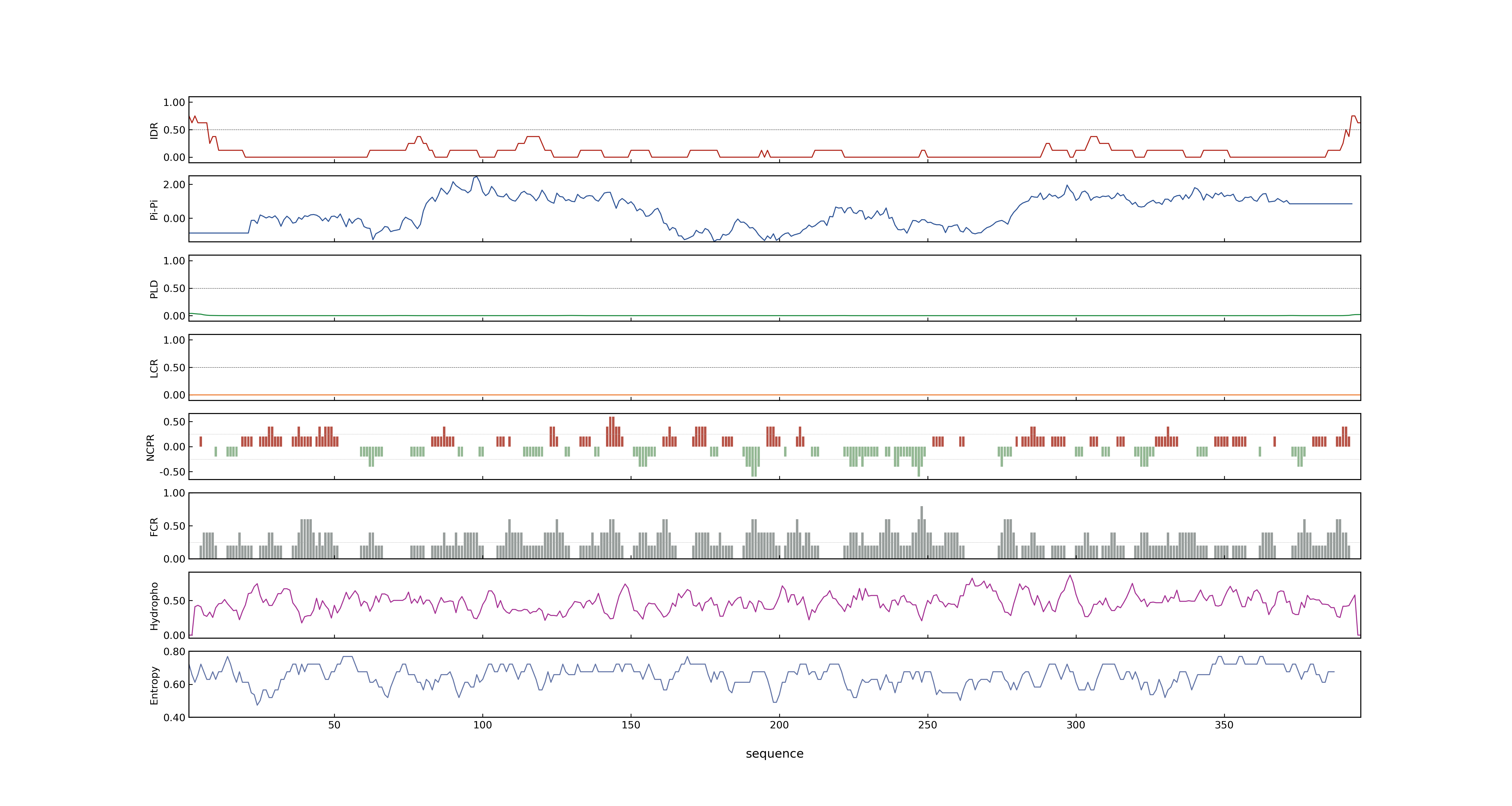
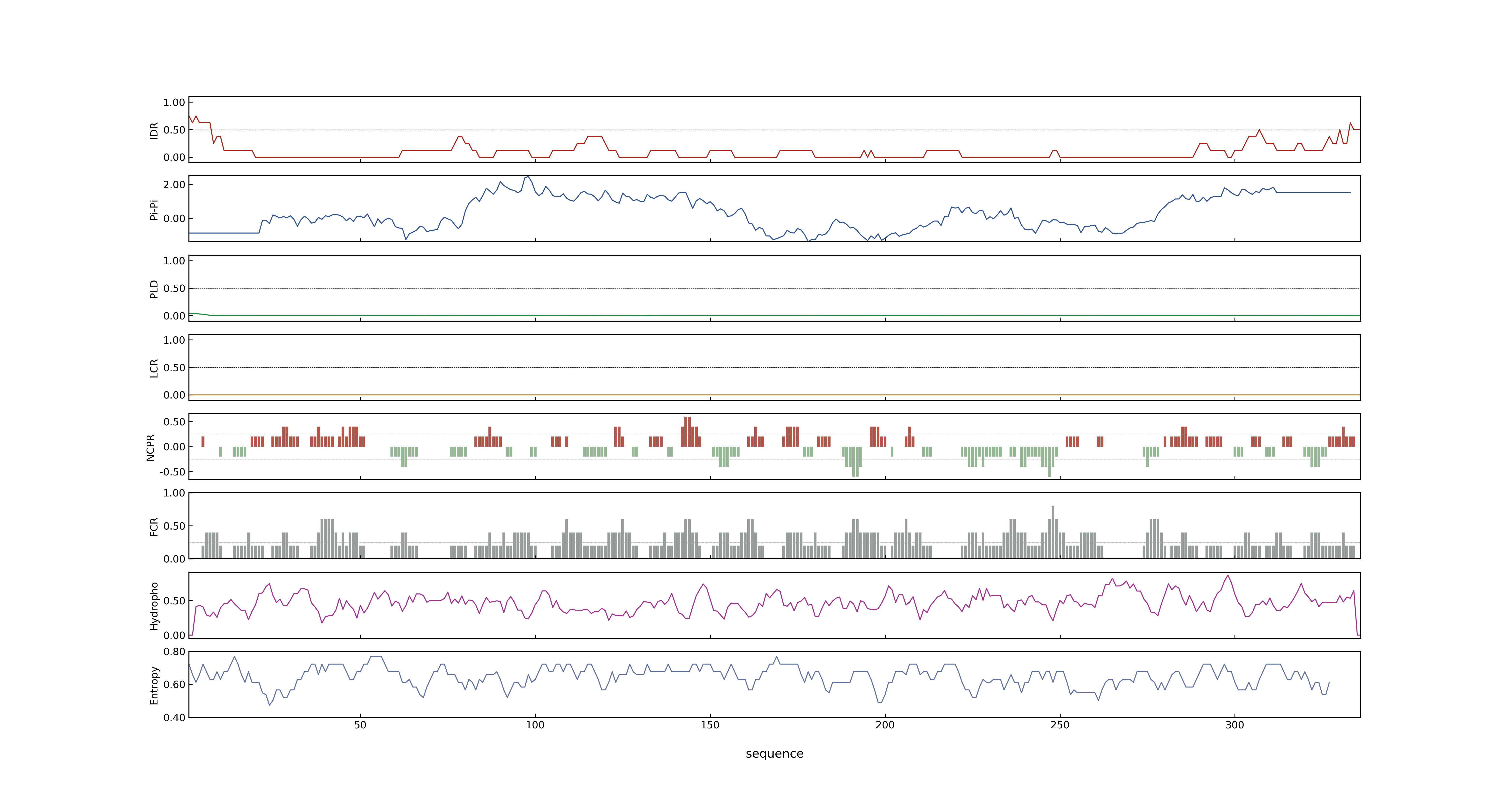
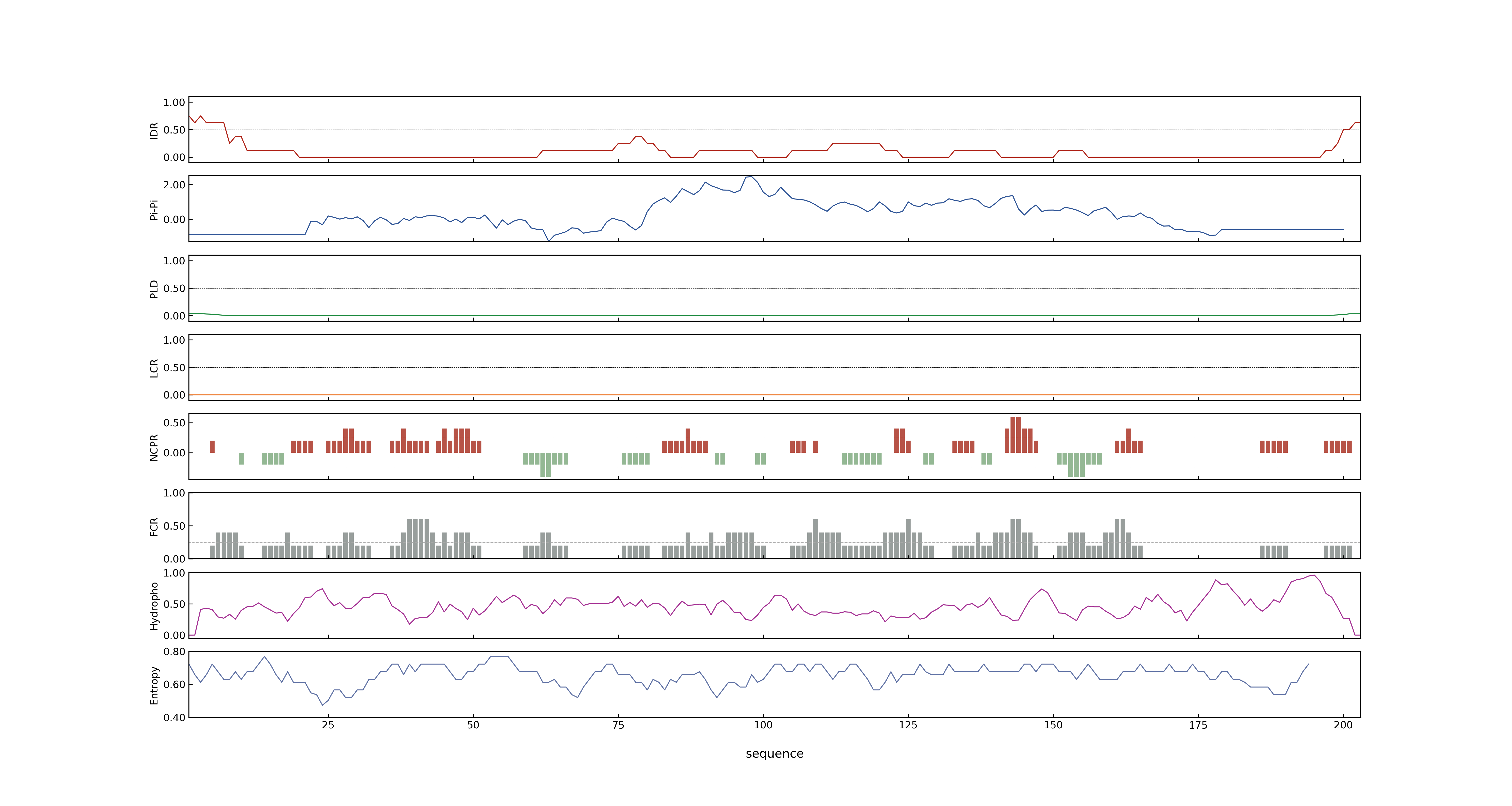
- MolPhase score
- LOC_Os02g33110.1: 0.00319378
- LOC_Os02g33110.2: 0.00134900
- LOC_Os02g33110.3: 0.01905337
- MolPhase Result
- Publication
- Duplication and independent selection of cell-wall invertase genes GIF1 and OsCIN1 during rice evolution and domestication, 2010, BMC Evol Biol.
- Cell Wall Invertase in Developing Rice Caryopsis: Molecular Cloning of OsCIN1 and Analysis of its Expression in Relation to its Role in Grain Filling, 2002, Plant and Cell Physiology.
-
Genbank accession number
- Key message
- During the course of grain filling in the caryopses, OsCIN1 transcript is detectable only in the very early stage of their development, 1~4 d after flowering, when the cell wall invertase activity is the highest and the increase in caryopsis length is rapid
- Cell Wall Invertase in Developing Rice Caryopsis: Molecular Cloning of OsCIN1 and Analysis of its Expression in Relation to its Role in Grain Filling
- OsCIN1 is expressed in roots, in sink- and source-leaves, and in panicles
- Results based on analyses of population genetics and gene phylogenetic tree of 25 cultivars and 25 wild rice sequences demonstrated that OsCIN1 was also artificially selected during rice domestication with a fixed mutation in the coding region, in contrast to GIF1 that was selected in the promoter region
- Duplication and independent selection of cell-wall invertase genes GIF1 and OsCIN1 during rice evolution and domestication
- Connection
- GIF1~OsCIN2~OsGIF1, OsCIN1, Duplication and independent selection of cell-wall invertase genes GIF1 and OsCIN1 during rice evolution and domestication, Here, we report that GIF1 and another CWI gene OsCIN1 constitute a pair of duplicate genes with differentiated expression and function through independent selection
- GIF1~OsCIN2~OsGIF1, OsCIN1, Duplication and independent selection of cell-wall invertase genes GIF1 and OsCIN1 during rice evolution and domestication, RESULTS: Through synteny analysis, we show that GIF1 and another cell-wall invertase gene OsCIN1 were paralogues derived from a segmental duplication originated during genome duplication of grasses
- GIF1~OsCIN2~OsGIF1, OsCIN1, Duplication and independent selection of cell-wall invertase genes GIF1 and OsCIN1 during rice evolution and domestication, Results based on analyses of population genetics and gene phylogenetic tree of 25 cultivars and 25 wild rice sequences demonstrated that OsCIN1 was also artificially selected during rice domestication with a fixed mutation in the coding region, in contrast to GIF1 that was selected in the promoter region
- GIF1~OsCIN2~OsGIF1, OsCIN1, Duplication and independent selection of cell-wall invertase genes GIF1 and OsCIN1 during rice evolution and domestication, GIF1 and OsCIN1 have evolved into different expression patterns and probable different kinetics parameters of enzymatic activity with the latter displaying less enzymatic activity
- GIF1~OsCIN2~OsGIF1, OsCIN1, Duplication and independent selection of cell-wall invertase genes GIF1 and OsCIN1 during rice evolution and domestication, Overexpression of GIF1 and OsCIN1 also resulted in different phenotypes, suggesting that OsCIN1 might regulate other unrecognized biological process
- GIF1~OsCIN2~OsGIF1, OsCIN1, Duplication and independent selection of cell-wall invertase genes GIF1 and OsCIN1 during rice evolution and domestication, Our discovery that the duplicated pair of GIF1 and OsCIN1 has experienced sub-functionalization implies that selection could act independently on each duplicate towards different functional specificity, which provides a vivid example for evolution of genetic novelties in a model crop
- GIF1~OsCIN2~OsGIF1, OsCIN1, Duplication and independent selection of cell-wall invertase genes GIF1 and OsCIN1 during rice evolution and domestication, Duplication and independent selection of cell-wall invertase genes GIF1 and OsCIN1 during rice evolution and domestication
Prev Next