- Information
- Symbol: OsCLP
- MSU: LOC_Os01g71080
- RAPdb: Os01g0937050
- PSP score
- LOC_Os01g71080.1: 0.0452
- PLAAC score
- LOC_Os01g71080.1: 0
- pLDDT score
- 90.35
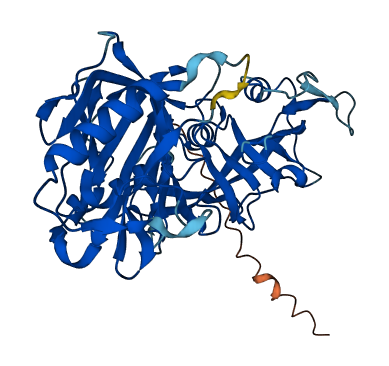
- Protein Structure from AlphaFold and UniProt
- MolPhase score
- LOC_Os01g71080.1: 0.45411822
- MolPhase Result
- Publication
- Genbank accession number
- Key message
- These data suggest that OsCLP, which has chitinase activity, may play an important role in plant defenses against pathogens
- In addition, exogenous treatment with OsCLP affected the growth of the basidiomycete fungus Rhizoctonia solani through degradation of the hyphal cell wall
- A T-DNA insertion mutant of OsCLP (osclp) showed significant retardation of root and shoot growth
- A comparative proteomic analysis was carried out using root tissue of wild-type and the osclp mutant to understand the OsCLP-mediated rice growth retardation
- Exogenous application of Ca(2+) resulted in successful recovery of both primary and lateral root growth in osclp
- Moreover, overexpression of OsCLP resulted in improved growth with modified seed shape and starch structure; however, the overall yield remained unaffected
- Taken together, our results highlight the involvement of OsCLP in rice growth by regulating the intracellular calcium concentrations
- Results obtained revealed that proteins related to glycolysis (phosphoglycerate kinase), stress adaption (chaperonin) and calcium signaling (calreticulin and CDPK1) were differentially regulated in osclp roots
- Fura-2 molecular probe staining, which is an intracellular calcium indicator, and ICP-MS analysis suggested that the intracellular calcium content was significantly lower in roots of osclp as compared to the wild-type
- Connection
Prev Next