- Information
- Symbol: OsChI1
- MSU: LOC_Os01g61160
- RAPdb: Os01g0827300
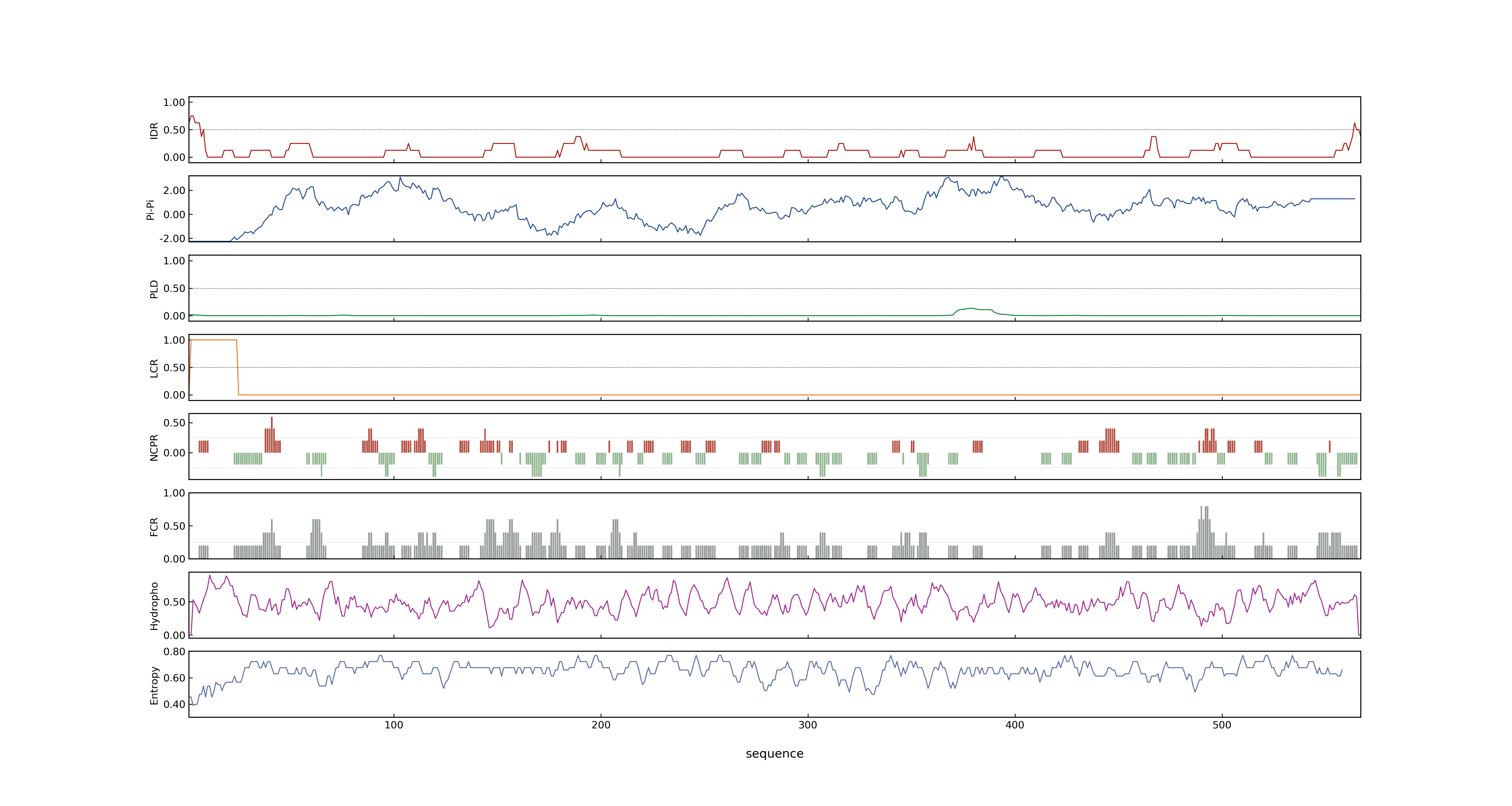
- PSP score
- LOC_Os01g61160.1: 0.0811
- PLAAC score
- LOC_Os01g61160.1: 0
- pLDDT score
- 94.74
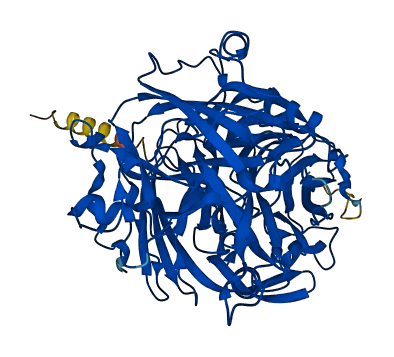
- Protein Structure from AlphaFold and UniProt
- MolPhase score
- LOC_Os01g61160.1: 0.00913203
- MolPhase Result
- Publication
-
Genbank accession number
- Key message
- In silico analysis of OsChI1 suggests that several genes coexpressed with OsChI1 in the root during various abiotic stresses, such as chilling, drought and salt stress, may play an important role in the ROS signaling pathway
- In order to investigate the molecular mechanism underlying chilling tolerance and possible crosstalk with other abiotic stresses, we selected a rice gene, OsChI1 (Os01g61160), for further analysis
- Potential roles of OsChI1 in response to abiotic stresses are discussed
- Overexpression of the OsChI1 gene, encoding a putative laccase precursor, increases tolerance to drought and salinity stress in transgenic Arabidopsis.
- In addition, we also observed increased transcript levels of the OsChI1 gene during dehydration and high salinity conditions
- Higher expression of the OsChI1 gene was also detected in roots and tissues at the vegetative and productive stages
- Transient expression of OsChI1 proteins tagged with fluorescence protein in rice protoplasts revealed that OsChI1 is localized in the plasma membrane
- The OsChI1 gene encodes a putative laccase precursor protein
- Connection
Prev Next