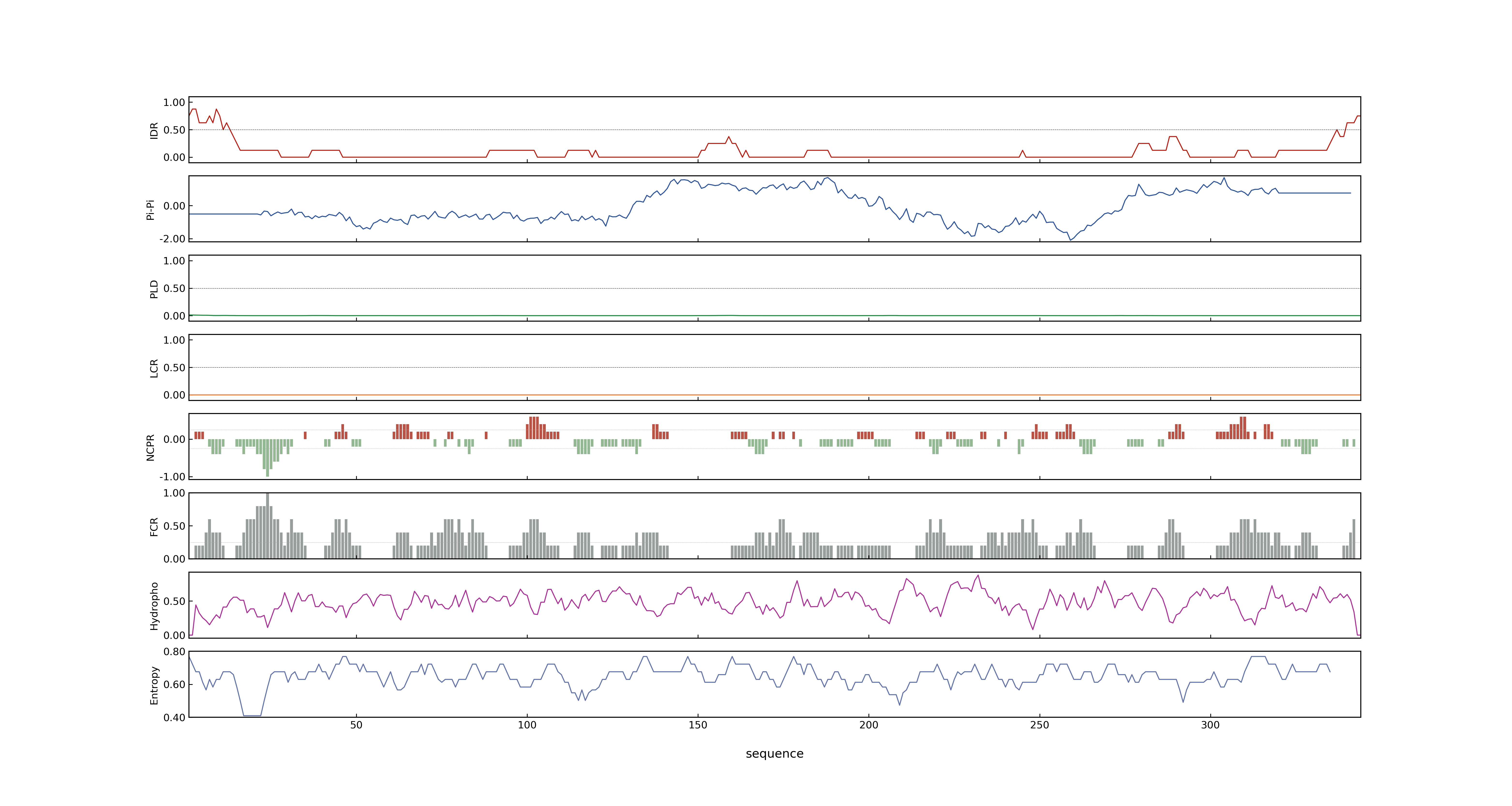
- Information
- Symbol: OsDMC1,DMC1B
- MSU: LOC_Os11g04954
- RAPdb: Os11g0146800
- PSP score
- LOC_Os11g04954.1: 0.0381
- PLAAC score
- LOC_Os11g04954.1: 0
- pLDDT score
- NA
- MolPhase score
- LOC_Os11g04954.1: 0.00007178
- MolPhase Result
- Publication
- Isolation and characterization of OsDMC1 , the rice homologue of the yeast DMC1 gene essential for meiosis, 2001, Sexual Plant Reproduction.
- DNA strand exchange activity of rice recombinase OsDmc1 monitored by fluorescence resonance energy transfer and the role of ATP hydrolysis, 2006, FEBS J.
- DNA binding and pairing activity of OsDmc1, a recombinase from rice, 2005, Plant Mol Biol.
- OsDMC1 is required for homologous pairing in Oryza sativa, 2007, Plant Mol Biol.
- Filament formation and robust strand exchange activities of the rice DMC1A and DMC1B proteins., 2008, Nucleic Acids Res.
- OsDMC1 is not required for homologous pairing in rice meiosis., 2016, Plant Physiol.
- Genbank accession number
- Key message
- The OsDMC1-RNAi lines grew normally during their vegetative phase but showed spikelet and pollen sterility
- The sterility phenotypes were associated with down-regulated OsDMC1 transcript and protein levels mediated by RNAi
- OsDMC1 was expressed at high-levels in reproductive organs, low-levels in roots, and undetectable levels in leaves and seedlings
- Isolation and characterization of OsDMC1 , the rice homologue of the yeast DMC1 gene essential for meiosis
- Further cytological observations of male meiocytes revealed that knock-down of OsDMC1 led to defects in bivalent formation and subsequent unequal chromosome segregation and irregular spore generation, and induced changes in male meiotic progression
- DNA binding and pairing activities of Oryza sativa disrupted meiotic cDNA1 (OsDmc1) from rice have been reported earlier
- A cloned cDNA corresponding to OsDMC1 from rice anther tissue was expressed in Escherichia coli
- Here, we analyzed the function of OsDMC1 in meiosis using an RNA interference approach
- These data indicate that OsDMC1 is essential for rice meiosis and plays an important role in homologous pairing
- These biochemical differences between the DMC1A and DMC1B proteins may provide important insight into their functional differences during meiosis in rice
- Moreover, OsDMC1 was not detected in pairing-defective mutants, such as pair2, pair3, Oscom1 and Osrad51c, while it was loaded onto meiotic chromosomes in zep1, Osmer3, Oszip4 and Oshei10
- The reduced number of bivalents and abnormal OsHEI10 foci in Osdmc1a Osdmc1b establishes an essential role for OsDMC1 in crossover formation
- Connection
- DMC1A~DMC1, OsDMC1~DMC1B, Filament formation and robust strand exchange activities of the rice DMC1A and DMC1B proteins., Filament formation and robust strand exchange activities of the rice DMC1A and DMC1B proteins.
- DMC1A~DMC1, OsDMC1~DMC1B, Filament formation and robust strand exchange activities of the rice DMC1A and DMC1B proteins., In rice, two Dmc1 genes, Dmc1A and Dmc1B, have been reported
- DMC1A~DMC1, OsDMC1~DMC1B, Filament formation and robust strand exchange activities of the rice DMC1A and DMC1B proteins., Although the Oryza sativa DMC1A protein has been partially characterized, however the biochemical properties of the DMC1B protein have not been defined
- DMC1A~DMC1, OsDMC1~DMC1B, Filament formation and robust strand exchange activities of the rice DMC1A and DMC1B proteins., In the present study, we expressed the Oryza sativa DMC1A and DMC1B proteins in bacteria and purified them
- DMC1A~DMC1, OsDMC1~DMC1B, Filament formation and robust strand exchange activities of the rice DMC1A and DMC1B proteins., The purified DMC1A and DMC1B proteins formed helical filaments along single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) and double-stranded DNA (dsDNA), and promoted robust strand exchange between ssDNA and dsDNA over five thousand base pairs in the presence of RPA, as a co-factor
- DMC1A~DMC1, OsDMC1~DMC1B, Filament formation and robust strand exchange activities of the rice DMC1A and DMC1B proteins., The DMC1A and DMC1B proteins also promoted strand exchange in the absence of RPA with long DNA substrates containing several thousand base pairs
- DMC1A~DMC1, OsDMC1~DMC1B, Filament formation and robust strand exchange activities of the rice DMC1A and DMC1B proteins., The strand-exchange activity of the Oryza sativa DMC1A protein was much higher than that of the DMC1B protein
- DMC1A~DMC1, OsDMC1~DMC1B, Filament formation and robust strand exchange activities of the rice DMC1A and DMC1B proteins., Consistently, the DNA-binding activity of the DMC1A protein was higher than that of the DMC1B protein
- DMC1A~DMC1, OsDMC1~DMC1B, Filament formation and robust strand exchange activities of the rice DMC1A and DMC1B proteins., These biochemical differences between the DMC1A and DMC1B proteins may provide important insight into their functional differences during meiosis in rice
- DMC1A~DMC1, OsDMC1~DMC1B, OsDMC1 is not required for homologous pairing in rice meiosis., Taken together, these results suggest that during meiosis, OsDMC1 is dispensable for homologous pairing in rice, which is quite different from the DMC1 homologs identified so far in other organisms
- OsCOM1, OsDMC1~DMC1B, OsDMC1 is not required for homologous pairing in rice meiosis., In the absence of OsDMC1, early recombination events probably occur normally, leading to normal localization of ÃÂÃÂÃÂóH2AX, PAIR3, OsMRE11, OsCOM1 and OsRAD51C
- OsCOM1, OsDMC1~DMC1B, OsDMC1 is not required for homologous pairing in rice meiosis., Moreover, OsDMC1 was not detected in pairing-defective mutants, such as pair2, pair3, Oscom1 and Osrad51c, while it was loaded onto meiotic chromosomes in zep1, Osmer3, Oszip4 and Oshei10
- OsDMC1~DMC1B, OsMRE11, OsDMC1 is not required for homologous pairing in rice meiosis., In the absence of OsDMC1, early recombination events probably occur normally, leading to normal localization of ÃÂÃÂÃÂóH2AX, PAIR3, OsMRE11, OsCOM1 and OsRAD51C
- OsDMC1~DMC1B, OsZIP4, OsDMC1 is not required for homologous pairing in rice meiosis., Moreover, OsDMC1 was not detected in pairing-defective mutants, such as pair2, pair3, Oscom1 and Osrad51c, while it was loaded onto meiotic chromosomes in zep1, Osmer3, Oszip4 and Oshei10
- OsDMC1~DMC1B, PAIR2, OsDMC1 is not required for homologous pairing in rice meiosis., Moreover, OsDMC1 was not detected in pairing-defective mutants, such as pair2, pair3, Oscom1 and Osrad51c, while it was loaded onto meiotic chromosomes in zep1, Osmer3, Oszip4 and Oshei10
- OsDMC1~DMC1B, PAIR3, OsDMC1 is not required for homologous pairing in rice meiosis., In the absence of OsDMC1, early recombination events probably occur normally, leading to normal localization of ÃÂÃÂÃÂóH2AX, PAIR3, OsMRE11, OsCOM1 and OsRAD51C
- OsDMC1~DMC1B, PAIR3, OsDMC1 is not required for homologous pairing in rice meiosis., Moreover, OsDMC1 was not detected in pairing-defective mutants, such as pair2, pair3, Oscom1 and Osrad51c, while it was loaded onto meiotic chromosomes in zep1, Osmer3, Oszip4 and Oshei10
- OsDMC1~DMC1B, ZEP1, OsDMC1 is not required for homologous pairing in rice meiosis., Moreover, OsDMC1 was not detected in pairing-defective mutants, such as pair2, pair3, Oscom1 and Osrad51c, while it was loaded onto meiotic chromosomes in zep1, Osmer3, Oszip4 and Oshei10
- OsDMC1~DMC1B, OsFIGNL1, The Rice AAA-ATPase OsFIGNL1 Is Essential for Male Meiosis., Yeast two-hybrid assays demonstrated OsFIGNL1 could interact with RAD51A1, RAD51A2, DMC1A, DMC1B, and these physical interactions were further confirmed by BiFC assay
Prev Next