- Information
- Symbol: OsDTS2,OsKSL4,OsKS4
- MSU: LOC_Os04g10060
- RAPdb: Os04g0179700
- PSP score
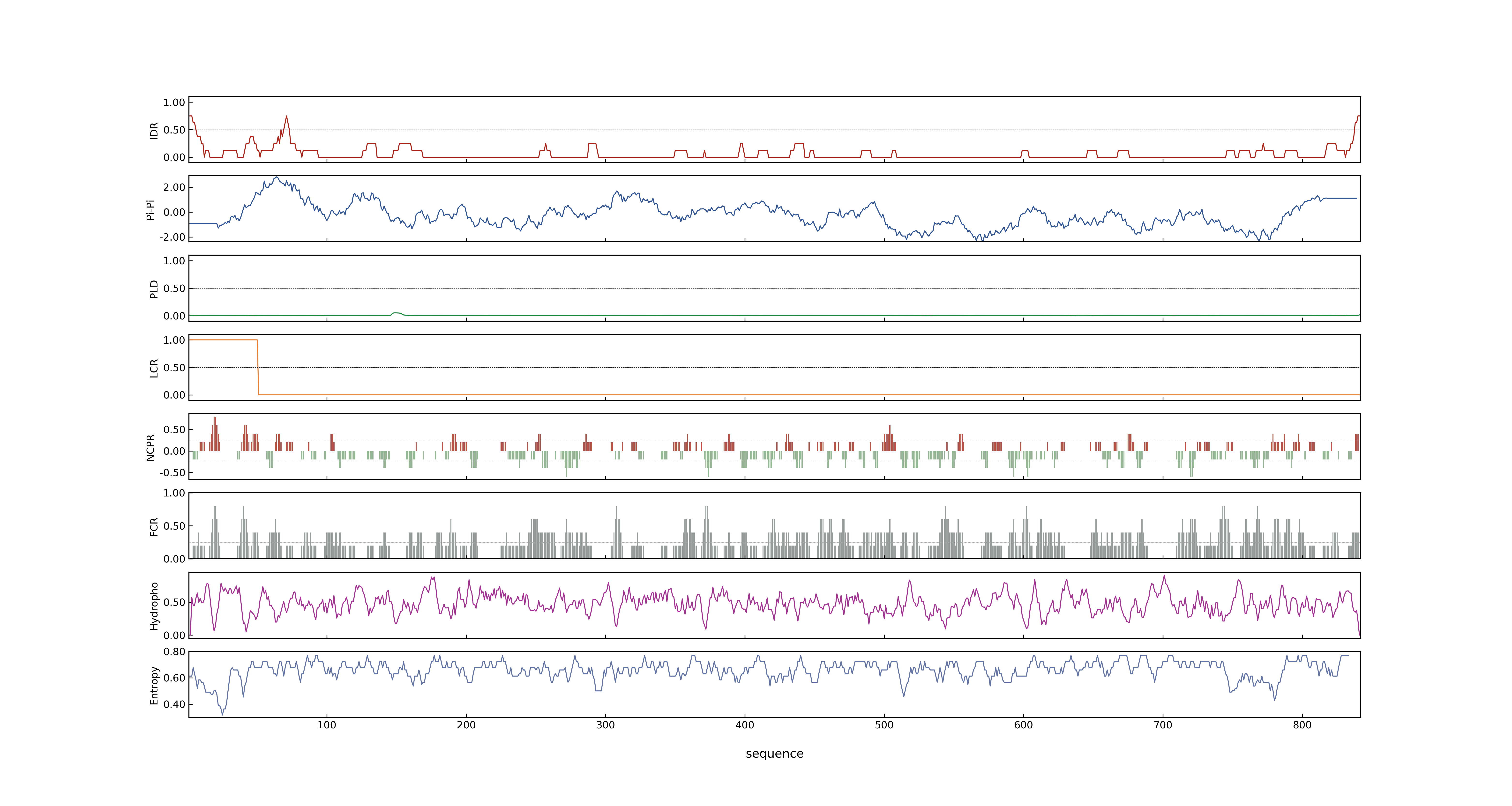
- LOC_Os04g10060.1: 0.5162
- PLAAC score
- LOC_Os04g10060.1: 0
- pLDDT score
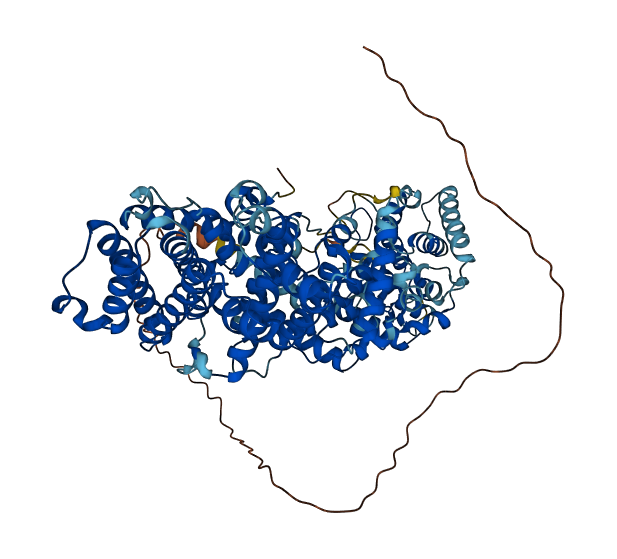
- 83.8
- Protein Structure from AlphaFold and UniProt
- MolPhase score
- LOC_Os04g10060.1: 0.49432864
- MolPhase Result
- Publication
- Diterpene Cyclases Responsible for the Biosynthesis of Phytoalexins, Momilactones A, B, and Oryzalexins AÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂâÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂF in Rice, 2014, Bioscience, Biotechnology and Biochemistry.
- OsTGAP1, a bZIP transcription factor, coordinately regulates the inductive production of diterpenoid phytoalexins in rice, 2009, J Biol Chem.
- Genetic evidence for natural product-mediated plant-plant allelopathy in rice Oryza sativa, 2012, New Phytol.
- Identification of syn-pimara-7,15-diene synthase reveals functional clustering of terpene synthases involved in rice phytoalexin/allelochemical biosynthesis, 2004, Plant Physiol.
-
Genbank accession number
- Key message
- Here, we apply reverse genetics, using knock-outs of the relevant diterpene synthases (copalyl diphosphate synthase 4 (OsCPS4) and kaurene synthase-like 4 (OsKSL4)), to demonstrate that rice momilactones are involved in allelopathy, including suppressing growth of the widespread rice paddy weed, barnyard grass (Echinochloa crus-galli)
- Further, OsDTS2 mRNA in leaves is up-regulated by conditions that stimulate phytoalexin biosynthesis but is constitutively expressed in roots, where momilactones are constantly synthesized as allelochemicals
- Connection
- OsCPS4~OsCyc1, OsDTS2~OsKSL4~OsKS4, OsTGAP1, a bZIP transcription factor, coordinately regulates the inductive production of diterpenoid phytoalexins in rice, The knock-out mutant for OsTGAP1 had almost no expression of the five clustered genes (OsCPS4, OsKSL4, CYP99A2, CYP99A3, and OsMAS) or production of momilactones upon elicitor treatment
- CYP99A3, OsDTS2~OsKSL4~OsKS4, OsTGAP1, a bZIP transcription factor, coordinately regulates the inductive production of diterpenoid phytoalexins in rice, The knock-out mutant for OsTGAP1 had almost no expression of the five clustered genes (OsCPS4, OsKSL4, CYP99A2, CYP99A3, and OsMAS) or production of momilactones upon elicitor treatment
- OsDTS2~OsKSL4~OsKS4, OsTGAP1~OsbZIP37, OsTGAP1, a bZIP transcription factor, coordinately regulates the inductive production of diterpenoid phytoalexins in rice, The knock-out mutant for OsTGAP1 had almost no expression of the five clustered genes (OsCPS4, OsKSL4, CYP99A2, CYP99A3, and OsMAS) or production of momilactones upon elicitor treatment
- CYP99A2, OsDTS2~OsKSL4~OsKS4, OsTGAP1, a bZIP transcription factor, coordinately regulates the inductive production of diterpenoid phytoalexins in rice, The knock-out mutant for OsTGAP1 had almost no expression of the five clustered genes (OsCPS4, OsKSL4, CYP99A2, CYP99A3, and OsMAS) or production of momilactones upon elicitor treatment
- MAS, OsDTS2~OsKSL4~OsKS4, OsTGAP1, a bZIP transcription factor, coordinately regulates the inductive production of diterpenoid phytoalexins in rice, The knock-out mutant for OsTGAP1 had almost no expression of the five clustered genes (OsCPS4, OsKSL4, CYP99A2, CYP99A3, and OsMAS) or production of momilactones upon elicitor treatment
- OsCPS4~OsCyc1, OsDTS2~OsKSL4~OsKS4, Genetic evidence for natural product-mediated plant-plant allelopathy in rice Oryza sativa, Here, we apply reverse genetics, using knock-outs of the relevant diterpene synthases (copalyl diphosphate synthase 4 (OsCPS4) and kaurene synthase-like 4 (OsKSL4)), to demonstrate that rice momilactones are involved in allelopathy, including suppressing growth of the widespread rice paddy weed, barnyard grass (Echinochloa crus-galli)
- OsDTS2~OsKSL4~OsKS4, OsTGAP1~OsbZIP37, OsTGAP1 is responsible for JA-inducible diterpenoid phytoalexin biosynthesis in rice roots with biological impacts on allelopathic interaction., Reporter analysis in planta revealed that OsTGAP1 activated the promoters of OsDXS3 and momilactone biosynthetic gene OsKSL4, presumably through binding to the TGACGT motif
Prev Next