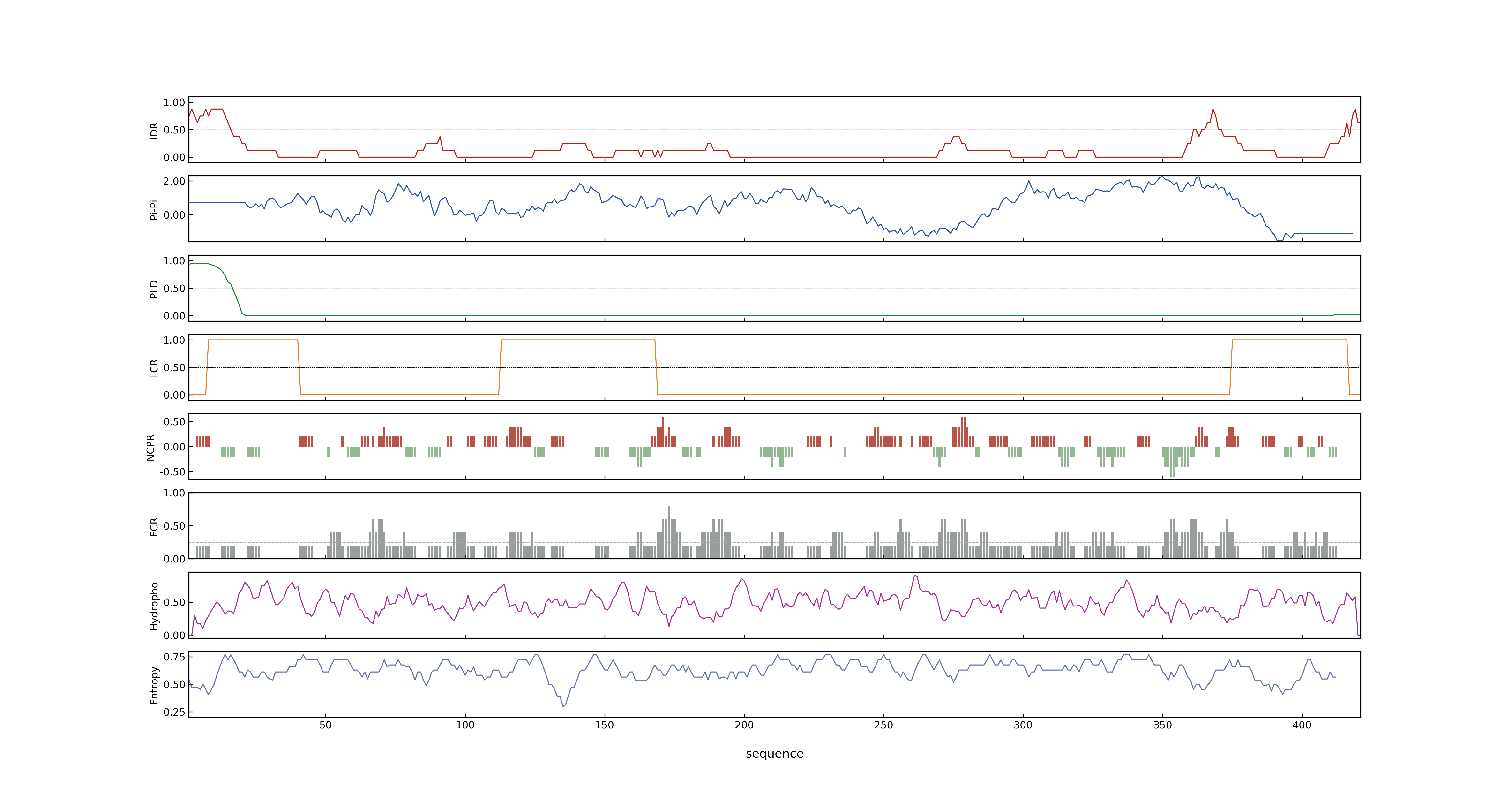
- Information
- Symbol: OsFMO,OsCOW1,NAL7
- MSU: LOC_Os03g06654
- RAPdb: Os03g0162000
- PSP score
- LOC_Os03g06654.1: 0.0275
- LOC_Os03g06654.2: 0.0275
- PLAAC score
- LOC_Os03g06654.1: 0
- LOC_Os03g06654.2: 0
- pLDDT score
- NA
- MolPhase score
- LOC_Os03g06654.1: 0.44830089
- LOC_Os03g06654.2: 0.44830089
- MolPhase Result
- Publication
- NARROW LEAF 7 controls leaf shape mediated by auxin in rice, 2008, Mol Genet Genomics.
- Cloning, characterization and expression of OsFMOt in rice encoding a flavin monooxygenase, 2013, J Genet.
- Constitutively wilted 1, a member of the rice YUCCA gene family, is required for maintaining water homeostasis and an appropriate root to shoot ratio, 2007, Plant Mol Biol.
- Genetic analysis of rice mutants responsible for narrow leaf phenotype and reduced vein number., 2016, Genes Genet Syst.
- Genbank accession number
- Key message
- Furthermore, a lower turgor potential and transpiration rate in their mature leaves indicates that oscow1 plants are water-deficient, due to insufficient water uptake that possibly stems from that diminished root to shoot ratio
- Our results demonstrated that IAA biosynthesis regulated by OsFMO(t) is likely localized and might play an essential role in shaping local IAA concentrations which, in turn, is critical for regulating normal growth and development in rice
- In this study, the full-length genomic DNA and cDNA of OsFMO(t), a FMO gene that was originally identified from a rolled-leaf mutant in rice, was isolated and cloned from wild type of the rolled-leaf mutant
- Spatio-temporal expression analysis using RT-PCR and histochemical analysis for GUS activity revealed that expression of OsFMO(t) was totally absent in the rolled-leaf mutant
- Homozygous plants with either a Tos17 or T-DNA-inserted allele of OsCOW1 exhibit phenotypes of rolled leaves, reduced leaf widths, and lower root to shoot ratios
- When oscow1 seedlings are grown under low-intensity light and high relative humidity, the rolled-leaf phenotype is greatly alleviated
- Overexpression of OsFMO(t) in transformed rice calli produced IAA-excessive phenotypes that showed browning and lethal effects when exogenous auxins such as naphthylacetic acid (NAA) were added to the medium
- These results suggested that the OsFMO(t) protein is involved in IAA biosynthesis in rice and its overexpression could lead to the malformation of calli
- Thus, our observations suggest that OsCOW1-mediated IAA biosynthesis plays an important role in maintaining root to shoot ratios and, in turn, affects water homeostasis in rice
- In this paper, we examined the function of four genes that regulate the width of the leaf blade and the vein number: NARROW LEAF1 (NAL1), NAL2, NAL3 and NAL7
- In contrast, the nal7 mutation showed a milder effect on leaf width and vein number, and both the large and small veins were similarly affected
- The nal7 mutation showed additive effects on both leaf width and vein number, when combined with the nal1 single or the nal2 nal3 double mutation
- In addition, observations of inner tissues revealed that cell differentiation was partially compromised in the nal2 nal3 nal7 mutant, consistent with the severe reduction in leaf width in this triple mutant
- Connection
- OsFMO~OsCOW1~NAL7, OsYUCCA1~OsYUC1, Cloning, characterization and expression of OsFMOt in rice encoding a flavin monooxygenase, OsFMO(t) showed high amino acid sequence identity with FMO proteins from other plants, in particular with YUCCA from Arabidopsis, FLOOZY from Petunia, and OsYUCCA1 from rice
- NAL1~qFLW4, OsFMO~OsCOW1~NAL7, Genetic analysis of rice mutants responsible for narrow leaf phenotype and reduced vein number., In this paper, we examined the function of four genes that regulate the width of the leaf blade and the vein number: NARROW LEAF1 (NAL1), NAL2, NAL3 and NAL7
- NAL1~qFLW4, OsFMO~OsCOW1~NAL7, Genetic analysis of rice mutants responsible for narrow leaf phenotype and reduced vein number., The nal7 mutation showed additive effects on both leaf width and vein number, when combined with the nal1 single or the nal2 nal3 double mutation
- NAL2~OsWOX3A~WOX3, OsFMO~OsCOW1~NAL7, Genetic analysis of rice mutants responsible for narrow leaf phenotype and reduced vein number., In this paper, we examined the function of four genes that regulate the width of the leaf blade and the vein number: NARROW LEAF1 (NAL1), NAL2, NAL3 and NAL7
- NAL2~OsWOX3A~WOX3, OsFMO~OsCOW1~NAL7, Genetic analysis of rice mutants responsible for narrow leaf phenotype and reduced vein number., The nal7 mutation showed additive effects on both leaf width and vein number, when combined with the nal1 single or the nal2 nal3 double mutation
- NAL2~OsWOX3A~WOX3, OsFMO~OsCOW1~NAL7, Genetic analysis of rice mutants responsible for narrow leaf phenotype and reduced vein number., In addition, observations of inner tissues revealed that cell differentiation was partially compromised in the nal2 nal3 nal7 mutant, consistent with the severe reduction in leaf width in this triple mutant
- NAL3, OsFMO~OsCOW1~NAL7, Genetic analysis of rice mutants responsible for narrow leaf phenotype and reduced vein number., In this paper, we examined the function of four genes that regulate the width of the leaf blade and the vein number: NARROW LEAF1 (NAL1), NAL2, NAL3 and NAL7
- NAL3, OsFMO~OsCOW1~NAL7, Genetic analysis of rice mutants responsible for narrow leaf phenotype and reduced vein number., The nal7 mutation showed additive effects on both leaf width and vein number, when combined with the nal1 single or the nal2 nal3 double mutation
- NAL3, OsFMO~OsCOW1~NAL7, Genetic analysis of rice mutants responsible for narrow leaf phenotype and reduced vein number., In addition, observations of inner tissues revealed that cell differentiation was partially compromised in the nal2 nal3 nal7 mutant, consistent with the severe reduction in leaf width in this triple mutant
Prev Next