- Information
- Symbol: OsGH3.8,OsGH3-8,OsMGH3
- MSU: LOC_Os07g40290
- RAPdb: Os07g0592600
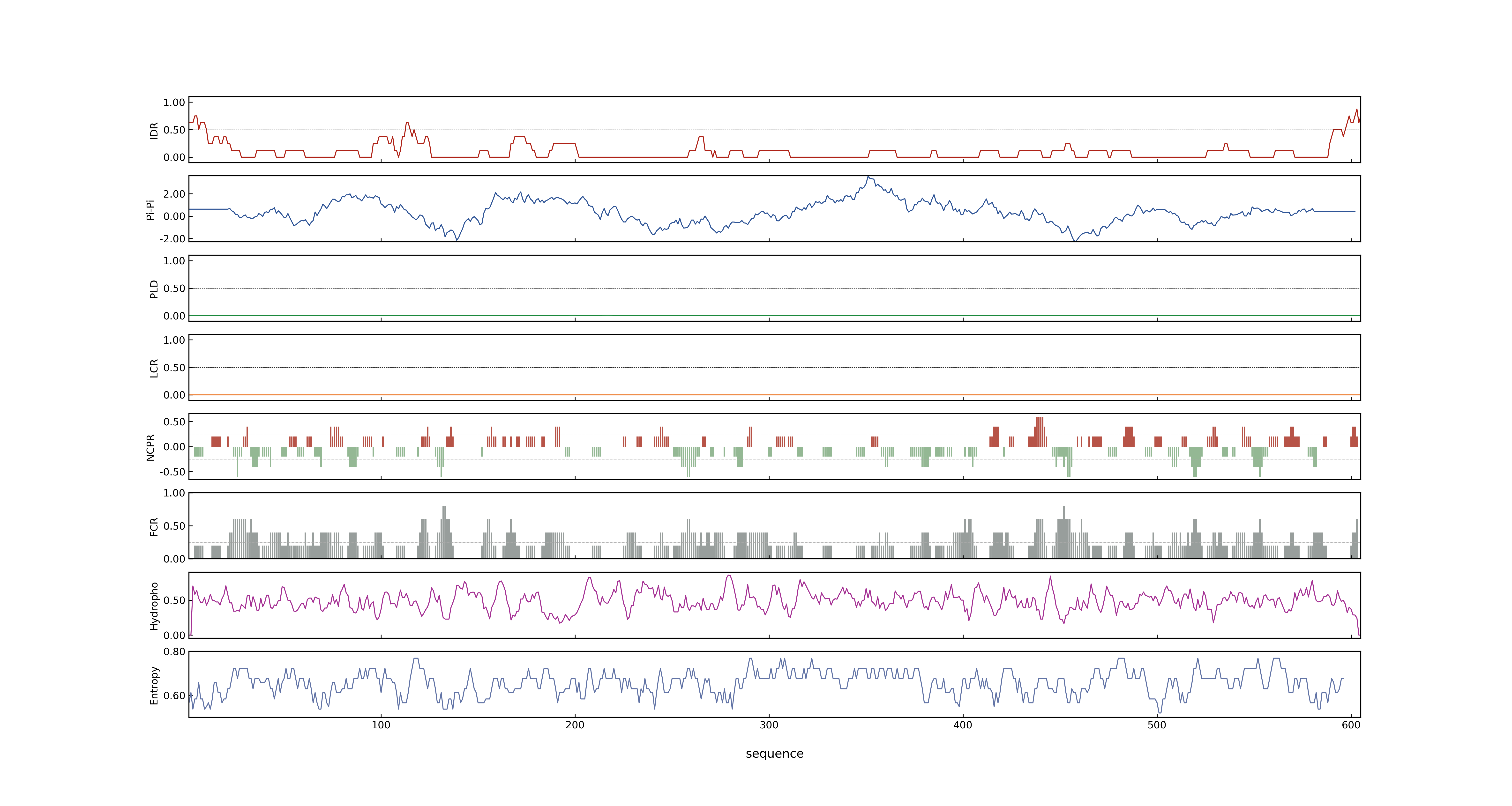
- PSP score
- LOC_Os07g40290.1: 0.0095
- PLAAC score
- LOC_Os07g40290.1: 0
- pLDDT score
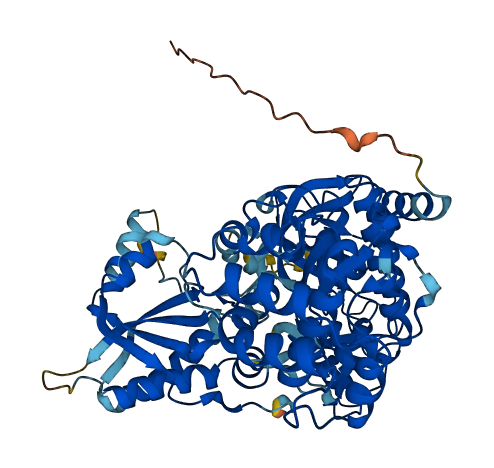
- 89.8
- Protein Structure from AlphaFold and UniProt
- MolPhase score
- LOC_Os07g40290.1: 0.26811057
- MolPhase Result
- Publication
- The auxin-responsive GH3 gene family in rice Oryza sativa, 2006, Funct Integr Genomics.
- Kinetic basis for the conjugation of auxin by a GH3 family indole-acetic acid-amido synthetase, 2010, J Biol Chem.
- OsMADS1, a rice MADS-box factor, controls differentiation of specific cell types in the lemma and palea and is an early-acting regulator of inner floral organs, 2005, Plant J.
- Activation of the indole-3-acetic acid-amido synthetase GH3-8 suppresses expansin expression and promotes salicylate- and jasmonate-independent basal immunity in rice, 2008, Plant Cell.
- Auxin-responsive OsMGH3, a common downstream target of OsMADS1 and OsMADS6, controls rice floret fertility, 2011, Plant Cell Physiol.
- Genbank accession number
- Key message
- OsMGH3/OsGH3-8 is expressed abundantly in rice florets and is regulated by two related and redundant transcription factors, OsMADS1 and OsMADS6, but its contribution to flower development is not known
- Here we use GH3-8 from Oryza sativa (rice; OsGH3-8), which functions as an indole-acetic acid (IAA)-amido synthetase, for detailed mechanistic studies
- The overexpression of OsMGH3 during the vegetative phase affects the overall plant architecture, whereas its inflorescence-specific overexpression creates short panicles with reduced branching, resembling in part the effects of OsMADS1 overexpression
- Florets in OsMGH3 knock-down plants were affected in carpel development and pollen viability, both of which reduced fertility
- Auxin-responsive OsMGH3, a common downstream target of OsMADS1 and OsMADS6, controls rice floret fertility
- Steady-state kinetic analysis shows that the OsGH3-8 requires either Mg(2+) or Mn(2+) for maximal activity and is specific for aspartate but accepts asparagine as a substrate with a 45-fold decrease in catalytic efficiency and accepts other auxin analogs, including phenyl-acetic acid, indole butyric acid, and naphthalene-acetic acid, as acyl-acid substrates with 1
- In contrast, the down-regulation of endogenous OsMGH3 caused phenotypes consistent with auxin overproduction or activated signaling, such as ectopic rooting from aerial nodes
- Through a screen for OsMADS1 targets we identify a flower-specific Nt-gh3 type gene, OsMGH3, as a downstream gene
- Connection
- OsGH3.8~OsGH3-8~OsMGH3, OsMADS1~LHS1~AFO, OsMADS1, a rice MADS-box factor, controls differentiation of specific cell types in the lemma and palea and is an early-acting regulator of inner floral organs, Through a screen for OsMADS1 targets we identify a flower-specific Nt-gh3 type gene, OsMGH3, as a downstream gene
- OsGH3.8~OsGH3-8~OsMGH3, OsMADS1~LHS1~AFO, OsMADS1, a rice MADS-box factor, controls differentiation of specific cell types in the lemma and palea and is an early-acting regulator of inner floral organs, The delayed transcription activation of OsMGH3 by dexamethasone-inducible OsMADS1 suggests indirect activation
- OsGH3.8~OsGH3-8~OsMGH3, OsMADS1~LHS1~AFO, OsMADS1, a rice MADS-box factor, controls differentiation of specific cell types in the lemma and palea and is an early-acting regulator of inner floral organs, The OsMGH3 floret expression profile suggests a novel role for OsMADS1 as an early-acting regulator of second and third whorl organ fate
- OsGH3.8~OsGH3-8~OsMGH3, OsMADS1~LHS1~AFO, Auxin-responsive OsMGH3, a common downstream target of OsMADS1 and OsMADS6, controls rice floret fertility, OsMGH3/OsGH3-8 is expressed abundantly in rice florets and is regulated by two related and redundant transcription factors, OsMADS1 and OsMADS6, but its contribution to flower development is not known
- OsGH3.8~OsGH3-8~OsMGH3, OsMADS1~LHS1~AFO, Auxin-responsive OsMGH3, a common downstream target of OsMADS1 and OsMADS6, controls rice floret fertility, We functionally characterize OsMGH3 by overexpression and knock-down analysis and show a partial overlap in these phenotypes with that of mutants in OsMADS1 and OsMADS6
- OsGH3.8~OsGH3-8~OsMGH3, OsMADS1~LHS1~AFO, Auxin-responsive OsMGH3, a common downstream target of OsMADS1 and OsMADS6, controls rice floret fertility, The overexpression of OsMGH3 during the vegetative phase affects the overall plant architecture, whereas its inflorescence-specific overexpression creates short panicles with reduced branching, resembling in part the effects of OsMADS1 overexpression
- OsGH3.8~OsGH3-8~OsMGH3, OsMADS1~LHS1~AFO, Auxin-responsive OsMGH3, a common downstream target of OsMADS1 and OsMADS6, controls rice floret fertility, Auxin-responsive OsMGH3, a common downstream target of OsMADS1 and OsMADS6, controls rice floret fertility
- OsGH3.8~OsGH3-8~OsMGH3, OsMADS6~MFO1, Auxin-responsive OsMGH3, a common downstream target of OsMADS1 and OsMADS6, controls rice floret fertility, OsMGH3/OsGH3-8 is expressed abundantly in rice florets and is regulated by two related and redundant transcription factors, OsMADS1 and OsMADS6, but its contribution to flower development is not known
- OsGH3.8~OsGH3-8~OsMGH3, OsMADS6~MFO1, Auxin-responsive OsMGH3, a common downstream target of OsMADS1 and OsMADS6, controls rice floret fertility, We functionally characterize OsMGH3 by overexpression and knock-down analysis and show a partial overlap in these phenotypes with that of mutants in OsMADS1 and OsMADS6
- OsGH3.8~OsGH3-8~OsMGH3, OsMADS6~MFO1, Auxin-responsive OsMGH3, a common downstream target of OsMADS1 and OsMADS6, controls rice floret fertility, Auxin-responsive OsMGH3, a common downstream target of OsMADS1 and OsMADS6, controls rice floret fertility
Prev Next