- Information
- Symbol: OsHMA2,OsHMA2v
- MSU: LOC_Os06g48720
- RAPdb: Os06g0700700
- PSP score
- LOC_Os06g48720.1: 0.0021
- PLAAC score
- LOC_Os06g48720.1: 0
- pLDDT score
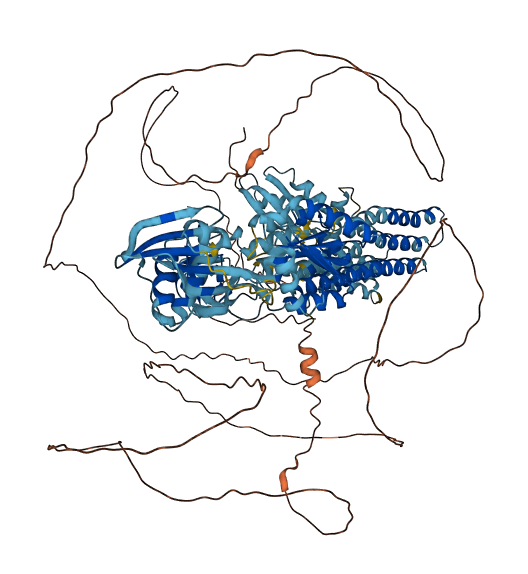
- 66.32
- Protein Structure from AlphaFold and UniProt
- MolPhase score
- LOC_Os06g48720.1: 0.00572362
- MolPhase Result
- Publication
- Cadmium retention in rice roots is influenced by cadmium availability, chelation and translocation, 2011, Plant Cell Environ.
- The OsHMA2 transporter is involved in root-to-shoot translocation of Zn and Cd in rice, 2012, Plant Cell Environ.
- Mutations in rice Oryza sativa heavy metal ATPase 2 OsHMA2 restrict the translocation of zinc and cadmium, 2012, Plant Cell Physiol.
- Preferential delivery of zinc to developing tissues in rice is mediated by P-type heavy metal ATPase OsHMA2, 2013, Plant Physiol.
- Silicon reduces cadmium accumulation by suppressing expression of transporter genes involved in cadmium uptake and translocation in rice., 2017, J Exp Bot.
- Genbank accession number
- Key message
- OsHMA2 was mainly expressed in the mature zone of the roots at the vegetative stage, but higher expression was also found in the nodes at the reproductive stage
- OsHMA2 was localized at the pericycle of the roots and at the phloem of enlarged and diffuse vascular bundles in the nodes
- The translocation ratios of zinc (Zn) and Cd were clearly lower in all mutants than in the wild type, suggesting that OsHMA2 is a major transporter of Zn and Cd from roots to shoots
- In silico search and preliminary analyses in yeast suggest OsHMA2 as a good candidate for the control of Cd xylem loading in rice
- Heterologous expression of OsHMA2 in yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) showed influx transport activity for zinc as well as cadmium
- Taken together, OsHMA2 in the nodes plays an important role in preferential distribution of zinc as well as cadmium through the phloem to the developing tissues
- The yeast expressing OsHMA2 was able to reverse the growth defect in the presence of excess Zn
- These results suggest that OsHMA2 plays a role in Zn and Cd loading to the xylem and participates in root-to-shoot translocation of these metals in rice
- Here we investigated the role of the Zn/Cd transporter OsHMA2
- The OsHMA2 transporter is involved in root-to-shoot translocation of Zn and Cd in rice
- Mutations in rice (Oryza sativa) heavy metal ATPase 2 (OsHMA2) restrict the translocation of zinc and cadmium
- The expression of OsHMA2 in rice was observed mainly in the roots where OsHMA2 transcripts were abundant in vascular bundles
- Furthermore, Zn and Cd concentrations of OsHMA2-suppressed rice decreased in the leaves, while the Zn concentration increased in the roots compared with the wild type (WT)
- Here, we report that rice (Oryza sativa) heavy metal ATPase2 (OsHMA2), a member of P-type ATPases, is involved in preferential delivery of zinc to the developing tissues in rice
- Preferential delivery of zinc to developing tissues in rice is mediated by P-type heavy metal ATPase OsHMA2
- Furthermore, the Cd concentration in the grains of OsHMA2-overexpressing rice as well as in OsSUT1-promoter OsHMA2 rice decreased to about half that of the WT, although the other metal concentrations were the same as in the WT
- By comparing each allele in the OsHMA2 protein structure and measuring the Cd translocation ratio, we identified the C-terminal region as essential for Cd translocation into shoots
- Connection
- OsHMA2~OsHMA2v, OsNRAMP5, Silicon reduces cadmium accumulation by suppressing expression of transporter genes involved in cadmium uptake and translocation in rice., The expression level of OsNramp5 and OsHMA2 was down-regulated by Si in the WTs, but not in the mutants
Prev Next