- Information
- Symbol: OsHsfC1b
- MSU: LOC_Os01g53220
- RAPdb: Os01g0733200
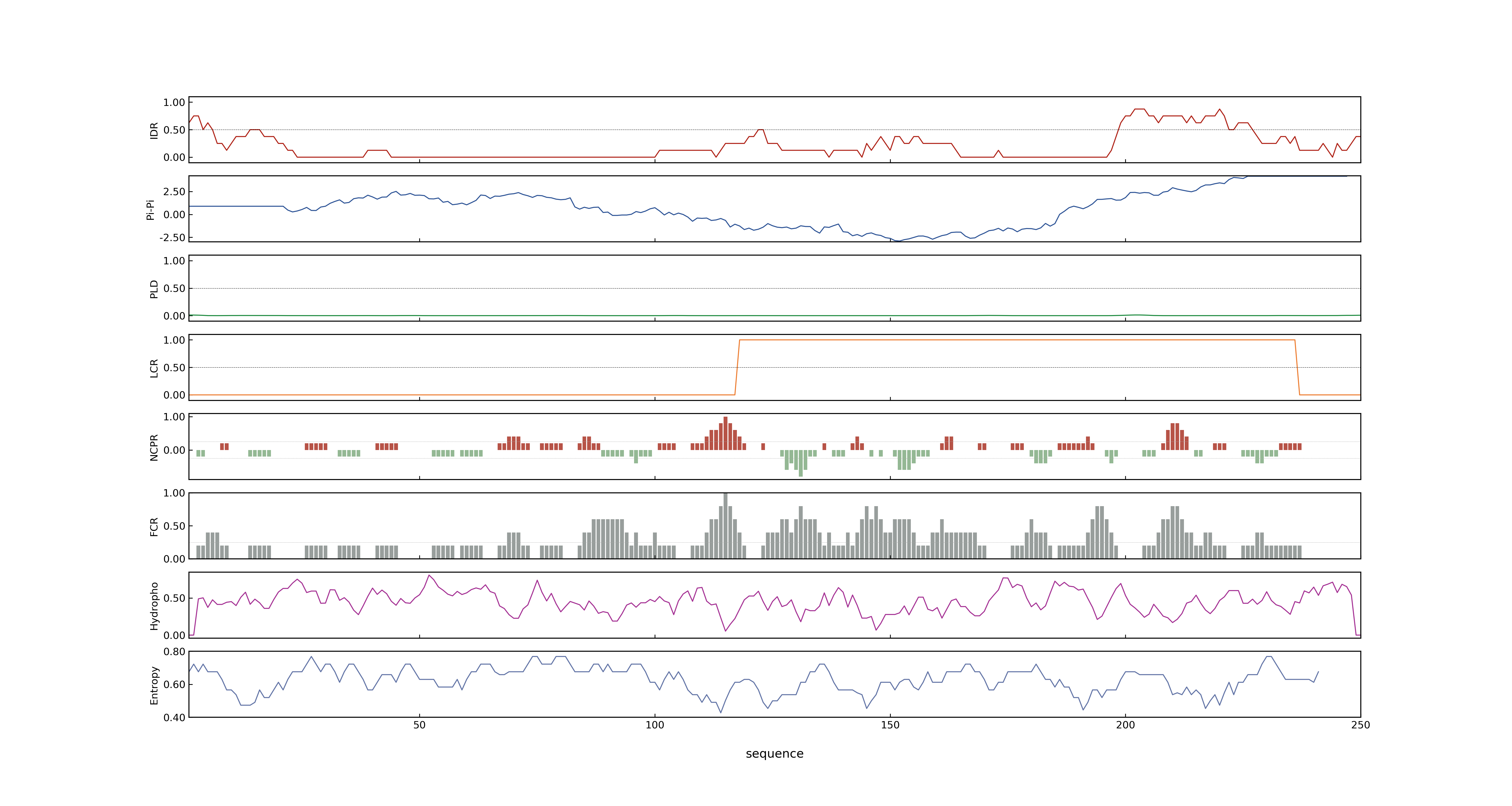
- PSP score
- LOC_Os01g53220.1: 0.0184
- PLAAC score
- LOC_Os01g53220.1: 0
- pLDDT score
- 74.1
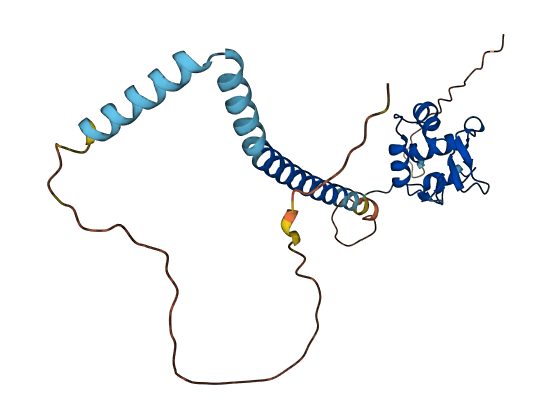
- Protein Structure from AlphaFold and UniProt
- MolPhase score
- LOC_Os01g53220.1: 0.98194557
- MolPhase Result
- Publication
- Identification and expression analysis of OsHsfs in rice, 2009, J Zhejiang Univ Sci B.
- Transcription factor OsHsfC1b regulates salt tolerance and development in Oryza sativa ssp. japonica, 2012, AoB Plants.
- Genbank accession number
- Key message
- Impaired function of OsHsfC1b in the hsfc1b mutant and the amiRNA lines led to decreased salt and osmotic stress tolerance, increased sensitivity to ABA, and temporal misregulation of salt-responsive genes involved in signalling and ion homeostasis
- METHODOLOGY: We analysed the expression of OsHsfC1b in the rice japonica cultivars Dongjin and Nipponbare exposed to salt stress as well as after mannitol, abscisic acid (ABA) and H(2)O(2) treatment
- CONCLUSIONS: OsHsfC1b plays a role in ABA-mediated salt stress tolerance in rice
- Here we characterized the function of the OsHsfC1b (Os01g53220) transcription factor from rice
- Transient expression of OsHsfC1b fused to GFP in protoplasts revealed nuclear localization of the transcription factor
- Transcription factor OsHsfC1b regulates salt tolerance and development in Oryza sativa ssp. japonica
- For functional characterization of OsHsfC1b, we analysed the physiological response of a T-DNA insertion line (hsfc1b) and two artificial micro-RNA (amiRNA) knock-down lines to salt, mannitol and ABA treatment
- Furthermore, OsHsfC1b is involved in the response to osmotic stress and is required for plant growth under non-stress conditions
- PRINCIPAL RESULTS: Expression of OsHsfC1b was induced by salt, mannitol and ABA, but not by H(2)O(2)
- Connection
Prev Next