- Information
- Symbol: OsMADS4
- MSU: LOC_Os05g34940
- RAPdb: Os05g0423400
- PSP score
- LOC_Os05g34940.2: 0.0108
- LOC_Os05g34940.3: 0.0096
- LOC_Os05g34940.1: 0.0044
- PLAAC score
- LOC_Os05g34940.2: 0
- LOC_Os05g34940.3: 0
- LOC_Os05g34940.1: 0
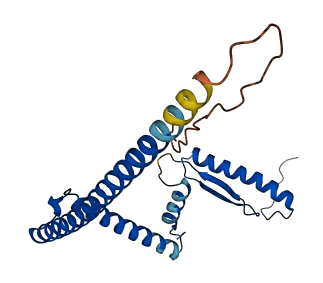
- pLDDT score
- 84.59
- Protein Structure from AlphaFold and UniProt
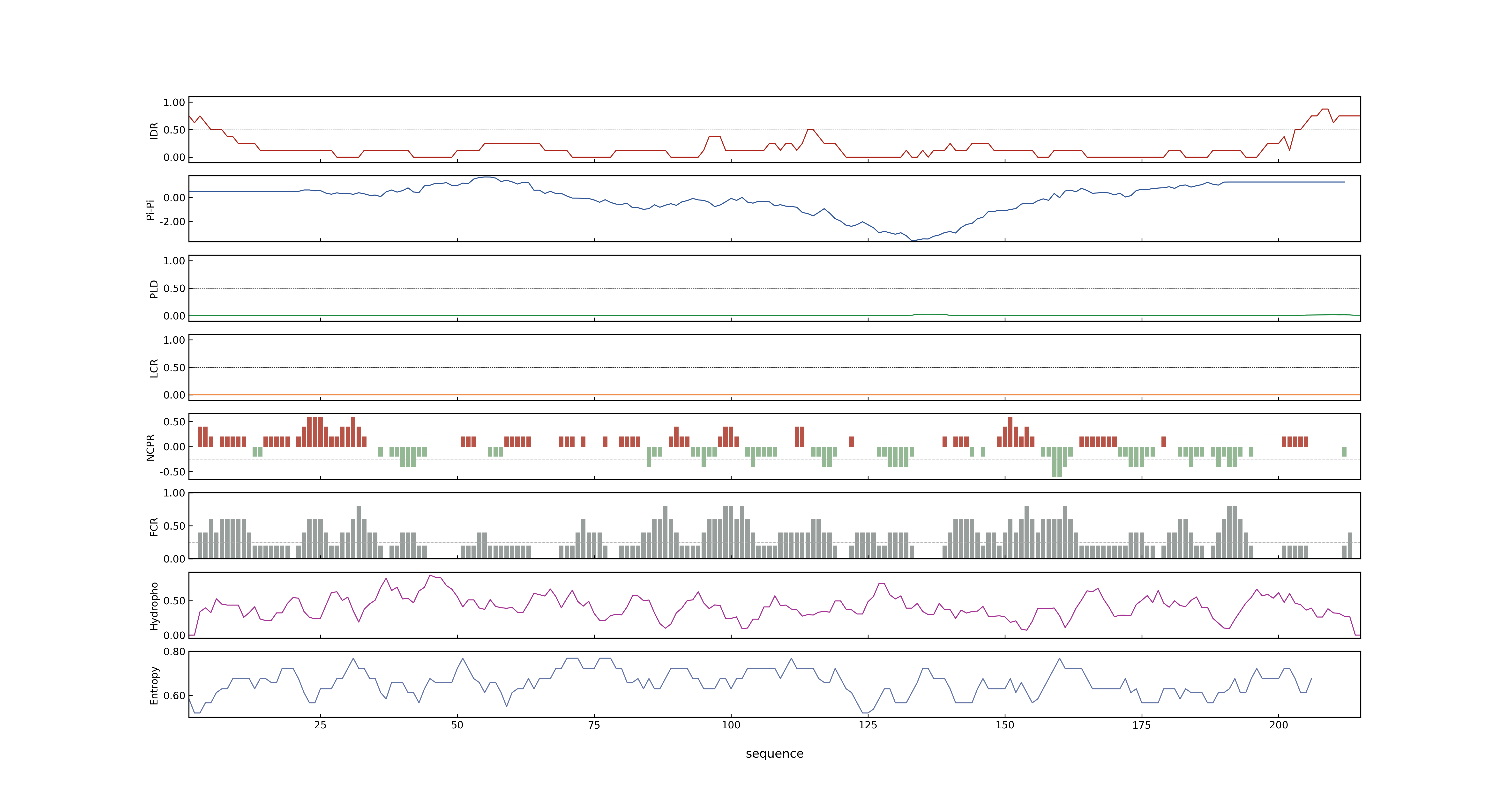
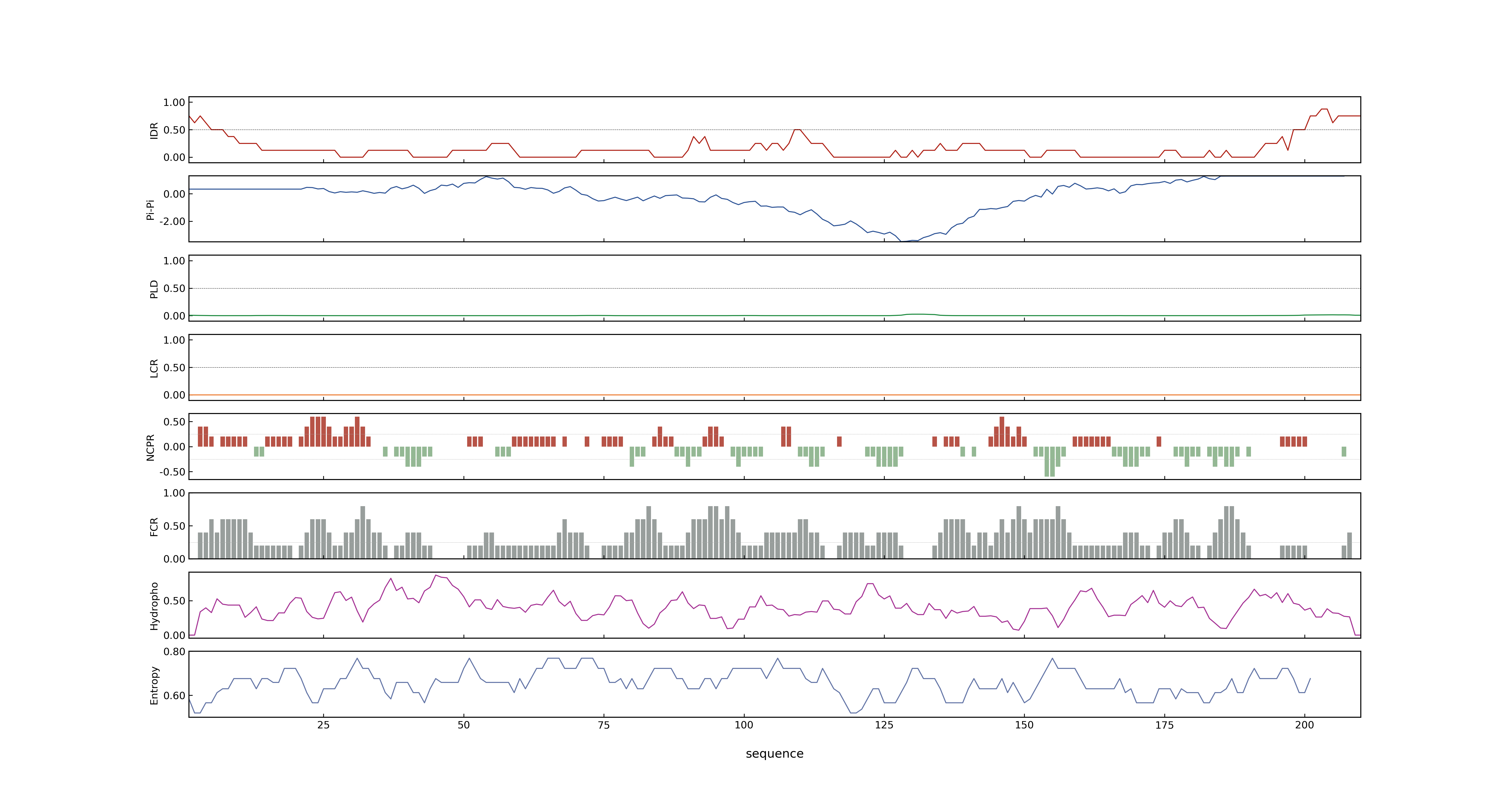
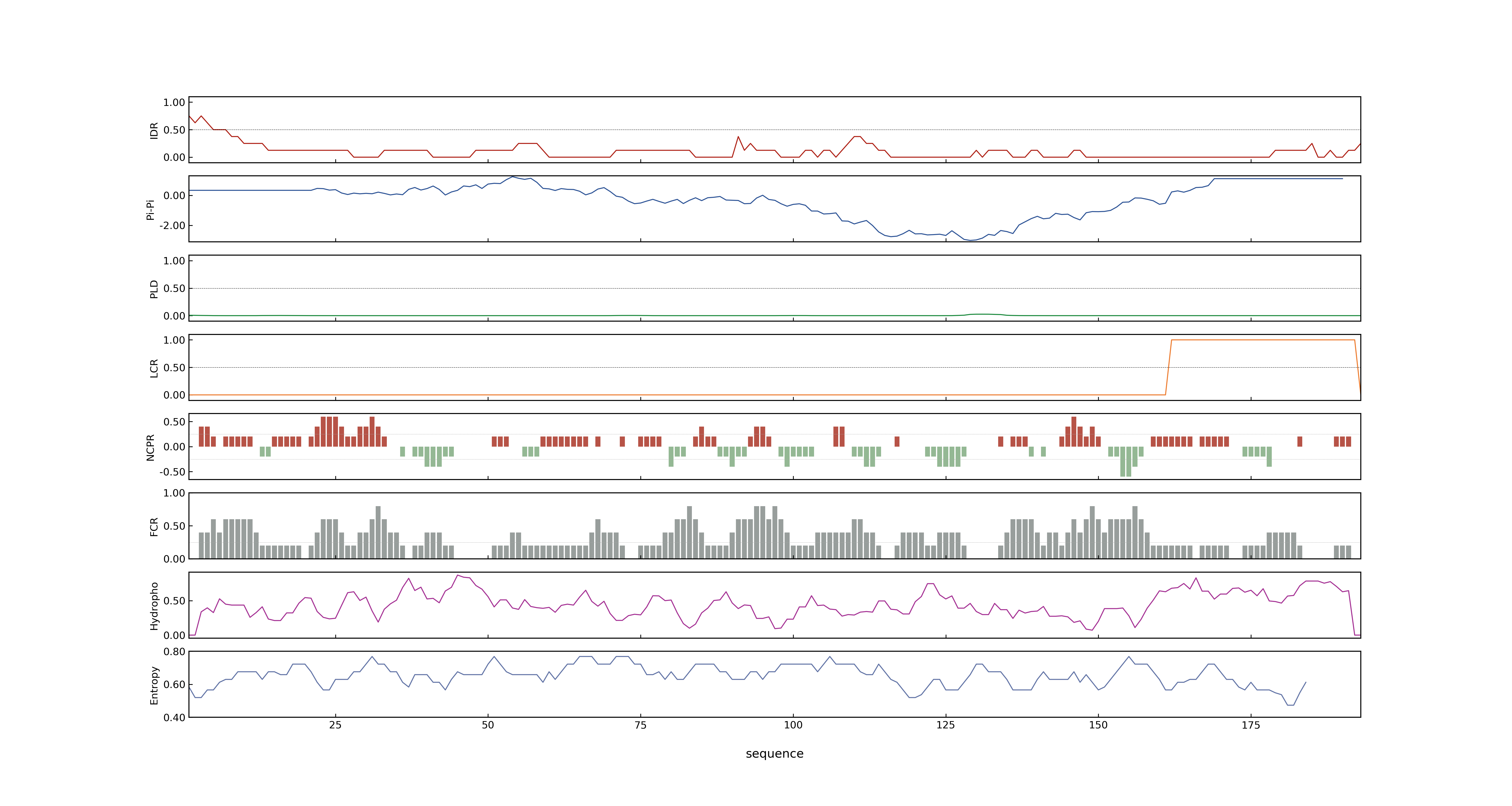
- MolPhase score
- LOC_Os05g34940.1: 0.14754779
- LOC_Os05g34940.2: 0.25042787
- LOC_Os05g34940.3: 0.00764847
- MolPhase Result
- Publication
- Functional analysis of the rice AP3 homologue OsMADS16 by RNA interference, 2003, Plant Mol Biol.
- Double-stranded RNA interference of a rice PI/GLO paralog, OsMADS2, uncovers its second-whorl-specific function in floral organ patterning, 2003, Genetics.
- MADS-box gene family in rice: genome-wide identification, organization and expression profiling during reproductive development and stress, 2007, BMC Genomics.
- Divergent regulatory OsMADS2 functions control size, shape and differentiation of the highly derived rice floret second-whorl organ, 2007, Genetics.
- Unequal genetic redundancy of rice PISTILLATA orthologs, OsMADS2 and OsMADS4, in lodicule and stamen development, 2008, Plant Cell Physiol.
- Dwarf and deformed flower 1, encoding an F-box protein, is critical for vegetative and floral development in rice Oryza sativa L., 2012, Plant J.
- Alteration of floral organ identity in rice through ectopic expression of OsMADS16, 2003, Planta.
- Genbank accession number
- Key message
- The global architecture of transcripts regulated by OsMADS2 gives insights into the regulation of cell division and vascular differentiation that together can form this highly modified grass organ with important functions in floret opening and stamen emergence independent of the paralogous gene OsMADS4
- Our results demonstrate that OsMADS16 is an AP3/DEF orthologue to specify the identities of lodicules and stamens in rice flower and also support that OsMADS4 is a PI orthologue
- Transcription of a rice PI homologous gene, OsMADS4, was also reduced remarkably in the transgenic plants
- Consistent with the mutant floral phenotype, DDF1 positively regulates B-class genes OsMADS4 and OsMADS16, and negatively regulates pistil specification gene DL
- Unequal genetic redundancy of rice PISTILLATA orthologs, OsMADS2 and OsMADS4, in lodicule and stamen development
- Our data demonstrate its essential role in lodicule development and implicate the second PI/GLO paralog, OsMADS4, to suffice for stamen specification
- Connection
- OsMADS16~SPW1, OsMADS4, Functional analysis of the rice AP3 homologue OsMADS16 by RNA interference, Our results demonstrate that OsMADS16 is an AP3/DEF orthologue to specify the identities of lodicules and stamens in rice flower and also support that OsMADS4 is a PI orthologue
- OsMADS16~SPW1, OsMADS4, Alteration of floral organ identity in rice through ectopic expression of OsMADS16, In addition, ectopic expression of OsMADS16 enhanced expression of OsMADS4, another B-function gene, causing superman phenotypes
- OsMADS16~SPW1, OsMADS4, Alteration of floral organ identity in rice through ectopic expression of OsMADS16, In the yeast two-hybrid system, OsMADS16 did not form a homodimer but, rather, the protein interacted with OsMADS4
- OsMADS2, OsMADS4, Divergent regulatory OsMADS2 functions control size, shape and differentiation of the highly derived rice floret second-whorl organ, The global architecture of transcripts regulated by OsMADS2 gives insights into the regulation of cell division and vascular differentiation that together can form this highly modified grass organ with important functions in floret opening and stamen emergence independent of the paralogous gene OsMADS4
- OsMADS2, OsMADS4, Unequal genetic redundancy of rice PISTILLATA orthologs, OsMADS2 and OsMADS4, in lodicule and stamen development, Two homologs of PISTILLATA have been identified in rice: OsMADS2 and OsMADS4
- OsMADS2, OsMADS4, Unequal genetic redundancy of rice PISTILLATA orthologs, OsMADS2 and OsMADS4, in lodicule and stamen development, Although OsMADS2 plays an important role in lodicule development, OsMADS4 also supports the specification of lodicule identity
- OsMADS2, OsMADS4, Unequal genetic redundancy of rice PISTILLATA orthologs, OsMADS2 and OsMADS4, in lodicule and stamen development, Consistent with their redundant functions, both OsMADS2 and OsMADS4 interact with the unique rice AP3 ortholog SPW1
- OsMADS2, OsMADS4, Unequal genetic redundancy of rice PISTILLATA orthologs, OsMADS2 and OsMADS4, in lodicule and stamen development, Unequal genetic redundancy of rice PISTILLATA orthologs, OsMADS2 and OsMADS4, in lodicule and stamen development
- DDF1, OsMADS4, Dwarf and deformed flower 1, encoding an F-box protein, is critical for vegetative and floral development in rice Oryza sativa L., Consistent with the mutant floral phenotype, DDF1 positively regulates B-class genes OsMADS4 and OsMADS16, and negatively regulates pistil specification gene DL
- OsMADS16~SPW1, OsMADS4, Dwarf and deformed flower 1, encoding an F-box protein, is critical for vegetative and floral development in rice Oryza sativa L., Consistent with the mutant floral phenotype, DDF1 positively regulates B-class genes OsMADS4 and OsMADS16, and negatively regulates pistil specification gene DL
- CFO1~OsMADS32, OsMADS4, OsMADS32 interacts with PI-like proteins and regulates rice flower development., By yeast two hybrid and bimolecular fluorescence complementation assays, we revealed that the insertion of eight amino acids or deletion of the internal region in the K1 subdomain of OsMADS32 affects the interaction between OsMADS32 with PISTILLATA (PI)-like proteins OsMADS2 and OsMADS4
- NSG, OsMADS4, nonstop glumes nsg, a novel mutant affects spikelet development in rice, The expression of OsMADS4, OsMADS16, DL and OsMADS3 decreased distinctly, and OsMADS1 increased in nsg panicle, suggests that NSG affected spikelet development through influencing the expression of floral hometic genes
Prev Next