- Information
- Symbol: OsMADS8,OsMADS24
- MSU: LOC_Os09g32948
- RAPdb: Os09g0507200
- PSP score
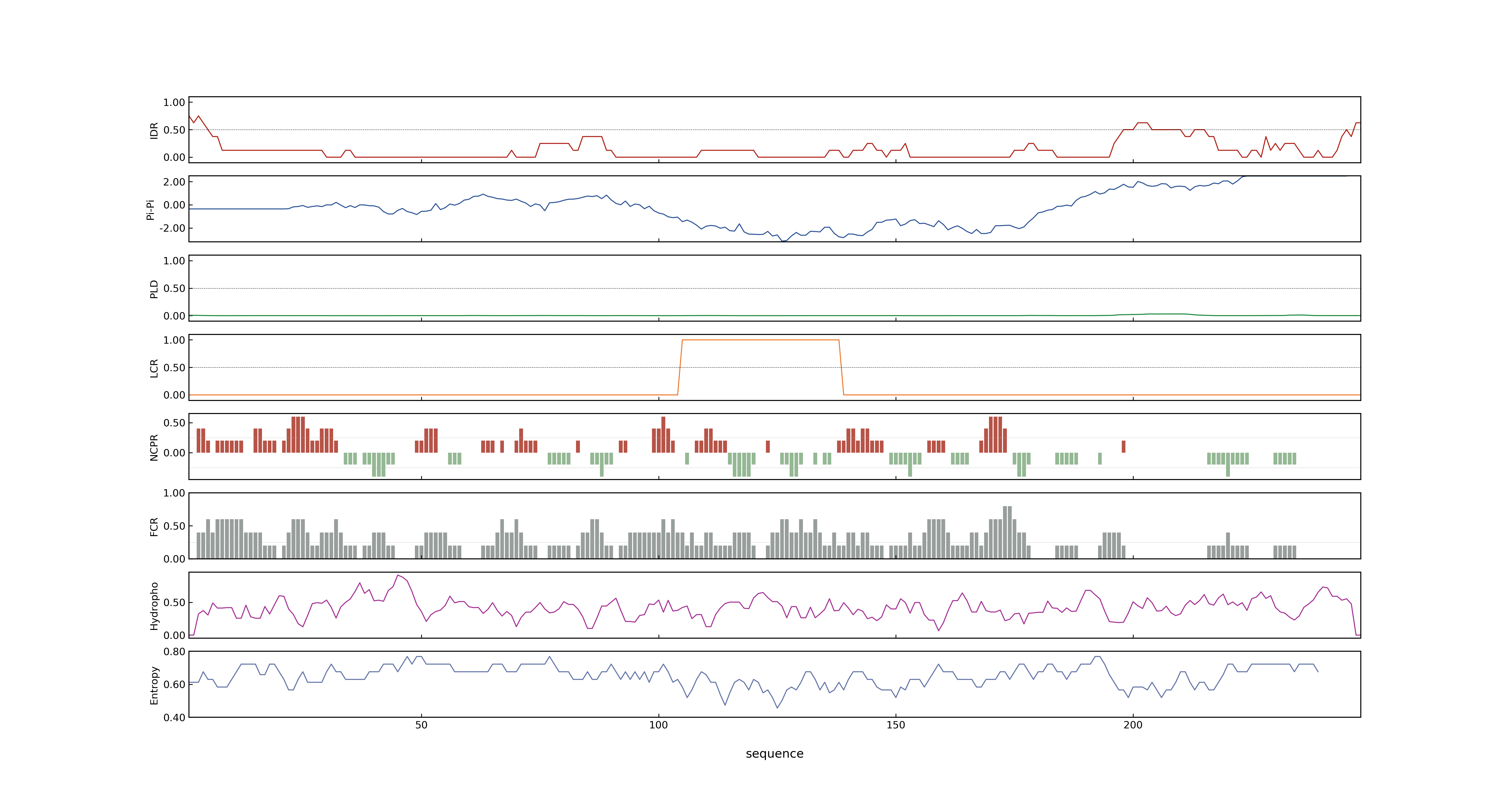
- LOC_Os09g32948.1: 0.3956
- PLAAC score
- LOC_Os09g32948.1: 0
- pLDDT score
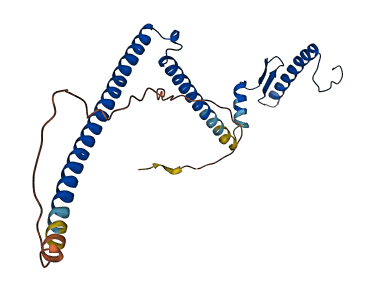
- 78.95
- Protein Structure from AlphaFold and UniProt
- MolPhase score
- LOC_Os09g32948.1: 0.56825000
- MolPhase Result
- Publication
- MADS-box gene family in rice: genome-wide identification, organization and expression profiling during reproductive development and stress, 2007, BMC Genomics.
- Functional conservation and diversification of class E floral homeotic genes in rice Oryza sativa, 2010, Plant J.
- Survey of rice proteins interacting with OsFCA and OsFY proteins which are homologous to the Arabidopsis flowering time proteins, FCA and FY, 2009, Plant Cell Physiol.
- Alteration of floral organ identity in rice through ectopic expression of OsMADS16, 2003, Planta.
- Genbank accession number
- Key message
- Plants affected in both OsMADS7 and OsMADS8 show severe phenotypes including late flowering, homeotic changes of lodicules, stamens and carpels into palea/lemma-like organs, and a loss of floral determinacy
- Simultaneous knockdown of the four rice SEP-like genes OsMADS1, OsMADS5, OsMADS7 and OsMADS8, leads to homeotic transformation of all floral organs except the lemma into leaf-like organs
- Connection
- OsMADS6~MFO1, OsMADS8~OsMADS24, Alteration of floral organ identity in rice through ectopic expression of OsMADS16, OsMADS16 also interacted with OsMADS6 and OSMADS8, both of which are homologous to SEPALLATA proteins required for the proper function of class-B and class-C genes in Arabidopsis
- OsMADS16~SPW1, OsMADS8~OsMADS24, Alteration of floral organ identity in rice through ectopic expression of OsMADS16, OsMADS16 also interacted with OsMADS6 and OSMADS8, both of which are homologous to SEPALLATA proteins required for the proper function of class-B and class-C genes in Arabidopsis
- OsMADS7~OsMADS45, OsMADS8~OsMADS24, Functional conservation and diversification of class E floral homeotic genes in rice Oryza sativa, Plants affected in both OsMADS7 and OsMADS8 show severe phenotypes including late flowering, homeotic changes of lodicules, stamens and carpels into palea/lemma-like organs, and a loss of floral determinacy
- OsMADS7~OsMADS45, OsMADS8~OsMADS24, Functional conservation and diversification of class E floral homeotic genes in rice Oryza sativa, Simultaneous knockdown of the four rice SEP-like genes OsMADS1, OsMADS5, OsMADS7 and OsMADS8, leads to homeotic transformation of all floral organs except the lemma into leaf-like organs
- OsMADS5, OsMADS8~OsMADS24, Functional conservation and diversification of class E floral homeotic genes in rice Oryza sativa, Simultaneous knockdown of the four rice SEP-like genes OsMADS1, OsMADS5, OsMADS7 and OsMADS8, leads to homeotic transformation of all floral organs except the lemma into leaf-like organs
- OsMADS1~LHS1~AFO, OsMADS8~OsMADS24, Functional conservation and diversification of class E floral homeotic genes in rice Oryza sativa, Simultaneous knockdown of the four rice SEP-like genes OsMADS1, OsMADS5, OsMADS7 and OsMADS8, leads to homeotic transformation of all floral organs except the lemma into leaf-like organs
- FCA~OsFCA, OsMADS8~OsMADS24, Survey of rice proteins interacting with OsFCA and OsFY proteins which are homologous to the Arabidopsis flowering time proteins, FCA and FY, Here, we found that the OsFCA protein could interact through its WW domain with the following proteins: OsFY, a protein containing a CID domain present in RNA-processing factors such as Pcf11 and Nrd1; a protein similar to splicing factor SF1; a protein similar to FUSE splicing factor; and OsMADS8
- OsFY, OsMADS8~OsMADS24, Survey of rice proteins interacting with OsFCA and OsFY proteins which are homologous to the Arabidopsis flowering time proteins, FCA and FY, Here, we found that the OsFCA protein could interact through its WW domain with the following proteins: OsFY, a protein containing a CID domain present in RNA-processing factors such as Pcf11 and Nrd1; a protein similar to splicing factor SF1; a protein similar to FUSE splicing factor; and OsMADS8
- FZP~BFL1, OsMADS8~OsMADS24, Regulatory role of FZP in the determination of panicle branching and spikelet formation in rice., FZP overexpression positively regulates the expression of a subset of the class B genes, AGL6 genes (OsMADS6 and OsMADS17) as well as class E genes (OsMADS1, OsMADS7 and OsMADS8) in floral meristem (FM)
Prev Next