- Information
- Symbol: OsNHX1
- MSU: LOC_Os07g47100
- RAPdb: Os07g0666900
- PSP score
- LOC_Os07g47100.2: 0.0775
- LOC_Os07g47100.1: 0.0775
- LOC_Os07g47100.3: 0.0461
- PLAAC score
- LOC_Os07g47100.2: 0
- LOC_Os07g47100.1: 0
- LOC_Os07g47100.3: 0
- pLDDT score
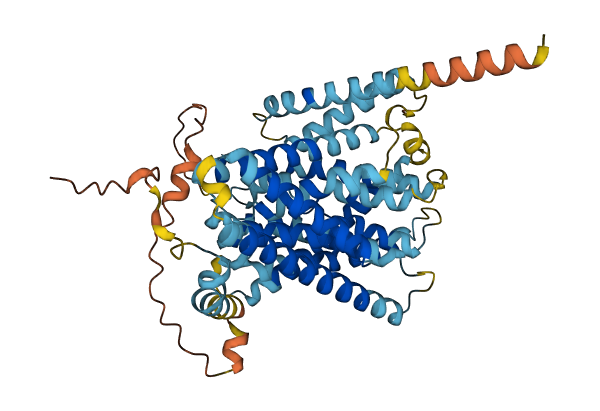
- 77.21
- Protein Structure from AlphaFold and UniProt
- MolPhase score
- LOC_Os07g47100.1: 0.21321712
- LOC_Os07g47100.2: 0.21321712
- LOC_Os07g47100.3: 0.00248433
- MolPhase Result
- Publication
- Molecular cloning and expression of the Na+/H+ exchanger gene in Oryza sativa, 1999, Biochim Biophys Acta.
- Salt-dependent regulation of chloride channel transcripts in rice, 2006, Plant Science.
- Molecular and functional analyses of rice NHX-type Na+/H+ antiporter genes, 2011, Planta.
- Function, intracellular localization and the importance in salt tolerance of a vacuolar Na+/H+ antiporter from rice, 2004, Plant Cell Physiol.
- OsbZIP71, a bZIP transcription factor, confers salinity and drought tolerance in rice, 2014, Plant Mol Biol.
- Enhanced Salt Tolerance Conferred by the Complete 2.3 kb cDNA of the Rice Vacuolar Na+/H+ Antiporter Gene Compared to 1.9 kb Coding Region with 5’ UTR in Transgenic Lines of Rice., 2016, Front Plant Sci.
- Genbank accession number
- Key message
- Real-time PCR analysis revealed that the abiotic stress-related genes, OsVHA-B, OsNHX1, COR413-TM1, and OsMyb4, were up-regulated in overexpressing lines, while these same genes were down-regulated in RNAi lines
- The expression of OsNHX1, OsNHX2, OsNHX3, and OsNHX5 is regulated differently in rice tissues and is increased by salt stress, hyperosmotic stress, and ABA
- When we studied the expression of beta-glucuronidase (GUS) driven by either the OsNHX1 or the OsNHX5 promoter, we observed activity in the stele, the emerging part of lateral roots, the vascular bundle, the water pore, and the basal part of seedling shoots with both promoters
- These results suggest that the product of the novel gene, OsNHX1, functions as a Na+/H+ exchanger, and plays important roles in salt tolerance of rice
- In addition, overexpression of OsNHX1 improved the salt tolerance of transgenic rice cells and plants
- These results suggest that OsNHX1 on the tonoplasts plays important roles in the compartmentation of Na(+) and K(+) highly accumulated in the cytoplasm into the vacuoles, and the amount of the antiporter is one of the most important factors determining salt tolerance in rice
- OsNHX1 promoter-GUS activity only was localized to the guard cells and trichome, whereas OsNHX5 promoter-GUS activity only was localized to the root tip and pollen grains
- Treatment with high concentrations of NaCl and KCl increased the transcript levels of OsNHX1 in rice roots and shoots
- It also shows that inclusion of the complete un-translated regions (UTRs) of the alternatively spliced OsNHX1 gene provides a higher level of tolerance to the transgenic rice
- Connection
- OsNHX1, OsNHX5, Molecular and functional analyses of rice NHX-type Na+/H+ antiporter genes, The exon-intron structure of the OsNHX genes and the phylogenetic tree of the OsNHX proteins suggest that the OsNHX proteins are categorized into two subgroups (OsNHX1 through OsNHX4 and OsNHX5)
- OsNHX1, OsNHX5, Molecular and functional analyses of rice NHX-type Na+/H+ antiporter genes, OsNHX1, OsNHX2, OsNHX3, and OsNHX5 can suppress the Na+, Li+, and hygromycin sensitivity of yeast nhx1 mutants and their sensitivity to a high K+ concentration
- OsNHX1, OsNHX5, Molecular and functional analyses of rice NHX-type Na+/H+ antiporter genes, The expression of OsNHX1, OsNHX2, OsNHX3, and OsNHX5 is regulated differently in rice tissues and is increased by salt stress, hyperosmotic stress, and ABA
- OsNHX1, OsNHX5, Molecular and functional analyses of rice NHX-type Na+/H+ antiporter genes, When we studied the expression of beta-glucuronidase (GUS) driven by either the OsNHX1 or the OsNHX5 promoter, we observed activity in the stele, the emerging part of lateral roots, the vascular bundle, the water pore, and the basal part of seedling shoots with both promoters
- OsNHX1, OsNHX5, Molecular and functional analyses of rice NHX-type Na+/H+ antiporter genes, OsNHX1 promoter-GUS activity only was localized to the guard cells and trichome, whereas OsNHX5 promoter-GUS activity only was localized to the root tip and pollen grains
- OsNHX1, OsNHX4, Molecular and functional analyses of rice NHX-type Na+/H+ antiporter genes, The exon-intron structure of the OsNHX genes and the phylogenetic tree of the OsNHX proteins suggest that the OsNHX proteins are categorized into two subgroups (OsNHX1 through OsNHX4 and OsNHX5)
- OsNHX1, OsNHX2~OsNHX3, Molecular and functional analyses of rice NHX-type Na+/H+ antiporter genes, OsNHX1, OsNHX2, OsNHX3, and OsNHX5 can suppress the Na+, Li+, and hygromycin sensitivity of yeast nhx1 mutants and their sensitivity to a high K+ concentration
- OsNHX1, OsNHX2~OsNHX3, Molecular and functional analyses of rice NHX-type Na+/H+ antiporter genes, The expression of OsNHX1, OsNHX2, OsNHX3, and OsNHX5 is regulated differently in rice tissues and is increased by salt stress, hyperosmotic stress, and ABA
- Osmyb4, OsNHX1, OsbZIP71, a bZIP transcription factor, confers salinity and drought tolerance in rice, Real-time PCR analysis revealed that the abiotic stress-related genes, OsVHA-B, OsNHX1, COR413-TM1, and OsMyb4, were up-regulated in overexpressing lines, while these same genes were down-regulated in RNAi lines
- OsbZIP71, OsNHX1, OsbZIP71, a bZIP transcription factor, confers salinity and drought tolerance in rice, Chromatin immunoprecipitation analysis confirmed that OsbZIP71 directly binds the promoters of OsNHX1 and COR413-TM1 in vivo
- OsNHX1, OsPEX11, OsPEX11, a Peroxisomal Biogenesis Factor 11, Contributes to Salt Stress Tolerance in Oryza sativa., Furthermore, qPCR data suggested that OsPEX11 acted as a positive regulator of salt tolerance by reinforcing the expression of several well-known rice transporters (OsHKT2;1, OsHKT1;5, OsLti6a, OsLti6b, OsSOS1, OsNHX1, and OsAKT1) involved in Na(+)/K(+) homeostasis in transgenic plants under salinity
- OsCPP5, OsNHX1, Five novel transcription factors as potential regulators of OsNHX1 gene expression in a salt tolerant rice genotype., This approach allowed us to identify five TFs belonging to three distinct TF families: one TCP (OsPCF2), one CPP (OsCPP5) and three NIN-like (OsNIN-like2, OsNIN-like3 and OsNIN-like4) binding to the OsNHX1 gene promoter
- OsCPP5, OsNHX1, Five novel transcription factors as potential regulators of OsNHX1 gene expression in a salt tolerant rice genotype., Five transcription factors (TFs) belonging to three distinct TF families: one TCP (OsPCF2), one CPP (OsCPP5) and three NIN-like (OsNIN-like2, OsNIN-like3 and OsNIN-like4) were identified as binding to OsNHX1 promoter
- OsCPP5, OsNHX1, Five novel transcription factors as potential regulators of OsNHX1 gene expression in a salt tolerant rice genotype., Transactivation activity assays performed in Arabidopsis and rice protoplasts showed that OsPCF2 and OsNIN-like4 are activators of the OsNHX1 gene expression, while OsCPP5 and OsNIN-like2 act as repressors
- OsNHX1, OsNIN-like2, Five novel transcription factors as potential regulators of OsNHX1 gene expression in a salt tolerant rice genotype., This approach allowed us to identify five TFs belonging to three distinct TF families: one TCP (OsPCF2), one CPP (OsCPP5) and three NIN-like (OsNIN-like2, OsNIN-like3 and OsNIN-like4) binding to the OsNHX1 gene promoter
- OsNHX1, OsNIN-like2, Five novel transcription factors as potential regulators of OsNHX1 gene expression in a salt tolerant rice genotype., Five transcription factors (TFs) belonging to three distinct TF families: one TCP (OsPCF2), one CPP (OsCPP5) and three NIN-like (OsNIN-like2, OsNIN-like3 and OsNIN-like4) were identified as binding to OsNHX1 promoter
- OsNHX1, OsNIN-like2, Five novel transcription factors as potential regulators of OsNHX1 gene expression in a salt tolerant rice genotype., Transactivation activity assays performed in Arabidopsis and rice protoplasts showed that OsPCF2 and OsNIN-like4 are activators of the OsNHX1 gene expression, while OsCPP5 and OsNIN-like2 act as repressors
- OsNHX1, OsNIN-like3, Five novel transcription factors as potential regulators of OsNHX1 gene expression in a salt tolerant rice genotype., This approach allowed us to identify five TFs belonging to three distinct TF families: one TCP (OsPCF2), one CPP (OsCPP5) and three NIN-like (OsNIN-like2, OsNIN-like3 and OsNIN-like4) binding to the OsNHX1 gene promoter
- OsNHX1, OsNIN-like3, Five novel transcription factors as potential regulators of OsNHX1 gene expression in a salt tolerant rice genotype., Five transcription factors (TFs) belonging to three distinct TF families: one TCP (OsPCF2), one CPP (OsCPP5) and three NIN-like (OsNIN-like2, OsNIN-like3 and OsNIN-like4) were identified as binding to OsNHX1 promoter
- OsNHX1, OsNIN-like4, Five novel transcription factors as potential regulators of OsNHX1 gene expression in a salt tolerant rice genotype., This approach allowed us to identify five TFs belonging to three distinct TF families: one TCP (OsPCF2), one CPP (OsCPP5) and three NIN-like (OsNIN-like2, OsNIN-like3 and OsNIN-like4) binding to the OsNHX1 gene promoter
- OsNHX1, OsNIN-like4, Five novel transcription factors as potential regulators of OsNHX1 gene expression in a salt tolerant rice genotype., Five transcription factors (TFs) belonging to three distinct TF families: one TCP (OsPCF2), one CPP (OsCPP5) and three NIN-like (OsNIN-like2, OsNIN-like3 and OsNIN-like4) were identified as binding to OsNHX1 promoter
- OsNHX1, OsNIN-like4, Five novel transcription factors as potential regulators of OsNHX1 gene expression in a salt tolerant rice genotype., Transactivation activity assays performed in Arabidopsis and rice protoplasts showed that OsPCF2 and OsNIN-like4 are activators of the OsNHX1 gene expression, while OsCPP5 and OsNIN-like2 act as repressors
- OsNHX1, OsNIN-like4, Five novel transcription factors as potential regulators of OsNHX1 gene expression in a salt tolerant rice genotype., In addition, although the OsNHX1 response to salt and PEG-induced drought stress in either shoots or roots was quite similar in both rice genotypes, the expression of OsPCF2 in roots under salt stress and the OsNIN-like4 in roots subjected to PEG was mainly up-regulated in Hasawi, indicating that these TFs may be associated with the salt and drought stress tolerance observed for this genotype
Prev Next