- Information
- Symbol: OsNPR1,NH1
- MSU: LOC_Os01g09800
- RAPdb: Os01g0194300
- PSP score
- LOC_Os01g09800.1: 0.1583
- PLAAC score
- LOC_Os01g09800.1: 0
- pLDDT score
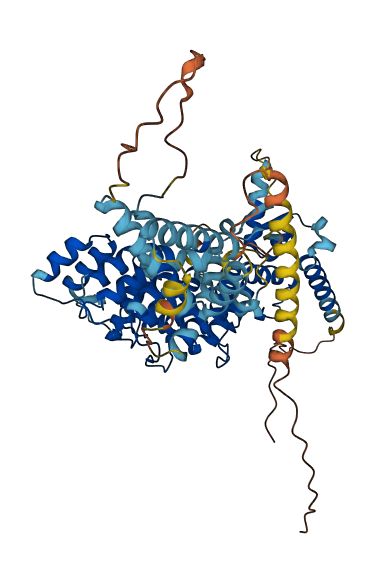
- 78.08
- Protein Structure from AlphaFold and UniProt
- MolPhase score
- LOC_Os01g09800.1: 0.87843626
- MolPhase Result
- Publication
- Mitogen-activated protein kinase OsMPK6 negatively regulates rice disease resistance to bacterial pathogens, 2007, Planta.
- Involvement of OsNPR1/NH1 in rice basal resistance to blast fungus Magnaporthe oryzae, 2011, European Journal of Plant Pathology.
- Isolation and characterization of the rice NPR1 promoter, 2009, Plant Biotechnology Reports.
- A rice transient assay system identifies a novel domain in NRR required for interaction with NH1/OsNPR1 and inhibition of NH1-mediated transcriptional activation, 2012, Plant Methods.
- OsWRKY71, a rice transcription factor, is involved in rice defense response, 2007, J Plant Physiol.
- Building a mutant resource for the study of disease resistance in rice reveals the pivotal role of several genes involved in defence, 2012, Mol Plant Pathol.
- Rice NRR, a negative regulator of disease resistance, interacts with Arabidopsis NPR1 and rice NH1, 2005, Plant J.
- Semi-dominant mutations in the CC-NB-LRR-type R gene, NLS1, lead to constitutive activation of defense responses in rice, 2011, Plant J.
- Functional analysis and expressional characterization of rice ankyrin repeat-containing protein, OsPIANK1, in basal defense against Magnaporthe oryzae attack, 2013, PLoS One.
- Cytokinins act synergistically with salicylic acid to activate defense gene expression in rice, 2013, Mol Plant Microbe Interact.
- Overexpression of a rice NPR1 homolog leads to constitutive activation of defense response and hypersensitivity to light, 2005, Mol Plant Microbe Interact.
- Reduced expression of glycolate oxidase leads to enhanced disease resistance in rice, 2013, PeerJ.
- OsNPR1 negatively regulates herbivore-induced JA and ethylene signaling and plant resistance to a chewing herbivore in rice, 2013, Physiol Plant.
- The nuclear ubiquitin proteasome degradation affects WRKY45 function in the rice defense program, 2012, Plant J.
- Functional analysis of rice NPR1-like genes reveals that OsNPR1/NH1 is the rice orthologue conferring disease resistance with enhanced herbivore susceptibility, 2007, Plant Biotechnol J.
- Functions of rice NAC transcriptional factors, ONAC122 and ONAC131, in defense responses against Magnaporthe grisea, 2013, Plant Mol Biol.
- The systemic acquired resistance regulator OsNPR1 Attenuates Growth by Repressing Auxin Signaling and promoting IAA-amido synthase expression., 2016, Plant Physiol.
- Genbank accession number
- Key message
- The antisense expression of OsNPR1 (as-npr1), which reduced the expression of the gene by 50%, increased elicited levels of JA and ethylene (ET) as well as of expression of a lipoxygenase gene OsHI-LOX and an ACC synthase gene OsACS2
- OsNPR1 negatively regulates herbivore-induced JA and ethylene signaling and plant resistance to a chewing herbivore in rice
- Here, using suppressive substrate hybridization, we identified a NPR1 gene from rice, OsNPR1, and found that its expression levels were upregulated in response to infestation by the rice striped stem borer (SSB) Chilo suppressalis and rice leaf folder (LF) Cnaphalocrocis medinalis, and to mechanical wounding and treatment with jasmonic acid (JA) and salicylic acid (SA)
- Furthermore, two marker genes in defense signaling pathway, OsNPR1 and OsPR1b, were constitutively expressed in OsWRKY71-overexpressing transgenic plants
- These results suggest that OsWRKY71 might function as a transcriptional regulator upstream of OsNPR1 and OsPR1b in rice defense signaling pathways
- These effects were diminished by RNAi-knockdown of OsNPR1 or WRKY45, the key regulators of the SA signaling pathway in rice, indicating that the effects of CK depend on these two regulators
- 1 and NH1, in the establishment of full basal resistance to rice blast
- OsNPR1/NH1, a rice homolog of NPR1 that is the key regulator of systemic acquired resistance in Arabidopsis thaliana, was shown to be involved in the resistance of rice to bacterial blight disease caused by Xanthomonas oryzae pv
- Involvement of OsNPR1/NH1 in rice basal resistance to blast fungus Magnaporthe oryzae
- In our study, three rice homologous genes, OsNPR1/NH1, OsNPR2/NH2 and OsNPR3, were found to be induced by rice bacterial blight Xanthomonas oryzae pv
- Over-expression of OsNPR1 conferred disease resistance to bacterial blight, but also enhanced herbivore susceptibility in transgenic plants
- These results indicate that NH1 may be involved in the regulation of SA in response to environmental changes
- Northern analysis shows that NH1ox rice spontaneously activates defense genes, contrasting with NPR1-overexpressing Arabidopsis, where defense genes are not activated until induction
- Different subcellular localizations of OsNPR1 antagonistically regulated SA- and jasmonic acid (JA)-responsive genes, but not SA and JA levels, indicating that OsNPR1 might mediate antagonistic cross-talk between the SA- and JA-dependent pathways in rice
- Wild-type NH1, but not a point mutant corresponding to npr1-1, interacts strongly with the rice transcription factor rTGA2
- The resistant plants showed increased expression of a subset of defense-responsive genes functioning in the NH1 (an Arabidopsis NPR1 orthologue)-involved defense signal transduction pathway
- However, when grown in growth chambers (GCs) under low light, NH1ox plants are dwarfed, indicating elevated sensitivity to light
- Greenhouse-grown NH1ox plants develop lesion-mimic spots on leaves at preflowering stage although no other developmental effects are observed
- Our results suggest that OsNPR1 is an early responding gene in herbivore-induced defense and that plants can use it to activate a specific and appropriate defense response against invaders by modulating signaling pathways
- Functional analysis of rice NPR1-like genes reveals that OsNPR1/NH1 is the rice orthologue conferring disease resistance with enhanced herbivore susceptibility
- TGA transcription factors are well known to participate in NPR1/NH1-mediated defense signaling, which is crucial to systemic acquired resistance in plants
- However, the role of OsNPR1/NH1 in rice basal resistance to blast fungus M
- oryzae, thus providing new insights into the role of OsNPR1 in rice disease resistance
- Rice NRR, a negative regulator of disease resistance, interacts with Arabidopsis NPR1 and rice NH1
- Silencing of GLO1 results in enhanced resistance to Xoo, increased expression of defense regulators NH1, NH3, and WRKY45, and activation of PR1 expression
- These results revealed that OsNPR1 is involved in rice basal resistance to the blast pathogen M
- The GC-grown NH1ox plants show much higher salicylic acid (SA) levels than the wild type, whereas greenhouse-grown NH1ox plants contain lower SA
- Expression of the rice gene OsNPR1 is induced by salicylic acid (SA)
- Connection
- OsNPR1~NH1, OsPR10a~PBZ1, Involvement of OsNPR1/NH1 in rice basal resistance to blast fungus Magnaporthe oryzae, Northern hybridization analysis showed that the expression of pathogenesis-related (PR) genes, such as PR-1a, PBZ1, CHI, GLU, and PAL, was significantly suppressed in the OsNPR1-RNAi plants
- OsNPR1~NH1, RH2, A rice transient assay system identifies a novel domain in NRR required for interaction with NH1/OsNPR1 and inhibition of NH1-mediated transcriptional activation, RH1 and RH3, but not RH2, also effectively repress NH1-mediated transcriptional activation
- OsNPR1~NH1, RH2, A rice transient assay system identifies a novel domain in NRR required for interaction with NH1/OsNPR1 and inhibition of NH1-mediated transcriptional activation, A substitution (AV to ED) in RH2 results in strong binding of mutant RH2ED to NH1 and effective repression of NH1-mediated activation
- OsNPR1~NH1, RH2, A rice transient assay system identifies a novel domain in NRR required for interaction with NH1/OsNPR1 and inhibition of NH1-mediated transcriptional activation, NRR, RH1, RH2, and RH3 share sequence similarity in a region beyond the previously identified NPR1-interacting domain
- NRR~CRCT, OsNPR1~NH1, A rice transient assay system identifies a novel domain in NRR required for interaction with NH1/OsNPR1 and inhibition of NH1-mediated transcriptional activation, NRR disrupts NH1 function, when over-expressed
- NRR~CRCT, OsNPR1~NH1, A rice transient assay system identifies a novel domain in NRR required for interaction with NH1/OsNPR1 and inhibition of NH1-mediated transcriptional activation, RESULTS: We have established a rice transient protoplast assay to demonstrate that NH1 is a transcriptional co-activator and that NRR represses NH1-mediated activation
- NRR~CRCT, OsNPR1~NH1, A rice transient assay system identifies a novel domain in NRR required for interaction with NH1/OsNPR1 and inhibition of NH1-mediated transcriptional activation, NRR, RH1, RH2, and RH3 share sequence similarity in a region beyond the previously identified NPR1-interacting domain
- NRR~CRCT, OsNPR1~NH1, A rice transient assay system identifies a novel domain in NRR required for interaction with NH1/OsNPR1 and inhibition of NH1-mediated transcriptional activation, Mutation W66A/F70A also greatly reduces the ability of NRR to repress NH1-mediated activation
- NRR~CRCT, OsNPR1~NH1, A rice transient assay system identifies a novel domain in NRR required for interaction with NH1/OsNPR1 and inhibition of NH1-mediated transcriptional activation, Our results demonstrate that the ability of NRR and its homologues to repress NH1-mediated transcriptional activation is tightly correlated with their ability to bind to NH1
- NRR~CRCT, OsNPR1~NH1, A rice transient assay system identifies a novel domain in NRR required for interaction with NH1/OsNPR1 and inhibition of NH1-mediated transcriptional activation, A rice transient assay system identifies a novel domain in NRR required for interaction with NH1/OsNPR1 and inhibition of NH1-mediated transcriptional activation
- OsNPR1~NH1, RH3, A rice transient assay system identifies a novel domain in NRR required for interaction with NH1/OsNPR1 and inhibition of NH1-mediated transcriptional activation, RH1 and RH3, but not RH2, also effectively repress NH1-mediated transcriptional activation
- OsNPR1~NH1, RH3, A rice transient assay system identifies a novel domain in NRR required for interaction with NH1/OsNPR1 and inhibition of NH1-mediated transcriptional activation, NRR, RH1, RH2, and RH3 share sequence similarity in a region beyond the previously identified NPR1-interacting domain
- OsNPR1~NH1, RH1, A rice transient assay system identifies a novel domain in NRR required for interaction with NH1/OsNPR1 and inhibition of NH1-mediated transcriptional activation, RH1 and RH3, but not RH2, also effectively repress NH1-mediated transcriptional activation
- OsNPR1~NH1, RH1, A rice transient assay system identifies a novel domain in NRR required for interaction with NH1/OsNPR1 and inhibition of NH1-mediated transcriptional activation, NRR, RH1, RH2, and RH3 share sequence similarity in a region beyond the previously identified NPR1-interacting domain
- ONAC122~OsNAC10, OsNPR1~NH1, Functions of rice NAC transcriptional factors, ONAC122 and ONAC131, in defense responses against Magnaporthe grisea, OsLOX, OsPR1a, OsWRKY45 and OsNH1) were down-regulated in plants silenced for ONAC122 or ONAC131 expression via the BMV-based silencing system
- ONAC131, OsNPR1~NH1, Functions of rice NAC transcriptional factors, ONAC122 and ONAC131, in defense responses against Magnaporthe grisea, OsLOX, OsPR1a, OsWRKY45 and OsNH1) were down-regulated in plants silenced for ONAC122 or ONAC131 expression via the BMV-based silencing system
- OsNPR1~NH1, OsPR1a~OsSCP, Functions of rice NAC transcriptional factors, ONAC122 and ONAC131, in defense responses against Magnaporthe grisea, OsLOX, OsPR1a, OsWRKY45 and OsNH1) were down-regulated in plants silenced for ONAC122 or ONAC131 expression via the BMV-based silencing system
- OsNPR1~NH1, OsWRKY45~WRKY45, Functions of rice NAC transcriptional factors, ONAC122 and ONAC131, in defense responses against Magnaporthe grisea, OsLOX, OsPR1a, OsWRKY45 and OsNH1) were down-regulated in plants silenced for ONAC122 or ONAC131 expression via the BMV-based silencing system
- OsNPR1~NH1, OsWRKY71, OsWRKY71, a rice transcription factor, is involved in rice defense response, Furthermore, two marker genes in defense signaling pathway, OsNPR1 and OsPR1b, were constitutively expressed in OsWRKY71-overexpressing transgenic plants
- OsNPR1~NH1, OsWRKY71, OsWRKY71, a rice transcription factor, is involved in rice defense response, These results suggest that OsWRKY71 might function as a transcriptional regulator upstream of OsNPR1 and OsPR1b in rice defense signaling pathways
- OsNPR1~NH1, OsPR1b, OsWRKY71, a rice transcription factor, is involved in rice defense response, Furthermore, two marker genes in defense signaling pathway, OsNPR1 and OsPR1b, were constitutively expressed in OsWRKY71-overexpressing transgenic plants
- OsNPR1~NH1, OsPR1b, OsWRKY71, a rice transcription factor, is involved in rice defense response, These results suggest that OsWRKY71 might function as a transcriptional regulator upstream of OsNPR1 and OsPR1b in rice defense signaling pathways
- NRR~CRCT, OsNPR1~NH1, Rice NRR, a negative regulator of disease resistance, interacts with Arabidopsis NPR1 and rice NH1, NRR interacts with NPR1 in the NPR1-interacting domain (NI25) consisting of 25 amino acids
- NRR~CRCT, OsNPR1~NH1, Rice NRR, a negative regulator of disease resistance, interacts with Arabidopsis NPR1 and rice NH1, NRR also interacts with NH1; however, NI25 was not sufficient for a strong interaction, indicating a difference between the rice and the Arabidopsis proteins
- NRR~CRCT, OsNPR1~NH1, Rice NRR, a negative regulator of disease resistance, interacts with Arabidopsis NPR1 and rice NH1, The fact that NRR compromises Xa21-mediated resistance indicates cross-talk or overlap between NH1- and Xa21-mediated pathways
- NRR~CRCT, OsNPR1~NH1, Rice NRR, a negative regulator of disease resistance, interacts with Arabidopsis NPR1 and rice NH1, Rice NRR, a negative regulator of disease resistance, interacts with Arabidopsis NPR1 and rice NH1
- NLS1, OsNPR1~NH1, Semi-dominant mutations in the CC-NB-LRR-type R gene, NLS1, lead to constitutive activation of defense responses in rice, In addition, because the morphology and constitutive defense responses of nls1-1D were not suppressed by blocking SA or NPR1 transcript accumulation, we suggest that NLS1 mediates both SA and NPR1-independent defense signaling pathways in rice
- OsNPR1~NH1, OsPR1b, Functional analysis and expressional characterization of rice ankyrin repeat-containing protein, OsPIANK1, in basal defense against Magnaporthe oryzae attack, oryzae was accompanied by enhanced transcriptional expression of SA- and JA-dependent genes such as NH1, WKRY13, PAL, AOS2, PR1b, and PR5
- OsNPR1~NH1, OsWRKY45~WRKY45, Cytokinins act synergistically with salicylic acid to activate defense gene expression in rice, These effects were diminished by RNAi-knockdown of OsNPR1 or WRKY45, the key regulators of the SA signaling pathway in rice, indicating that the effects of CK depend on these two regulators
- GLO1, OsNPR1~NH1, Reduced expression of glycolate oxidase leads to enhanced disease resistance in rice, Silencing of GLO1 results in enhanced resistance to Xoo, increased expression of defense regulators NH1, NH3, and WRKY45, and activation of PR1 expression
- OsNPR1~NH1, OsWRKY45~WRKY45, Reduced expression of glycolate oxidase leads to enhanced disease resistance in rice, Silencing of GLO1 results in enhanced resistance to Xoo, increased expression of defense regulators NH1, NH3, and WRKY45, and activation of PR1 expression
- OsACS2, OsNPR1~NH1, OsNPR1 negatively regulates herbivore-induced JA and ethylene signaling and plant resistance to a chewing herbivore in rice, The antisense expression of OsNPR1 (as-npr1), which reduced the expression of the gene by 50%, increased elicited levels of JA and ethylene (ET) as well as of expression of a lipoxygenase gene OsHI-LOX and an ACC synthase gene OsACS2
- OsHI-LOX, OsNPR1~NH1, OsNPR1 negatively regulates herbivore-induced JA and ethylene signaling and plant resistance to a chewing herbivore in rice, The antisense expression of OsNPR1 (as-npr1), which reduced the expression of the gene by 50%, increased elicited levels of JA and ethylene (ET) as well as of expression of a lipoxygenase gene OsHI-LOX and an ACC synthase gene OsACS2
- NH2, OsNPR1~NH1, Functional analysis of rice NPR1-like genes reveals that OsNPR1/NH1 is the rice orthologue conferring disease resistance with enhanced herbivore susceptibility, In our study, three rice homologous genes, OsNPR1/NH1, OsNPR2/NH2 and OsNPR3, were found to be induced by rice bacterial blight Xanthomonas oryzae pv
- OsCBSX3, OsNPR1~NH1, Over-Expression of Rice CBS Domain Containing Protein, OsCBSX3, Confers Rice Resistance to Magnaporthe oryzae Inoculation., Consistently, the over-expression of OsCBSX3 enhances the transcript levels of immunity associated marker genes including PR1a, PR1b, PR5, AOS2, PAL, NH1, and OsWRKY13 in plants inoculated with M
- OsNPR1~NH1, OsWAK25, Overexpression of Rice Wall-Associated Kinase 25 OsWAK25 Alters Resistance to Bacterial and Fungal Pathogens., We generated OsWAK25 overexpression lines and show that these lines exhibit a lesion mimic phenotype and enhanced expression of rice NH1 (NPR1 homolog 1), OsPAL2, PBZ1 and PR10
- CRK10, OsNPR1~NH1, A Genetic Screen Identifies a Requirement for Cysteine-Rich-Receptor-Like Kinases in Rice NH1 OsNPR1-Mediated Immunity., We also show that elevated levels of NH1 expression lead to enhanced CRK10 expression and that the rice TGA2
- CRK10, OsNPR1~NH1, A Genetic Screen Identifies a Requirement for Cysteine-Rich-Receptor-Like Kinases in Rice NH1 OsNPR1-Mediated Immunity., These experiments demonstrate a requirement for CRKs in NH1-mediated immunity and establish a molecular link between NH1 and induction of CRK10 expression
- OsCUL3a, OsNPR1~NH1, OsCUL3a Negatively Regulates Cell Death and Immunity by Degrading OsNPR1 in Rice., OsCUL3a Negatively Regulates Cell Death and Immunity by Degrading OsNPR1 in Rice.
- OsCUL3a, OsNPR1~NH1, OsCUL3a Negatively Regulates Cell Death and Immunity by Degrading OsNPR1 in Rice., Strikingly, OsCUL3a interacts with and degrades OsNPR1, which acts as a positive regulator of cell death in rice
- OsCUL3a, OsNPR1~NH1, OsCUL3a Negatively Regulates Cell Death and Immunity by Degrading OsNPR1 in Rice., Accumulation of OsNPR1 protein is greater in the oscul3a mutant than in the wild type
- OsCUL3a, OsNPR1~NH1, OsCUL3a Negatively Regulates Cell Death and Immunity by Degrading OsNPR1 in Rice., Furthermore, the oscul3a osnpr1 double mutant does not exhibit the lesion mimic phenotype of the oscul3a mutant
- OsCUL3a, OsNPR1~NH1, OsCUL3a Negatively Regulates Cell Death and Immunity by Degrading OsNPR1 in Rice., Our data demonstrate that OsCUL3a negatively regulates cell death and immunity by degrading OsNPR1 in rice
Prev Next