- Information
- Symbol: OsPCS1
- MSU: LOC_Os05g34290
- RAPdb: Os05g0415200
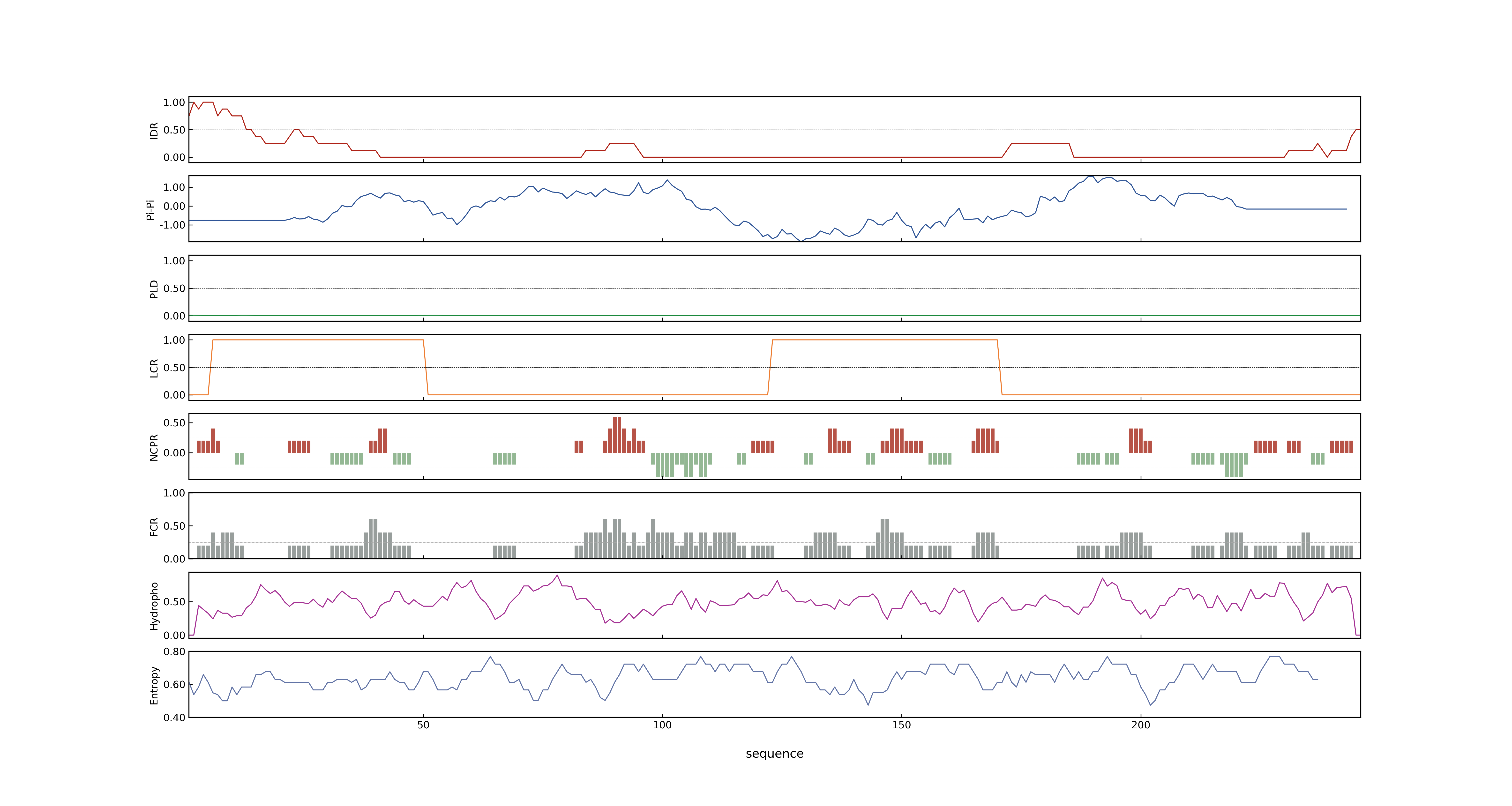
- PSP score
- LOC_Os05g34290.1: 0.04
- PLAAC score
- LOC_Os05g34290.1: 0
- pLDDT score
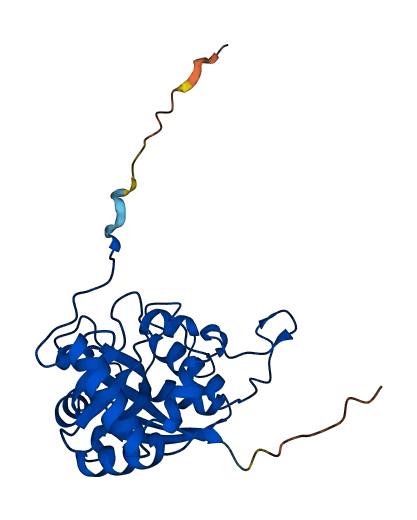
- 92.1
- Protein Structure from AlphaFold and UniProt
- MolPhase score
- LOC_Os05g34290.1: 0.21917414
- MolPhase Result
- Publication
- Identification of alternatively spliced transcripts of rice phytochelatin synthase 2 gene OsPCS2 involved in mitigation of cadmium and arsenic stresses., 2017, Plant Mol Biol.
- Phytochelatin synthase OsPCS1 plays a crucial role in reducing arsenic levels in rice grains., 2017, Plant J.
- Phytochelatin synthase has contrasting effects on cadmium and arsenic accumulation in rice grains., 2017, Plant Cell Physiol.
-
Genbank accession number
- Key message
- Analysis of the transgenic rice lines grown under metal(loid) stress revealed almost complete absence of both OsPCS1 and OsPCS2 transcripts in the developing seeds coupled with the significant reduction in the content of Cd (~51%) and As (~35%) in grains compared with the non-transgenic plant
- Map-based cloning identified the responsible genes as OsABCC1 in has1 and OsPCS1 in has2
- In vitro phytochelatin synthesis assay indicated that OsPCS1 was more sensitive to activation by As than by cadmium, whereas OsPCS2 was more weakly activated by As than by cadmium
- The levels of As in grains and node I were similar between the two mutants, suggesting that OsABCC1 preferentially cooperates with OsPCS1 to sequester As, although rice has another phytochelatin synthase, OsPCS2
- Quantitative RT-PCR of each OsPCS transcript in rice seedlings suggested that expression of OsPCS1full, the longest OsPCS1 variant, was most abundant, followed by OsPCS2
- To address physiological functions in toxic element tolerance and accumulation, two independent OsPCS1 mutant rice lines (a T-DNA and a Tos17 insertion line) were identified
- The OsPCS1 mutants exhibited increased sensitivity to As(III) and Cd in hydroponic experiments, showing the importance of OsPCS1-dependent PC synthesis for rice As(III) and Cd tolerance
- Using rice as a cereal model, we examined physiological roles of OsPCS1 in the distribution and detoxification of arsenic (As) and cadmium (Cd), two toxic elements associated with major food safety concerns
- Connection
- OsABCC1~MRP1, OsPCS1, Phytochelatin synthase OsPCS1 plays a crucial role in reducing arsenic levels in rice grains., Map-based cloning identified the responsible genes as OsABCC1 in has1 and OsPCS1 in has2
- OsABCC1~MRP1, OsPCS1, Phytochelatin synthase OsPCS1 plays a crucial role in reducing arsenic levels in rice grains., The levels of As in grains and node I were similar between the two mutants, suggesting that OsABCC1 preferentially cooperates with OsPCS1 to sequester As, although rice has another phytochelatin synthase, OsPCS2
- OsPCS1, OsPCS2, Phytochelatin synthase OsPCS1 plays a crucial role in reducing arsenic levels in rice grains., The levels of As in grains and node I were similar between the two mutants, suggesting that OsABCC1 preferentially cooperates with OsPCS1 to sequester As, although rice has another phytochelatin synthase, OsPCS2
- OsPCS1, OsPCS2, Phytochelatin synthase OsPCS1 plays a crucial role in reducing arsenic levels in rice grains., In vitro phytochelatin synthesis assay indicated that OsPCS1 was more sensitive to activation by As than by cadmium, whereas OsPCS2 was more weakly activated by As than by cadmium
- OsPCS1, OsPCS2, Phytochelatin synthase has contrasting effects on cadmium and arsenic accumulation in rice grains., First, we isolated four different transcript variants of OsPCS1 as well as one from OsPCS2
- OsPCS1, OsPCS2, Phytochelatin synthase has contrasting effects on cadmium and arsenic accumulation in rice grains., Quantitative RT-PCR of each OsPCS transcript in rice seedlings suggested that expression of OsPCS1full, the longest OsPCS1 variant, was most abundant, followed by OsPCS2
Prev Next