- Information
- Symbol: OsPLS1
- MSU: LOC_Os06g45120
- RAPdb: Os06g0662000
- PSP score
- LOC_Os06g45120.1: 0.0134
- LOC_Os06g45120.2: 0.0063
- PLAAC score
- LOC_Os06g45120.1: 0
- LOC_Os06g45120.2: 0
- pLDDT score
- 88.62
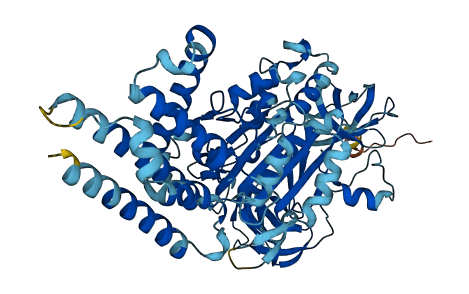
- Protein Structure from AlphaFold and UniProt
- MolPhase score
- LOC_Os06g45120.1: 0.08146195
- LOC_Os06g45120.2: 0.06060947
- MolPhase Result
- Publication
-
Genbank accession number
- Key message
- A single cytosine deletion in the OsPLS1 gene encoding vacuolar-type H+-ATPase subunit A1 leads to premature leaf senescence and seed dormancy in rice.
- The OsPSL1/VHA-A1 transcript levels progressively declined with the age-dependent leaf senescence in both the ospls1 mutant and its wild type
- The significant decrease in both OsPSL1/VHA-A1 gene expression and VHA enzyme activity in the ospls1 mutant strongly suggests a negative regulatory role for the normal OsPLS1/VHA-A1 gene in the onset of rice leaf senescence
- To conclude, OsPLS1 is implicated in leaf senescence and seed dormancy in rice
- Despite normal development in early seedlings, the ospls1 mutant leaves displayed lesion-mimics and early senescence, and a high transpiration rate after tillering
- Using a map-based cloning approach, we determined that a cytosine deletion in the OsPLS1 gene encoding vacuolar H(+)-ATPase subunit A1 (VHA-A1) underlies the phenotypic abnormalities in the ospls1 mutant
- The ospls1 mutant featured higher salicylic acid (SA) levels and reactive oxygen species (ROS) accumulation, and activation of signal transduction by up-regulation of WRKY genes in leaves
- Consistent with this, the ospls1 mutant exhibited hypersensitivity to exogenous SA and/or H2O2
- Connection
Prev Next