- Information
- Symbol: OsSRT1
- MSU: LOC_Os04g20270
- RAPdb: Os04g0271000
- PSP score
- LOC_Os04g20270.2: 0.0781
- LOC_Os04g20270.1: 0.0781
- PLAAC score
- LOC_Os04g20270.2: 0
- LOC_Os04g20270.1: 0
- pLDDT score
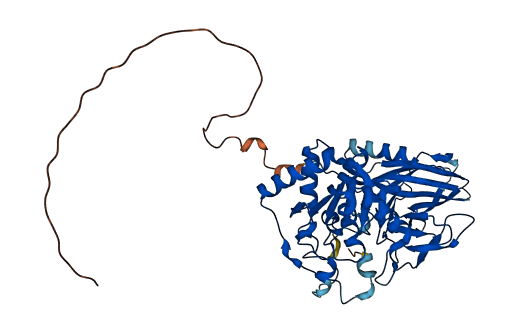
- 87.11
- Protein Structure from AlphaFold and UniProt
- MolPhase score
- LOC_Os04g20270.1: 0.37865814
- LOC_Os04g20270.2: 0.37865814
- MolPhase Result
- Publication
- Down-regulation of a SILENT INFORMATION REGULATOR2-related histone deacetylase gene, OsSRT1, induces DNA fragmentation and cell death in rice, 2007, Plant Physiol.
- The rice NAD+-dependent histone deacetylase OsSRT1 targets preferentially to stress- and metabolism-related genes and transposable elements, 2013, PLoS One.
- OsSRT1 is involved in rice seed development through regulation of starch metabolism gene expression, 2016, Plant Science.
- Rice NAD+-dependent histone deacetylase OsSRT1 represses glycolysis and regulates the moonlighting function of GAPDH as a transcriptional activator of glycolytic genes., 2017, Nucleic Acids Res.
- Genbank accession number
- Key message
- OsSRT1 RNA interference induced an increase of histone H3K9 (lysine-9 of H3) acetylation and a decrease of H3K9 dimethylation, leading to H(2)O(2) production, DNA fragmentation, cell death, and lesions mimicking plant hypersensitive responses during incompatible interactions with pathogens, whereas overexpression of OsSRT1 enhanced tolerance to oxidative stress
- Down-regulation of a SILENT INFORMATION REGULATOR2-related histone deacetylase gene, OsSRT1, induces DNA fragmentation and cell death in rice
- OsSRT1 is involved in rice seed development through regulation of starch metabolism gene expression
- In this work, we investigated the role of OsSRT1 in rice seed development
- Down-regulation of OsSRT1 induced higher expression of Rice Starch Regulator1 (RSR1) and amylases genes in developing seeds, which resulted in a decrease of starch synthesis and an increase of starch degradation, leading to abnormal seed development
- ChIP assay showed that OsSRT1 was required to reduce histone H3K9 acetylation on starch metabolism genes and transposons in developing seeds
- In addition, OsSRT1 was detected to directly bind to starch metabolism genes such as OsAmy3B, OsAmy3E, OsBmy4, and OsBmy9
- OsSRT1 is a NAD+-dependent histone deacetylase, closely related to the human SIRT6 that plays key roles in genome stability and metabolic homeostasis
- We show that OsSRT1 reduces GAPDH lysine acetylation and nuclear accumulation that are enhanced by oxidative stress
- Rice NAD+-dependent histone deacetylase OsSRT1 represses glycolysis and regulates the moonlighting function of GAPDH as a transcriptional activator of glycolytic genes.
- The results indicate that OsSRT1 represses glycolysis by both regulating epigenetic modification of histone and inhibiting the moonlighting function of GAPDH as a transcriptional activator of glycolytic genes in rice
- Connection
- OsSRT1, RSR1, OsSRT1 is involved in rice seed development through regulation of starch metabolism gene expression, Down-regulation of OsSRT1 induced higher expression of Rice Starch Regulator1 (RSR1) and amylases genes in developing seeds, which resulted in a decrease of starch synthesis and an increase of starch degradation, leading to abnormal seed development
- OsGAPDH1, OsSRT1, Rice NAD+-dependent histone deacetylase OsSRT1 represses glycolysis and regulates the moonlighting function of GAPDH as a transcriptional activator of glycolytic genes, OsSRT1-dependent lysine deacetylation of OsGAPDH1 represses transcriptional activity of the protein.
Prev Next