- Information
- Symbol: OsWRKY45,WRKY45
- MSU: LOC_Os05g25770
- RAPdb: Os05g0322900
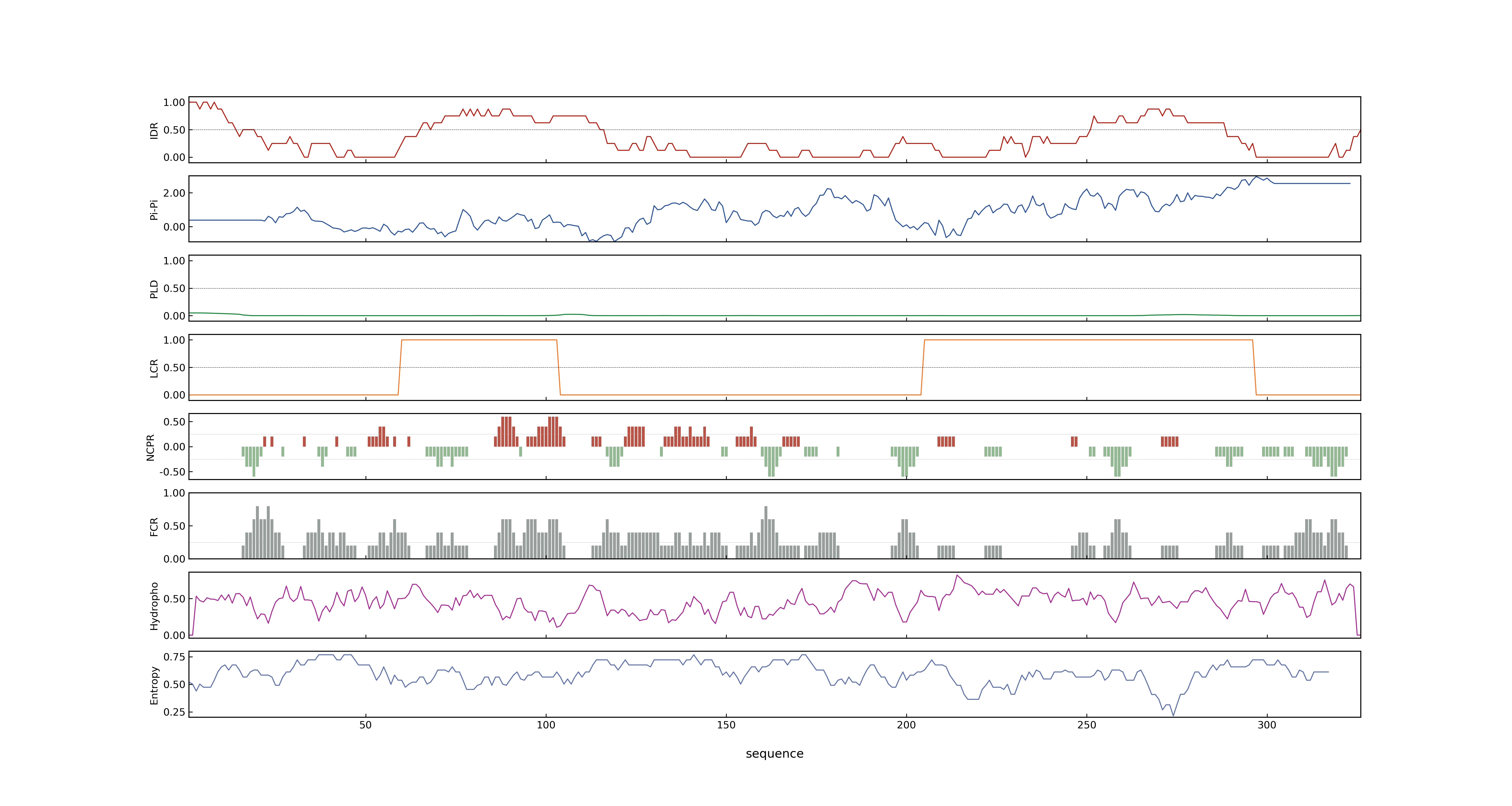
- PSP score
- LOC_Os05g25770.1: 0.2418
- PLAAC score
- LOC_Os05g25770.1: 0
- pLDDT score
- 64.34
- Protein Structure from AlphaFold and UniProt
- MolPhase score
- LOC_Os05g25770.1: 0.99736732
- MolPhase Result
- Publication
- Over-expression of the stress-induced OsWRKY45 enhances disease resistance and drought tolerance in Arabidopsis, 2009, Environmental and Experimental Botany.
- OsWRKY45 alleles play different roles in abscisic acid signalling and salt stress tolerance but similar roles in drought and cold tolerance in rice, 2011, J Exp Bot.
- Rice WRKY45 plays important roles in fungal and bacterial disease resistance, 2012, Mol Plant Pathol.
- The WRKY Gene Family in Rice Oryza sativa, 2007, J Integr Plant Biol.
- Cytokinins act synergistically with salicylic acid to activate defense gene expression in rice, 2013, Mol Plant Microbe Interact.
- Suppression of the rice fatty-acid desaturase gene OsSSI2 enhances resistance to blast and leaf blight diseases in rice, 2009, Mol Plant Microbe Interact.
- Reduced expression of glycolate oxidase leads to enhanced disease resistance in rice, 2013, PeerJ.
- Rice WRKY45 plays a crucial role in benzothiadiazole-inducible blast resistance, 2007, Plant Cell.
- A pair of allelic WRKY genes play opposite roles in rice-bacteria interactions, 2009, Plant Physiol.
- Blast resistance of CC-NB-LRR protein Pb1 is mediated by WRKY45 through protein-protein interaction, 2013, Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A.
- Annotations and functional analyses of the rice WRKY gene superfamily reveal positive and negative regulators of abscisic acid signaling in aleurone cells, 2005, Plant Physiol.
- The nuclear ubiquitin proteasome degradation affects WRKY45 function in the rice defense program, 2012, Plant J.
- Functions of rice NAC transcriptional factors, ONAC122 and ONAC131, in defense responses against Magnaporthe grisea, 2013, Plant Mol Biol.
- Development of disease-resistant rice by optimized expression of WRKY45., 2014, Plant Biotechnol J.
- Development of disease-resistant rice by pathogen-responsive expression of WRKY45., 2015, Plant Biotechnol J.
- Abiotic Stresses Antagonize the Rice Defence Pathway through the Tyrosine-Dephosphorylation of OsMPK6., 2015, PLoS Pathog.
- Transposon-derived small RNA is responsible for modified function of WRKY45 locus., 2016, Nat Plants.
- The Transcription Factor OsWRKY45 Negatively Modulates the Resistance of Rice to the Brown Planthopper Nilaparvata lugens., 2016, Int J Mol Sci.
- Genbank accession number
- Key message
- We have reported previously that a transcription factor identified in rice, WRKY45 (OsWRKY45), plays a pivotal role in BTH-induced disease resistance by mediating SA signalling
- OsWRKY45 alleles play different roles in abscisic acid signalling and salt stress tolerance but similar roles in drought and cold tolerance in rice
- Together, these results indicate that the OsWRKY45 may be involved in the signal pathways of both biotic and abiotic stress response
- Over-expression of the stress-induced OsWRKY45 enhances disease resistance and drought tolerance in Arabidopsis
- Here it is shown that the alleles OsWRKY45-1 and OsWRKY45-2 play different roles in abscisic acid (ABA) signalling and salt stress adaptation in rice
- OsWRKY45-1 transgenic plants showed no obvious difference from negative controls in response to salt stress
- In contrast, OsWRKY45-2-overexpressing lines showed increased ABA sensitivity and reduced salt stress tolerance, and OsWRKY45-2-suppressing lines showed reduced ABA sensitivity and increased salt stress tolerance
- These results suggest that OsWRKY45-1 negatively and OsWRKY45-2 positively regulates ABA signalling and, in addition, OsWRKY45-2 but not OsWRKY45-1 negatively regulates rice response to salt stress
- OsWRKY45-1-overexpressing lines showed reduced ABA sensitivity, whereas OsWRKY45-1-knockout lines showed increased ABA sensitivity
- OsWRKY45-1-regulated Xoo resistance was accompanied by increased accumulation of salicylic acid and jasmonic acid and induced expression of a subset of defense-responsive genes, while OsWRKY45-2-regulated Xoo resistance was accompanied by increased accumulation of jasmonic acid but not salicylic acid and induced expression of another subset of defense-responsive genes
- OsWRKY45-1 and OsWRKY45-2 transgenic plants showed differential expression of a set of ABA- and abiotic stress-responsive genes, but they showed similar responses to cold and drought stresses
- The relationship between OsWRKY45 expression and ABA signalling is discussed
- OsWRKY45-1-overexpressing plants showed increased susceptibility and OsWRKY45-1-knockout plants showed enhanced resistance to Xoo and Xoc
- In contrast, OsWRKY45-2-overexpressing plants showed enhanced resistance and OsWRKY45-2-suppressing plants showed increased susceptibility to Xoo and Xoc
- Interestingly, excessive WRKY45 expression rendered rice plants sensitive to low temperature and salinity, and stress sensitivity was correlated with the induction of defence genes by these stresses
- Previously, we reported that rice transformants overexpressing WRKY45 driven by the maize ubiquitin promoter were strongly resistant to both pathogens; however, their growth and yield were negatively affected because of the trade-off between the two conflicting traits
- Comparisons among different transformant lines showed that, overall, the strength of WRKY45 expression was positively correlated with disease resistance and negatively correlated with agronomic traits
- The agronomic traits of two lines expressing WRKY45 driven by the OsUbi7 promoter (PO sUbi7 lines) were nearly comparable to those of untransformed rice, and both lines were pathogen resistant
- The rice transcription factor WRKY45 plays a central role in the salicylic acid signalling pathway and mediates chemical-induced resistance to multiple pathogens, including Magnaporthe oryzae and Xanthomonas oryzae pv
- WRKY45 is an important transcription factor in the salicylic acid signalling pathway in rice that mediates chemical-induced resistance against multiple pathogens
- Here, a new strategy to confer rice with strong disease resistance without any negative effects on agronomic traits was established by expressing WRKY45 under the control of pathogen-responsive promoters in combination with a translational enhancer derived from a 5’-untranslated region (UTR) of rice alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH)
- Thus, expressing WRKY45 under the control of the PR1b promoter with the ADH 5’-UTR is an excellent strategy to develop disease-resistant rice, and the line established could serve as a mother line for breeding disease-resistant rice
- The activation of WRKY45 by benzothiadiazole (BTH) was reduced under low temperature and high salinity, probably through abscisic acid (ABA) signalling
- Phosphorylation of WRKY45, the central transcription factor in salicylic-acid (SA)-signalling-dependent pathogen defence in rice, via the OsMKK10-2-OsMPK6 cascade, was required to fully activate WRKY45
- An ABA treatment dephosphorylated/inactivated OsMPK6 via protein tyrosine phosphatases, OsPTP1/2, leading to the impaired activation of WRKY45 and a reduction in Magnaporthe oryzae resistance, even after BTH treatment
- Here we show that a TE-siRNA, TE-siR815, causes opposite functions for the two alleles, WRKY45-1 and WRKY45-2, of the WRKY45 transcription factor in rice resistance to Xanthomonas oryzae pv
- These results suggest that TE-siR815 contributes to the natural variation of the WRKY45 locus and TE-siR815-induced suppression of ST1 results in the negative role of WRKY45-1 but positive role of WRKY45-2 in regulating disease resistance
- The Transcription Factor OsWRKY45 Negatively Modulates the Resistance of Rice to the Brown Planthopper Nilaparvata lugens.
- These findings suggest that OsWRKY45 plays important but contrasting roles in regulating the resistance of rice to pathogens and herbivores, and attention should be paid if OsWRKY45 is used to develop disease or herbivore-resistant rice
- The antisense expression of OsWRKY45 (as-wrky) enhanced BPH-induced levels of ethylene, reduced feeding and oviposition preference as well as the survival rate of BPH, and delayed the development of BPH nymphs
- Connection
- ONAC122~OsNAC10, OsWRKY45~WRKY45, Functions of rice NAC transcriptional factors, ONAC122 and ONAC131, in defense responses against Magnaporthe grisea, OsLOX, OsPR1a, OsWRKY45 and OsNH1) were down-regulated in plants silenced for ONAC122 or ONAC131 expression via the BMV-based silencing system
- ONAC131, OsWRKY45~WRKY45, Functions of rice NAC transcriptional factors, ONAC122 and ONAC131, in defense responses against Magnaporthe grisea, OsLOX, OsPR1a, OsWRKY45 and OsNH1) were down-regulated in plants silenced for ONAC122 or ONAC131 expression via the BMV-based silencing system
- OsPR1a~OsSCP, OsWRKY45~WRKY45, Functions of rice NAC transcriptional factors, ONAC122 and ONAC131, in defense responses against Magnaporthe grisea, OsLOX, OsPR1a, OsWRKY45 and OsNH1) were down-regulated in plants silenced for ONAC122 or ONAC131 expression via the BMV-based silencing system
- OsNPR1~NH1, OsWRKY45~WRKY45, Functions of rice NAC transcriptional factors, ONAC122 and ONAC131, in defense responses against Magnaporthe grisea, OsLOX, OsPR1a, OsWRKY45 and OsNH1) were down-regulated in plants silenced for ONAC122 or ONAC131 expression via the BMV-based silencing system
- OsNPR1~NH1, OsWRKY45~WRKY45, Cytokinins act synergistically with salicylic acid to activate defense gene expression in rice, These effects were diminished by RNAi-knockdown of OsNPR1 or WRKY45, the key regulators of the SA signaling pathway in rice, indicating that the effects of CK depend on these two regulators
- OsSSI2, OsWRKY45~WRKY45, Suppression of the rice fatty-acid desaturase gene OsSSI2 enhances resistance to blast and leaf blight diseases in rice, Taken together, our results suggest that induction of SA-responsive genes, including WRKY45, is likely responsible for enhanced disease resistance in OsSSI2-kd rice plants
- GLO1, OsWRKY45~WRKY45, Reduced expression of glycolate oxidase leads to enhanced disease resistance in rice, Silencing of GLO1 results in enhanced resistance to Xoo, increased expression of defense regulators NH1, NH3, and WRKY45, and activation of PR1 expression
- OsNPR1~NH1, OsWRKY45~WRKY45, Reduced expression of glycolate oxidase leads to enhanced disease resistance in rice, Silencing of GLO1 results in enhanced resistance to Xoo, increased expression of defense regulators NH1, NH3, and WRKY45, and activation of PR1 expression
- OsWRKY45~WRKY45, Pb1, Blast resistance of CC-NB-LRR protein Pb1 is mediated by WRKY45 through protein-protein interaction, The Pb1 protein interacted with WRKY45, a transcription factor involved in induced resistance via the salicylic acid signaling pathway that is regulated by the ubiquitin proteasome system
- OsWRKY45~WRKY45, Pb1, Blast resistance of CC-NB-LRR protein Pb1 is mediated by WRKY45 through protein-protein interaction, Pb1-mediated panicle blast resistance was largely compromised when WRKY45 was knocked down in a Pb1-containing rice cultivar
- OsWRKY45~WRKY45, Pb1, Blast resistance of CC-NB-LRR protein Pb1 is mediated by WRKY45 through protein-protein interaction, Leaf-blast resistance by Pb1 overexpression (Pb1-ox) was also compromised in WRKY45 knockdown/Pb1-ox rice
- OsWRKY45~WRKY45, Pb1, Blast resistance of CC-NB-LRR protein Pb1 is mediated by WRKY45 through protein-protein interaction, Blast infection induced higher accumulation of WRKY45 in Pb1-ox than in control Nipponbare rice
- OsWRKY45~WRKY45, Pb1, Blast resistance of CC-NB-LRR protein Pb1 is mediated by WRKY45 through protein-protein interaction, Overexpression of Pb1-Quad, a coiled-coil domain mutant that had weak interaction with WRKY45, resulted in significantly weaker blast resistance than that of wild-type Pb1
- OsWRKY45~WRKY45, Pb1, Blast resistance of CC-NB-LRR protein Pb1 is mediated by WRKY45 through protein-protein interaction, These results suggest that the blast resistance of Pb1 depends on its interaction with WRKY45 in the nucleus
- OsWRKY45~WRKY45, Pb1, Blast resistance of CC-NB-LRR protein Pb1 is mediated by WRKY45 through protein-protein interaction, In a transient system using rice protoplasts, coexpression of Pb1 enhanced WRKY45 accumulation and increased WRKY45-dependent transactivation activity, suggesting that protection of WRKY45 from ubiquitin proteasome system degradation is possibly involved in Pb1-dependent blast resistance
- OsWRKY45~WRKY45, Pb1, Blast resistance of CC-NB-LRR protein Pb1 is mediated by WRKY45 through protein-protein interaction, Blast resistance of CC-NB-LRR protein Pb1 is mediated by WRKY45 through protein-protein interaction
- OsMPK6~OsMPK4, OsWRKY45~WRKY45, Abiotic Stresses Antagonize the Rice Defence Pathway through the Tyrosine-Dephosphorylation of OsMPK6., An ABA treatment dephosphorylated/inactivated OsMPK6 via protein tyrosine phosphatases, OsPTP1/2, leading to the impaired activation of WRKY45 and a reduction in Magnaporthe oryzae resistance, even after BTH treatment
- OsMPK6~OsMPK4, OsWRKY45~WRKY45, Abiotic Stresses Antagonize the Rice Defence Pathway through the Tyrosine-Dephosphorylation of OsMPK6Abiotic Stresses Antagonize the Rice Defence Pathway through the Tyrosine-Dephosphorylation of OsMPK6, An ABA treatment dephosphorylated/inactivated OsMPK6 via protein tyrosine phosphatases, OsPTP1/2, leading to the impaired activation of WRKY45 and a reduction in Magnaporthe oryzae resistance, even after BTH treatment
- OsPTP1, OsWRKY45~WRKY45, Abiotic Stresses Antagonize the Rice Defence Pathway through the Tyrosine-Dephosphorylation of OsMPK6Abiotic Stresses Antagonize the Rice Defence Pathway through the Tyrosine-Dephosphorylation of OsMPK6, An ABA treatment dephosphorylated/inactivated OsMPK6 via protein tyrosine phosphatases, OsPTP1/2, leading to the impaired activation of WRKY45 and a reduction in Magnaporthe oryzae resistance, even after BTH treatment
- OsPTP2, OsWRKY45~WRKY45, Abiotic Stresses Antagonize the Rice Defence Pathway through the Tyrosine-Dephosphorylation of OsMPK6Abiotic Stresses Antagonize the Rice Defence Pathway through the Tyrosine-Dephosphorylation of OsMPK6, An ABA treatment dephosphorylated/inactivated OsMPK6 via protein tyrosine phosphatases, OsPTP1/2, leading to the impaired activation of WRKY45 and a reduction in Magnaporthe oryzae resistance, even after BTH treatment
- OsMPK6~OsMPK4, OsWRKY45~WRKY45, Abiotic Stresses Antagonize the Rice Defence Pathway through the Tyrosine-Dephosphorylation of OsMPK6Abiotic Stresses Antagonize the Rice Defence Pathway through the Tyrosine-Dephosphorylation of OsMPK6, Phosphorylation of WRKY45, the central transcription factor in salicylic-acid (SA)-signalling-dependent pathogen defence in rice, via the OsMKK10-2-OsMPK6 cascade, was required to fully activate WRKY45
- OsMKK10-2~MPKK10.2, OsWRKY45~WRKY45, Abiotic Stresses Antagonize the Rice Defence Pathway through the Tyrosine-Dephosphorylation of OsMPK6Abiotic Stresses Antagonize the Rice Defence Pathway through the Tyrosine-Dephosphorylation of OsMPK6, Phosphorylation of WRKY45, the central transcription factor in salicylic-acid (SA)-signalling-dependent pathogen defence in rice, via the OsMKK10-2-OsMPK6 cascade, was required to fully activate WRKY45
- OsWRKY45~WRKY45, RNRS1~St1~SDL, Transposon-derived small RNA is responsible for modified function of WRKY45 locus., These results suggest that TE-siR815 contributes to the natural variation of the WRKY45 locus and TE-siR815-induced suppression of ST1 results in the negative role of WRKY45-1 but positive role of WRKY45-2 in regulating disease resistance
- DTH2~OsCOL9~OsCCT08, OsWRKY45~WRKY45, CONSTANS-Like 9 OsCOL9 Interacts with Receptor for Activated C-Kinase 1OsRACK1 to Regulate Blast Resistance through Salicylic Acid and Ethylene Signaling Pathways., Further analysis indicated that OsCOL9 over-expression increased the expressions of phytohormone biosynthetic genes, NPR1, WRKY45, OsACO1 and OsACS1, which were related to SA and ET biosynthesis
- OsDjA6, OsWRKY45~WRKY45, The DnaJ protein OsDjA6 negatively regulates rice innate immunity to the blast fungus Magnaporthe oryzae., In addition, the expression levels of WRKY45, NPR1, and PR5 are increased in the OsDjA6 RNAi plants, indicating that OsDjA6 may mediate resistance by affecting the salicylic acid pathway
- OsMPK6~OsMPK4, OsWRKY45~WRKY45, WRKY45 phosphorylation at threonine 266 acts negatively on WRKY45-dependent blast resistance in rice., WRKY45 is a central regulator of disease resistance mediated by salicylic acid signaling in rice and its activation involves phosphorylation by OsMPK6
- OsMPK6~OsMPK4, OsWRKY45~WRKY45, WRKY45 phosphorylation at threonine 266 acts negatively on WRKY45-dependent blast resistance in rice., OsMPK6 phosphorylates WRKY45 at Thr266, Ser294, and Ser299 in vitro
- OsWRKY45~WRKY45, Pb1, Panicle blast 1 Pb1 resistance is dependent on at least four QTLs in the rice genome., We found that the expression of WRKY45 gene downstream of Pb1 was weakly induced by rice blast inoculation at the full heading stage in K209
Prev Next