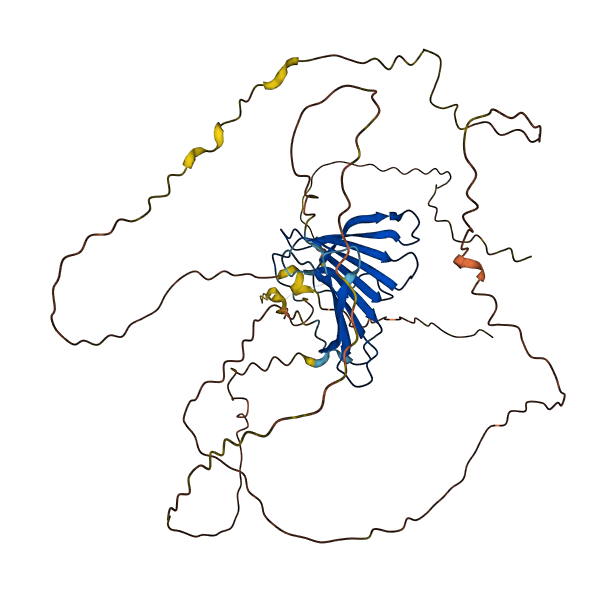
- Information
- Symbol: OsWRKY53
- MSU: LOC_Os05g27730
- RAPdb: Os05g0343400
- PSP score
- LOC_Os05g27730.1: 0.9888
- PLAAC score
- LOC_Os05g27730.1: 0
- pLDDT score
- 58.46
- Protein Structure from AlphaFold and UniProt
- MolPhase score
- LOC_Os05g27730.1: 0.99971634
- MolPhase Result
- Publication
- Involvement of the elicitor-induced gene OsWRKY53 in the expression of defense-related genes in rice, 2007, Biochim Biophys Acta.
- Promoter Analysis of the Elicitor-Induced WRKY GeneOsWRKY53, Which Is Involved in Defense Responses in Rice, 2014, Bioscience, Biotechnology and Biochemistry.
- The WRKY Gene Family in Rice Oryza sativa, 2007, J Integr Plant Biol.
- Involvement of the OsMKK4-OsMPK1 Cascade and its Downstream Transcription Factor OsWRKY53 in the Wounding Response in Rice, 2014, Plant Pathol J.
- The rice transcription factor WRKY53 suppresses herbivore-induced defenses by acting as a negative feedback modulator of map kinase activity., 2015, Plant Physiol.
- OsWRKY53, a versatile switch in regulating herbivore-induced defense responses in rice., 2016, Plant Signal Behav.
- Transcription factor OsWRKY53 positively regulates brassinosteroid signaling and plant architecture., 2017, Plant Physiol.
- Genbank accession number
- Key message
- OsWRKY53, a chitin oligosaccharide elicitor-responsive rice WRKY gene, has been found to be involved in defense responses in rice
- Promoter Analysis of the Elicitor-Induced WRKY GeneOsWRKY53, Which Is Involved in Defense Responses in Rice
- We identified three tandem W-box elements, putative recognition sites for WRKY transcription factors, as cis elements that are essential to the elicitor-responsiveness of OsWRKY53 by deletion and mutation analysis of the promoter by dual luciferase assay
- OsWRKY53 was also induced in suspension-cultured rice cells by a fungal cerebroside elicitor and in rice plants by infection with the blast fungus Magnaporthe grisea
- A microarray analysis revealed that several defense-related genes, including pathogenesis-related protein genes such as PBZ1, were upregulated in rice cells overexpressing OsWRKY53
- These results strongly suggest that OsWRKY53 is a transcription factor that plays important roles in elicitor-induced defense signaling pathways in rice
- Involvement of the elicitor-induced gene OsWRKY53 in the expression of defense-related genes in rice
- Involvement of the OsMKK4-OsMPK1 Cascade and its Downstream Transcription Factor OsWRKY53 in the Wounding Response in Rice
- Taken together, components involving in the wounding signaling pathway, OsMKK4-OsMPK1-OsWRKY53, can be important players in regulating crosstalk between abiotic stress and biotic stress.
- OsWRKY53 is also shown to be a negative regulator of plant growth
- The transcript levels of OsWRKY53 are independent of endogenous jasmonic acid (JA), but positively regulated by the mitogen-activated protein kinases (MPKs), OsMPK3/OsMPK6
- Recently, a rice WRKY transcription factor OsWRKY53 has been reported to function as a negative feedback modulator of OsMPK3/OsMPK6 and thereby to control the size of the investment a rice plant makes to defend against a chewing herbivore, the striped stem borer Chilo suppressalis
- We investigated the performance of a piecing-sucking herbivore, the brown planthopper (BPH) Nilaparvata lugens, on transgenic plants that silence or overexpress OsWRKY53, and found that OsWRKY53 activates rice defenses against BPH by activating an H2O2 burst and suppressing ethylene biosynthesis
- Phenotypic analyses showed that OsWRKY53 overexpression led to enlarged leaf angles and increased grain size, in contrast to the erect leaves and smaller seeds in oswrky53 mutant
- Transcription factor OsWRKY53 positively regulates brassinosteroid signaling and plant architecture.
- In addition, the oswrky53 exhibited decreased BR sensitivity, whereas OsWRKY53 overexpression plants were hypersensitive to BR, suggesting that OsWRKY53 positively regulates rice BR signaling
- Moreover, we show that OsWRKY53 can interact with and be phosphorylated by OsMAPKK4-OsMAPK6 cascade, and the phosphorylation is required for the biological function of OsWRKY53 in regulating BR responses
- Furthermore, we found that BR promotes OsWRKY53 protein accumulation but represses OsWRKY53 transcript level
- Taken together, this study revealed the novel role of OsWRKY53 as a regulator of rice BR signaling, and also suggested a potential role of OsWRKY53 in mediating the crosstalk between the hormone and other signaling pathways
- Connection
- OsMPK6~OsMPK4, OsWRKY53, The rice transcription factor WRKY53 suppresses herbivore-induced defenses by acting as a negative feedback modulator of map kinase activity, The transcript levels of OsWRKY53 are independent of endogenous jasmonic acid (JA), but positively regulated by the mitogen-activated protein kinases (MPKs), OsMPK3/OsMPK6
- OsMPK6~OsMPK4, OsWRKY53, The rice transcription factor WRKY53 suppresses herbivore-induced defenses by acting as a negative feedback modulator of map kinase activity, OsWRKY53 physically interacts with OsMPK3/OsMPK6 and suppresses their activity in vitro
- Lsi1~OsNIP2;1~OsLsi1, OsWRKY53, Overexpression of Lsi1 in cold-sensitive rice mediates transcriptional regulatory networks and enhances resistance to chilling stress, Our results suggest that when overexpressed Lsi1 in cold-sensitive rice, it possibility regulates the transcription factor OsWRKY53 in addition to the genes involved in the ROS metabolism, thus mediating resistance to chilling stress
Prev Next