- Information
- Symbol: RFT1
- MSU: LOC_Os06g06300
- RAPdb: Os06g0157500
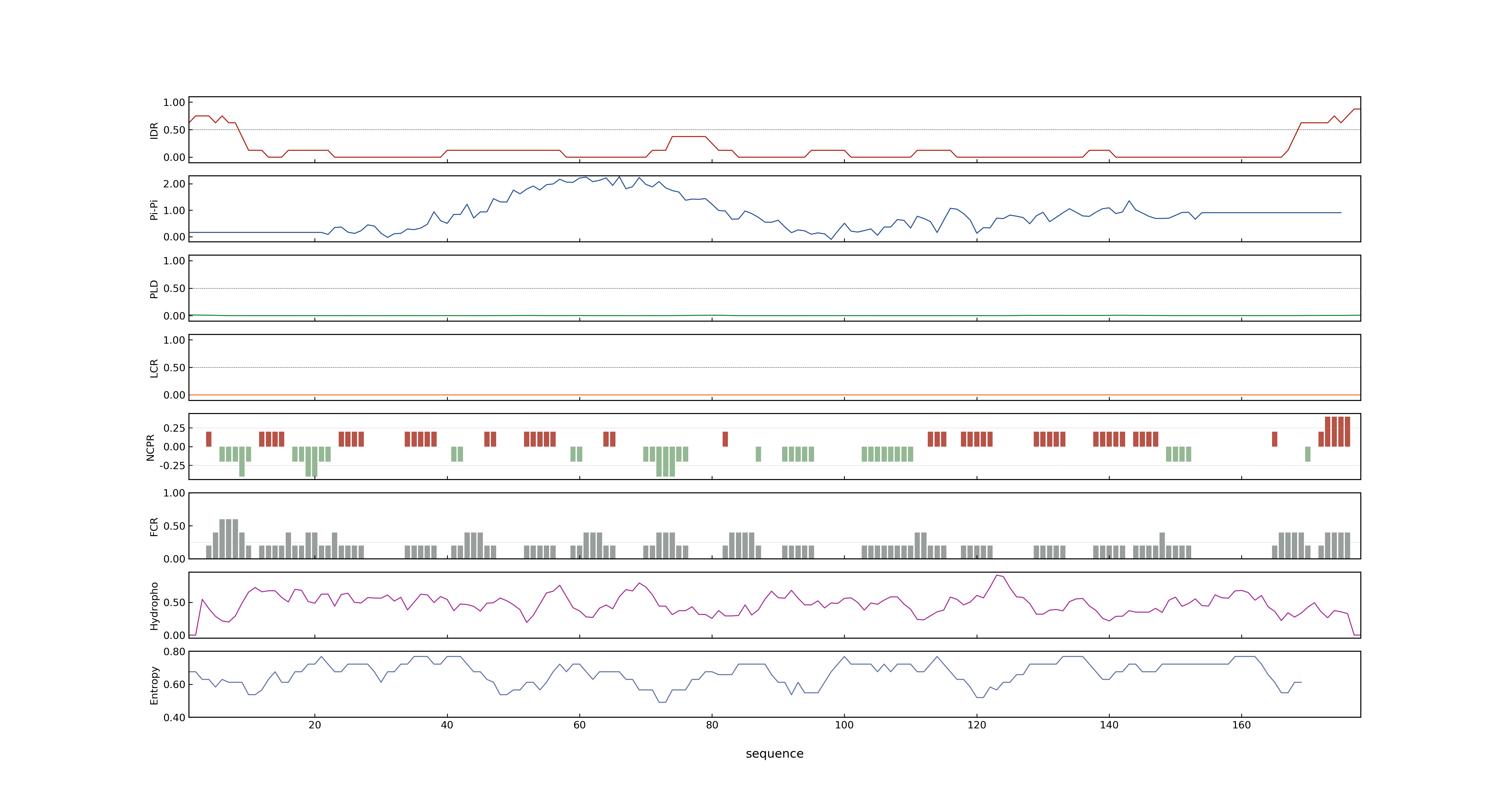
- PSP score
- LOC_Os06g06300.1: 0.0156
- PLAAC score
- LOC_Os06g06300.1: 0
- pLDDT score
- 93.24
- Protein Structure from AlphaFold and UniProt
- MolPhase score
- LOC_Os06g06300.1: 0.01282211
- MolPhase Result
- Publication
- Knockdown of SAMS genes encoding S-adenosyl-l-methionine synthetases causes methylation alterations of DNAs and histones and leads to late flowering in rice, 2011, J Plant Physiol.
- Heading date gene, dth3 controlled late flowering in O. Glaberrima Steud. by down-regulating Ehd1, 2011, Plant Cell Rep.
- Molecular dissection of the roles of phytochrome in photoperiodic flowering in rice, 2011, Plant Physiol.
- Hd3a and RFT1 are essential for flowering in rice, 2008, Development.
- A gene network for long-day flowering activates RFT1 encoding a mobile flowering signal in rice, 2009, Development.
- OsMADS50 and OsMADS56 function antagonistically in regulating long day LD-dependent flowering in rice, 2009, Plant Cell Environ.
- Rice Indeterminate 1 OsId1 is necessary for the expression of Ehd1 Early heading date 1 regardless of photoperiod, 2008, Plant J.
- OsCOL4 is a constitutive flowering repressor upstream of Ehd1 and downstream of OsphyB, 2010, Plant J.
- LHD1, an allele of DTH8/Ghd8, controls late heading date in common wild rice Oryza rufipogon, 2012, J Integr Plant Biol.
- Ehd4 encodes a novel and Oryza-genus-specific regulator of photoperiodic flowering in rice, 2013, PLoS Genet.
- A major QTL, Ghd8, plays pleiotropic roles in regulating grain productivity, plant height, and heading date in rice, 2011, Mol Plant.
- The histone methyltransferase SDG724 mediates H3K36me2/3 deposition at MADS50 and RFT1 and promotes flowering in rice, 2012, Plant Cell.
- Flowering time genes Heading date 1 and Early heading date 1 together control panicle development in rice, 2011, Plant Cell Physiol.
- Ehd2, a rice ortholog of the maize INDETERMINATE1 gene, promotes flowering by up-regulating Ehd1, 2008, Plant Physiol.
- Association of functional nucleotide polymorphisms at DTH2 with the northward expansion of rice cultivation in Asia, 2013, Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A.
- Natural variation of the RICE FLOWERING LOCUS T 1 contributes to flowering time divergence in rice, 2013, PLoS One.
- Distinct regulatory role for RFL, the rice LFY homolog, in determining flowering time and plant architecture, 2008, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
- OsVIL2 functions with PRC2 to induce flowering by repressing OsLFL1 in rice, 2013, Plant J.
- Hd16, a gene for casein kinase I, is involved in the control of rice flowering time by modulating the day-length response, 2013, Plant J.
- Rice Flowering Locus T 1 plays an important role in heading date influencing yield traits in rice., 2017, Sci Rep.
- Genbank accession number
- AB838427
- AB838440
- AB838444
- AB838458
- AB838550
- AB838570
- AB838575
- AB838576
- AB838577
- AB838578
- AB838579
- AB838580
- AB838581
- AB838582
- AB838584
- AB838585
- AB838586
- AB838587
- AB838588
- AB838589
- AB062676
- AB838427
- AB838440
- AB838444
- AB838458
- AB838550
- AB838570
- AB838575
- AB838576
- AB838577
- AB838578
- AB838579
- AB838580
- AB838581
- AB838582
- AB838584
- AB838585
- AB838586
- AB838587
- AB838588
- AB838589
- AB062676
- AB838427
- AB838440
- AB838444
- AB838458
- AB838550
- AB838570
- AB838575
- AB838576
- AB838577
- AB838578
- AB838579
- AB838580
- AB838581
- AB838582
- AB838584
- AB838585
- AB838586
- AB838587
- AB838588
- AB838589
- AB062676
- AB838427
- AB838440
- AB838444
- AB838458
- AB838550
- AB838570
- AB838575
- AB838576
- AB838577
- AB838578
- AB838579
- AB838580
- AB838581
- AB838582
- AB838584
- AB838585
- AB838586
- AB838587
- AB838588
- AB838589
- AB062676
- AB838427
- AB838440
- AB838444
- AB838458
- AB838550
- AB838570
- AB838575
- AB838576
- AB838577
- AB838578
- AB838579
- AB838580
- AB838581
- AB838582
- AB838584
- AB838585
- AB838586
- AB838587
- AB838588
- AB838589
- AB062676
- AB838427
- AB838440
- AB838444
- AB838458
- AB838550
- AB838570
- AB838575
- AB838576
- AB838577
- AB838578
- AB838579
- AB838580
- AB838581
- AB838582
- AB838584
- AB838585
- AB838586
- AB838587
- AB838588
- AB838589
- AB062676
- AB838427
- AB838440
- AB838444
- AB838458
- AB838550
- AB838570
- AB838575
- AB838576
- AB838577
- AB838578
- AB838579
- AB838580
- AB838581
- AB838582
- AB838584
- AB838585
- AB838586
- AB838587
- AB838588
- AB838589
- AB062676
- AB838427
- AB838440
- AB838444
- AB838458
- AB838550
- AB838570
- AB838575
- AB838576
- AB838577
- AB838578
- AB838579
- AB838580
- AB838581
- AB838582
- AB838584
- AB838585
- AB838586
- AB838587
- AB838588
- AB838589
- AB062676
- AB838427
- AB838440
- AB838444
- AB838458
- AB838550
- AB838570
- AB838575
- AB838576
- AB838577
- AB838578
- AB838579
- AB838580
- AB838581
- AB838582
- AB838584
- AB838585
- AB838586
- AB838587
- AB838588
- AB838589
- AB062676
- AB838427
- AB838440
- AB838444
- AB838458
- AB838550
- AB838570
- AB838575
- AB838576
- AB838577
- AB838578
- AB838579
- AB838580
- AB838581
- AB838582
- AB838584
- AB838585
- AB838586
- AB838587
- AB838588
- AB838589
- AB062676
- AB838427
- AB838440
- AB838444
- AB838458
- AB838550
- AB838570
- AB838575
- AB838576
- AB838577
- AB838578
- AB838579
- AB838580
- AB838581
- AB838582
- AB838584
- AB838585
- AB838586
- AB838587
- AB838588
- AB838589
- AB062676
- AB838427
- AB838440
- AB838444
- AB838458
- AB838550
- AB838570
- AB838575
- AB838576
- AB838577
- AB838578
- AB838579
- AB838580
- AB838581
- AB838582
- AB838584
- AB838585
- AB838586
- AB838587
- AB838588
- AB838589
- AB062676
- AB838427
- AB838440
- AB838444
- AB838458
- AB838550
- AB838570
- AB838575
- AB838576
- AB838577
- AB838578
- AB838579
- AB838580
- AB838581
- AB838582
- AB838584
- AB838585
- AB838586
- AB838587
- AB838588
- AB838589
- AB062676
- AB838427
- AB838440
- AB838444
- AB838458
- AB838550
- AB838570
- AB838575
- AB838576
- AB838577
- AB838578
- AB838579
- AB838580
- AB838581
- AB838582
- AB838584
- AB838585
- AB838586
- AB838587
- AB838588
- AB838589
- AB062676
- AB838427
- AB838440
- AB838444
- AB838458
- AB838550
- AB838570
- AB838575
- AB838576
- AB838577
- AB838578
- AB838579
- AB838580
- AB838581
- AB838582
- AB838584
- AB838585
- AB838586
- AB838587
- AB838588
- AB838589
- AB062676
- AB838427
- AB838440
- AB838444
- AB838458
- AB838550
- AB838570
- AB838575
- AB838576
- AB838577
- AB838578
- AB838579
- AB838580
- AB838581
- AB838582
- AB838584
- AB838585
- AB838586
- AB838587
- AB838588
- AB838589
- AB062676
- AB838427
- AB838440
- AB838444
- AB838458
- AB838550
- AB838570
- AB838575
- AB838576
- AB838577
- AB838578
- AB838579
- AB838580
- AB838581
- AB838582
- AB838584
- AB838585
- AB838586
- AB838587
- AB838588
- AB838589
- AB062676
- AB838427
- AB838440
- AB838444
- AB838458
- AB838550
- AB838570
- AB838575
- AB838576
- AB838577
- AB838578
- AB838579
- AB838580
- AB838581
- AB838582
- AB838584
- AB838585
- AB838586
- AB838587
- AB838588
- AB838589
- AB062676
- AB838427
- AB838440
- AB838444
- AB838458
- AB838550
- AB838570
- AB838575
- AB838576
- AB838577
- AB838578
- AB838579
- AB838580
- AB838581
- AB838582
- AB838584
- AB838585
- AB838586
- AB838587
- AB838588
- AB838589
- AB062676
- AB838427
- AB838440
- AB838444
- AB838458
- AB838550
- AB838570
- AB838575
- AB838576
- AB838577
- AB838578
- AB838579
- AB838580
- AB838581
- AB838582
- AB838584
- AB838585
- AB838586
- AB838587
- AB838588
- AB838589
- AB062676
- AB838427
- AB838440
- AB838444
- AB838458
- AB838550
- AB838570
- AB838575
- AB838576
- AB838577
- AB838578
- AB838579
- AB838580
- AB838581
- AB838582
- AB838584
- AB838585
- AB838586
- AB838587
- AB838588
- AB838589
- AB062676
- Key message
- In addition, expression of the Hd3a and Rice Flowering-locus T 1 (RFT1) florigen genes was up-regulated in leaves of the Hd1 Ehd1 line at the time of the floral transition
- Knockdown of OsSAMS1, 2 and 3 led to distinguished late flowering and greatly reduced the expression of the flowering key genes, Early heading date 1 (Ehd1), Hd3a and RFT1 (rice FT-like genes)
- RICE FLOWERING LOCUS T 1 (RFT1/FT-L3) is the closest homologue of Heading date 3a (Hd3a), which is thought to encode a mobile flowering signal and promote floral transition under short-day (SD) conditions
- Although RFT1 RNAi plants flowered normally, double RFT1-Hd3a RNAi plants did not flower up to 300 days after sowing (DAS), indicating that Hd3a and RFT1 are essential for flowering in rice
- RFT1 expression was very low in wild-type plants, but there was a marked increase in RFT1 expression by 70 DAS in Hd3a RNAi plants, which flowered 90 DAS
- Hd3a and RFT1 are essential for flowering in rice
- We show here that RICE FLOWERING LOCUS T 1 (RFT1), the closest homolog to Heading date 3a (Hd3a), is a major floral activator under LD conditions
- An RFT1:GFP fusion protein localized in the shoot apical meristem (SAM) under LD conditions, suggesting that RFT1 is a florigen gene in rice
- By regulating Ehd1, RFT1, and Hd3a, Ghd8 delayed flowering under long-day conditions, but promoted flowering under short-day conditions
- To assign the position of Ehd2 within the flowering pathway of rice, we compared transcript levels of previously isolated flowering-time genes, such as Ehd1, a member of the unique pathway, Hd3a, and Rice FT-like1 (RFT1; rice florigens), between the wild-type plants and the ehd2 mutants
- Severely reduced expression of these genes in ehd2 under both short- and long-day conditions suggests that Ehd2 acts as a flowering promoter mainly by up-regulating Ehd1 and by up-regulating the downstream Hd3a and RFT1 genes in the unique genetic network of photoperiodic flowering in rice
- The Early heading date 1 (Ehd1) which promotes the RFT1, was up-regulated by DTH3 in both LD and SD conditions
- A rice ortholog of Arabidopsis APETALA1, OsMADS14, was expressed in the floral meristem in wild-type but not in RFT1 RNAi plants, suggesting that OsMADS14 is activated by RFT1 protein in the SAM after the transition to flowering
- Among these regulators, Ehd1, a rice-specific floral inducer, integrates multiple pathways to regulate RFT1, leading to flowering under appropriate photoperiod conditions
- OsId1 regulates the expression of Ehd1 (Early heading date 1) and its downstream genes, including Hd3a (a rice ortholog of FT) and RFT1 (Rice Flowering Locus T1), under both SD and LD conditions
- This indicates that LHD1 may delay flowering by repressing the expression of Ehd1, Hd3a and RFT1 under long-day conditions
- We also found that LHD1 could down-regulate the expression of several floral transition activators such as Ehd1, Hd3a and RFT1 under long-day conditions, but not under short-day conditions
- Furthermore, SNPs in the regulatory region of RFT1 and the E105K substitution in 1,397 accessions show strong linkage disequilibrium with a flowering time-associated SNP
- These findings indicate that natural mutations in RFT1 provide flowering time divergence under long-day conditions
- These results indicate that Hd3a and RFT1 act as floral activators under SD conditions, and that RFT1 expression is partly regulated by chromatin modification
- This suggests that the divergent functions of paralogs RFT1 and Hd3a, and of MADS50 and MADS51, are in part due to differential H3K36me2/3 deposition, which also correlates with higher expression levels of MADS50 and RFT1 in flowering promotion in rice
- The histone methyltransferase SDG724 mediates H3K36me2/3 deposition at MADS50 and RFT1 and promotes flowering in rice
- Furthermore, mutants in OsMADS50, a rice ortholog of Arabidopsis SUPPRESOR OF OVEREXPRESSION OF CONSTANS 1 (SOC1) did not flower up to 300 days after sowing under LD conditions, indicating that OsMADS50, which acts upstream of RFT1, promotes flowering under LD conditions
- We propose that both positive (OsMADS50 and Ehd1) and negative (Hd1, phyB and Ghd7) regulators of RFT1 form a gene network that regulates LD flowering in rice
- A gene network for long-day flowering activates RFT1 encoding a mobile flowering signal in rice
- Here, we demonstrate that functional defects in the florigen gene RFT1 are the main cause of late flowering in an indica cultivar, Nona Bokra
- Mapping and complementation studies revealed that sequence polymorphisms in the RFT1 regulatory and coding regions are likely to cause late flowering under long-day conditions
- Sequencing of the RFT1 region in rice accessions from a global collection showed that the E105K mutation is found only in indica, and indicated a strong association between the RFT1 haplotype and extremely late flowering in a functional Hd1 background
- The RFT1 (ZS97) allele was shown to delay heading and increase plant height, grain weight, grain number and grain yield, indicating that RFT1 plays an important role in the growth and development of rice
- Connection
- Ehd1, RFT1, Knockdown of SAMS genes encoding S-adenosyl-l-methionine synthetases causes methylation alterations of DNAs and histones and leads to late flowering in rice, Knockdown of OsSAMS1, 2 and 3 led to distinguished late flowering and greatly reduced the expression of the flowering key genes, Early heading date 1 (Ehd1), Hd3a and RFT1 (rice FT-like genes)
- OsSAMS1, RFT1, Knockdown of SAMS genes encoding S-adenosyl-l-methionine synthetases causes methylation alterations of DNAs and histones and leads to late flowering in rice, Knockdown of OsSAMS1, 2 and 3 led to distinguished late flowering and greatly reduced the expression of the flowering key genes, Early heading date 1 (Ehd1), Hd3a and RFT1 (rice FT-like genes)
- Hd3a, RFT1, Knockdown of SAMS genes encoding S-adenosyl-l-methionine synthetases causes methylation alterations of DNAs and histones and leads to late flowering in rice, Knockdown of OsSAMS1, 2 and 3 led to distinguished late flowering and greatly reduced the expression of the flowering key genes, Early heading date 1 (Ehd1), Hd3a and RFT1 (rice FT-like genes)
- Ehd1, RFT1, Heading date gene, dth3 controlled late flowering in O. Glaberrima Steud. by down-regulating Ehd1, The Early heading date 1 (Ehd1) which promotes the RFT1, was up-regulated by DTH3 in both LD and SD conditions
- OsMADS50~OsSOC1~DTH3, RFT1, Heading date gene, dth3 controlled late flowering in O. Glaberrima Steud. by down-regulating Ehd1, The Early heading date 1 (Ehd1) which promotes the RFT1, was up-regulated by DTH3 in both LD and SD conditions
- OsMADS14, RFT1, Hd3a and RFT1 are essential for flowering in rice, In the absence of Hd3a and RFT1 expression, transcription of OsMADS14 and OsMADS15, two rice orthologues of Arabidopsis APETALA1, was strongly reduced, suggesting that they act downstream of Hd3a and RFT1
- OsMADS15~DEP, RFT1, Hd3a and RFT1 are essential for flowering in rice, In the absence of Hd3a and RFT1 expression, transcription of OsMADS14 and OsMADS15, two rice orthologues of Arabidopsis APETALA1, was strongly reduced, suggesting that they act downstream of Hd3a and RFT1
- Hd3a, RFT1, Hd3a and RFT1 are essential for flowering in rice, RICE FLOWERING LOCUS T 1 (RFT1/FT-L3) is the closest homologue of Heading date 3a (Hd3a), which is thought to encode a mobile flowering signal and promote floral transition under short-day (SD) conditions
- Hd3a, RFT1, Hd3a and RFT1 are essential for flowering in rice, Although RFT1 RNAi plants flowered normally, double RFT1-Hd3a RNAi plants did not flower up to 300 days after sowing (DAS), indicating that Hd3a and RFT1 are essential for flowering in rice
- Hd3a, RFT1, Hd3a and RFT1 are essential for flowering in rice, RFT1 expression was very low in wild-type plants, but there was a marked increase in RFT1 expression by 70 DAS in Hd3a RNAi plants, which flowered 90 DAS
- Hd3a, RFT1, Hd3a and RFT1 are essential for flowering in rice, In the absence of Hd3a and RFT1 expression, transcription of OsMADS14 and OsMADS15, two rice orthologues of Arabidopsis APETALA1, was strongly reduced, suggesting that they act downstream of Hd3a and RFT1
- Hd3a, RFT1, Hd3a and RFT1 are essential for flowering in rice, These results indicate that Hd3a and RFT1 act as floral activators under SD conditions, and that RFT1 expression is partly regulated by chromatin modification
- Hd3a, RFT1, Hd3a and RFT1 are essential for flowering in rice, Hd3a and RFT1 are essential for flowering in rice
- Ehd1, RFT1, A gene network for long-day flowering activates RFT1 encoding a mobile flowering signal in rice, We propose that both positive (OsMADS50 and Ehd1) and negative (Hd1, phyB and Ghd7) regulators of RFT1 form a gene network that regulates LD flowering in rice
- Ehd1, RFT1, A gene network for long-day flowering activates RFT1 encoding a mobile flowering signal in rice, Among these regulators, Ehd1, a rice-specific floral inducer, integrates multiple pathways to regulate RFT1, leading to flowering under appropriate photoperiod conditions
- Ghd7, RFT1, A gene network for long-day flowering activates RFT1 encoding a mobile flowering signal in rice, We propose that both positive (OsMADS50 and Ehd1) and negative (Hd1, phyB and Ghd7) regulators of RFT1 form a gene network that regulates LD flowering in rice
- Hd1, RFT1, A gene network for long-day flowering activates RFT1 encoding a mobile flowering signal in rice, We propose that both positive (OsMADS50 and Ehd1) and negative (Hd1, phyB and Ghd7) regulators of RFT1 form a gene network that regulates LD flowering in rice
- PHYB~OsphyB, RFT1, A gene network for long-day flowering activates RFT1 encoding a mobile flowering signal in rice, We propose that both positive (OsMADS50 and Ehd1) and negative (Hd1, phyB and Ghd7) regulators of RFT1 form a gene network that regulates LD flowering in rice
- OsMADS50~OsSOC1~DTH3, RFT1, A gene network for long-day flowering activates RFT1 encoding a mobile flowering signal in rice, Furthermore, mutants in OsMADS50, a rice ortholog of Arabidopsis SUPPRESOR OF OVEREXPRESSION OF CONSTANS 1 (SOC1) did not flower up to 300 days after sowing under LD conditions, indicating that OsMADS50, which acts upstream of RFT1, promotes flowering under LD conditions
- OsMADS50~OsSOC1~DTH3, RFT1, A gene network for long-day flowering activates RFT1 encoding a mobile flowering signal in rice, We propose that both positive (OsMADS50 and Ehd1) and negative (Hd1, phyB and Ghd7) regulators of RFT1 form a gene network that regulates LD flowering in rice
- OsMADS14, RFT1, A gene network for long-day flowering activates RFT1 encoding a mobile flowering signal in rice, A rice ortholog of Arabidopsis APETALA1, OsMADS14, was expressed in the floral meristem in wild-type but not in RFT1 RNAi plants, suggesting that OsMADS14 is activated by RFT1 protein in the SAM after the transition to flowering
- Ehd1, RFT1, OsMADS50 and OsMADS56 function antagonistically in regulating long day LD-dependent flowering in rice, In the osmads50 mutants and 56OX transgenic plants, transcripts of Ehd1, Hd3a and RFT1 were reduced, although that of OsLFL1 increased
- Hd3a, RFT1, OsMADS50 and OsMADS56 function antagonistically in regulating long day LD-dependent flowering in rice, In the osmads50 mutants and 56OX transgenic plants, transcripts of Ehd1, Hd3a and RFT1 were reduced, although that of OsLFL1 increased
- OsLFL1, RFT1, OsMADS50 and OsMADS56 function antagonistically in regulating long day LD-dependent flowering in rice, In the osmads50 mutants and 56OX transgenic plants, transcripts of Ehd1, Hd3a and RFT1 were reduced, although that of OsLFL1 increased
- OsMADS50~OsSOC1~DTH3, RFT1, OsMADS50 and OsMADS56 function antagonistically in regulating long day LD-dependent flowering in rice, In the osmads50 mutants and 56OX transgenic plants, transcripts of Ehd1, Hd3a and RFT1 were reduced, although that of OsLFL1 increased
- Ehd1, RFT1, Rice Indeterminate 1 OsId1 is necessary for the expression of Ehd1 Early heading date 1 regardless of photoperiod, OsId1 regulates the expression of Ehd1 (Early heading date 1) and its downstream genes, including Hd3a (a rice ortholog of FT) and RFT1 (Rice Flowering Locus T1), under both SD and LD conditions
- OsCOL4, RFT1, OsCOL4 is a constitutive flowering repressor upstream of Ehd1 and downstream of OsphyB, Transcripts of Ehd1, Hd3a, and RFT1 were increased in the oscol4 mutants, but reduced in the OsCOL4-D mutants
- Ehd1, RFT1, OsCOL4 is a constitutive flowering repressor upstream of Ehd1 and downstream of OsphyB, Transcripts of Ehd1, Hd3a, and RFT1 were increased in the oscol4 mutants, but reduced in the OsCOL4-D mutants
- Hd3a, RFT1, OsCOL4 is a constitutive flowering repressor upstream of Ehd1 and downstream of OsphyB, Transcripts of Ehd1, Hd3a, and RFT1 were increased in the oscol4 mutants, but reduced in the OsCOL4-D mutants
- Ehd1, RFT1, LHD1, an allele of DTH8/Ghd8, controls late heading date in common wild rice Oryza rufipogon, We also found that LHD1 could down-regulate the expression of several floral transition activators such as Ehd1, Hd3a and RFT1 under long-day conditions, but not under short-day conditions
- Ehd1, RFT1, LHD1, an allele of DTH8/Ghd8, controls late heading date in common wild rice Oryza rufipogon, This indicates that LHD1 may delay flowering by repressing the expression of Ehd1, Hd3a and RFT1 under long-day conditions
- Hd5~DTH8~Ghd8~OsHAP3H~LHD1~EF8~CAR8~OsNF-YB11, RFT1, LHD1, an allele of DTH8/Ghd8, controls late heading date in common wild rice Oryza rufipogon, We also found that LHD1 could down-regulate the expression of several floral transition activators such as Ehd1, Hd3a and RFT1 under long-day conditions, but not under short-day conditions
- Hd5~DTH8~Ghd8~OsHAP3H~LHD1~EF8~CAR8~OsNF-YB11, RFT1, LHD1, an allele of DTH8/Ghd8, controls late heading date in common wild rice Oryza rufipogon, This indicates that LHD1 may delay flowering by repressing the expression of Ehd1, Hd3a and RFT1 under long-day conditions
- Hd3a, RFT1, LHD1, an allele of DTH8/Ghd8, controls late heading date in common wild rice Oryza rufipogon, We also found that LHD1 could down-regulate the expression of several floral transition activators such as Ehd1, Hd3a and RFT1 under long-day conditions, but not under short-day conditions
- Hd3a, RFT1, LHD1, an allele of DTH8/Ghd8, controls late heading date in common wild rice Oryza rufipogon, This indicates that LHD1 may delay flowering by repressing the expression of Ehd1, Hd3a and RFT1 under long-day conditions
- Hd3a, RFT1, Ehd4 encodes a novel and Oryza-genus-specific regulator of photoperiodic flowering in rice, We show that Ehd4 up-regulates the expression of the “florigen” genes Hd3a and RFT1 through Ehd1, but it acts independently of other known Ehd1 regulators
- Ehd4, RFT1, Ehd4 encodes a novel and Oryza-genus-specific regulator of photoperiodic flowering in rice, We show that Ehd4 up-regulates the expression of the “florigen” genes Hd3a and RFT1 through Ehd1, but it acts independently of other known Ehd1 regulators
- Ehd1, RFT1, Ehd4 encodes a novel and Oryza-genus-specific regulator of photoperiodic flowering in rice, We show that Ehd4 up-regulates the expression of the “florigen” genes Hd3a and RFT1 through Ehd1, but it acts independently of other known Ehd1 regulators
- Hd5~DTH8~Ghd8~OsHAP3H~LHD1~EF8~CAR8~OsNF-YB11, RFT1, A major QTL, Ghd8, plays pleiotropic roles in regulating grain productivity, plant height, and heading date in rice, By regulating Ehd1, RFT1, and Hd3a, Ghd8 delayed flowering under long-day conditions, but promoted flowering under short-day conditions
- Ehd1, RFT1, A major QTL, Ghd8, plays pleiotropic roles in regulating grain productivity, plant height, and heading date in rice, By regulating Ehd1, RFT1, and Hd3a, Ghd8 delayed flowering under long-day conditions, but promoted flowering under short-day conditions
- Hd3a, RFT1, A major QTL, Ghd8, plays pleiotropic roles in regulating grain productivity, plant height, and heading date in rice, By regulating Ehd1, RFT1, and Hd3a, Ghd8 delayed flowering under long-day conditions, but promoted flowering under short-day conditions
- Hd3a, RFT1, The histone methyltransferase SDG724 mediates H3K36me2/3 deposition at MADS50 and RFT1 and promotes flowering in rice, This suggests that the divergent functions of paralogs RFT1 and Hd3a, and of MADS50 and MADS51, are in part due to differential H3K36me2/3 deposition, which also correlates with higher expression levels of MADS50 and RFT1 in flowering promotion in rice
- OsMADS50~OsSOC1~DTH3, RFT1, The histone methyltransferase SDG724 mediates H3K36me2/3 deposition at MADS50 and RFT1 and promotes flowering in rice, Chromatin immunoprecipitation assays showed that lvp1 had reduced levels of H3K36me2/3 at MADS50 and RFT1
- OsMADS50~OsSOC1~DTH3, RFT1, The histone methyltransferase SDG724 mediates H3K36me2/3 deposition at MADS50 and RFT1 and promotes flowering in rice, This suggests that the divergent functions of paralogs RFT1 and Hd3a, and of MADS50 and MADS51, are in part due to differential H3K36me2/3 deposition, which also correlates with higher expression levels of MADS50 and RFT1 in flowering promotion in rice
- OsMADS50~OsSOC1~DTH3, RFT1, The histone methyltransferase SDG724 mediates H3K36me2/3 deposition at MADS50 and RFT1 and promotes flowering in rice, The histone methyltransferase SDG724 mediates H3K36me2/3 deposition at MADS50 and RFT1 and promotes flowering in rice
- OsMADS51~OsMADS65, RFT1, The histone methyltransferase SDG724 mediates H3K36me2/3 deposition at MADS50 and RFT1 and promotes flowering in rice, This suggests that the divergent functions of paralogs RFT1 and Hd3a, and of MADS50 and MADS51, are in part due to differential H3K36me2/3 deposition, which also correlates with higher expression levels of MADS50 and RFT1 in flowering promotion in rice
- RFT1, SDG724~lvp1, The histone methyltransferase SDG724 mediates H3K36me2/3 deposition at MADS50 and RFT1 and promotes flowering in rice, Chromatin immunoprecipitation assays showed that lvp1 had reduced levels of H3K36me2/3 at MADS50 and RFT1
- RFT1, SDG724~lvp1, The histone methyltransferase SDG724 mediates H3K36me2/3 deposition at MADS50 and RFT1 and promotes flowering in rice, The histone methyltransferase SDG724 mediates H3K36me2/3 deposition at MADS50 and RFT1 and promotes flowering in rice
- Ehd1, RFT1, Flowering time genes Heading date 1 and Early heading date 1 together control panicle development in rice, In addition, expression of the Hd3a and Rice Flowering-locus T 1 (RFT1) florigen genes was up-regulated in leaves of the Hd1 Ehd1 line at the time of the floral transition
- Hd1, RFT1, Flowering time genes Heading date 1 and Early heading date 1 together control panicle development in rice, In addition, expression of the Hd3a and Rice Flowering-locus T 1 (RFT1) florigen genes was up-regulated in leaves of the Hd1 Ehd1 line at the time of the floral transition
- Hd3a, RFT1, Flowering time genes Heading date 1 and Early heading date 1 together control panicle development in rice, In addition, expression of the Hd3a and Rice Flowering-locus T 1 (RFT1) florigen genes was up-regulated in leaves of the Hd1 Ehd1 line at the time of the floral transition
- Ehd1, RFT1, Ehd2, a rice ortholog of the maize INDETERMINATE1 gene, promotes flowering by up-regulating Ehd1, To assign the position of Ehd2 within the flowering pathway of rice, we compared transcript levels of previously isolated flowering-time genes, such as Ehd1, a member of the unique pathway, Hd3a, and Rice FT-like1 (RFT1; rice florigens), between the wild-type plants and the ehd2 mutants
- Ehd1, RFT1, Ehd2, a rice ortholog of the maize INDETERMINATE1 gene, promotes flowering by up-regulating Ehd1, Severely reduced expression of these genes in ehd2 under both short- and long-day conditions suggests that Ehd2 acts as a flowering promoter mainly by up-regulating Ehd1 and by up-regulating the downstream Hd3a and RFT1 genes in the unique genetic network of photoperiodic flowering in rice
- Hd3a, RFT1, Ehd2, a rice ortholog of the maize INDETERMINATE1 gene, promotes flowering by up-regulating Ehd1, To assign the position of Ehd2 within the flowering pathway of rice, we compared transcript levels of previously isolated flowering-time genes, such as Ehd1, a member of the unique pathway, Hd3a, and Rice FT-like1 (RFT1; rice florigens), between the wild-type plants and the ehd2 mutants
- Hd3a, RFT1, Ehd2, a rice ortholog of the maize INDETERMINATE1 gene, promotes flowering by up-regulating Ehd1, Severely reduced expression of these genes in ehd2 under both short- and long-day conditions suggests that Ehd2 acts as a flowering promoter mainly by up-regulating Ehd1 and by up-regulating the downstream Hd3a and RFT1 genes in the unique genetic network of photoperiodic flowering in rice
- Ehd2~RID1, RFT1, Ehd2, a rice ortholog of the maize INDETERMINATE1 gene, promotes flowering by up-regulating Ehd1, To assign the position of Ehd2 within the flowering pathway of rice, we compared transcript levels of previously isolated flowering-time genes, such as Ehd1, a member of the unique pathway, Hd3a, and Rice FT-like1 (RFT1; rice florigens), between the wild-type plants and the ehd2 mutants
- Ehd2~RID1, RFT1, Ehd2, a rice ortholog of the maize INDETERMINATE1 gene, promotes flowering by up-regulating Ehd1, Severely reduced expression of these genes in ehd2 under both short- and long-day conditions suggests that Ehd2 acts as a flowering promoter mainly by up-regulating Ehd1 and by up-regulating the downstream Hd3a and RFT1 genes in the unique genetic network of photoperiodic flowering in rice
- Ehd1, RFT1, OsVIL2 functions with PRC2 to induce flowering by repressing OsLFL1 in rice, In osvil2 mutants OsLFL1 expression was increased, but that of Ehd1, Hd3a and RFT1 was reduced
- Hd3a, RFT1, OsVIL2 functions with PRC2 to induce flowering by repressing OsLFL1 in rice, In osvil2 mutants OsLFL1 expression was increased, but that of Ehd1, Hd3a and RFT1 was reduced
- OsLFL1, RFT1, OsVIL2 functions with PRC2 to induce flowering by repressing OsLFL1 in rice, In osvil2 mutants OsLFL1 expression was increased, but that of Ehd1, Hd3a and RFT1 was reduced
- OsVIL2, RFT1, OsVIL2 functions with PRC2 to induce flowering by repressing OsLFL1 in rice, In osvil2 mutants OsLFL1 expression was increased, but that of Ehd1, Hd3a and RFT1 was reduced
- Ehd1, RFT1, Hd16, a gene for casein kinase I, is involved in the control of rice flowering time by modulating the day-length response, In a near-isogenic line with the weak-photoperiod-sensitivity allele of Hd16, transcription levels of Ehd1, Hd3a, and RFT1 increased under long-day conditions, and transcription levels of Hd3a and RFT1 decreased under short-day conditions
- CKI~EL1~Hd16, RFT1, Hd16, a gene for casein kinase I, is involved in the control of rice flowering time by modulating the day-length response, In a near-isogenic line with the weak-photoperiod-sensitivity allele of Hd16, transcription levels of Ehd1, Hd3a, and RFT1 increased under long-day conditions, and transcription levels of Hd3a and RFT1 decreased under short-day conditions
- Hd3a, RFT1, Hd16, a gene for casein kinase I, is involved in the control of rice flowering time by modulating the day-length response, In a near-isogenic line with the weak-photoperiod-sensitivity allele of Hd16, transcription levels of Ehd1, Hd3a, and RFT1 increased under long-day conditions, and transcription levels of Hd3a and RFT1 decreased under short-day conditions
- Ghd7.1~Hd2~OsPRR37~DTH7, RFT1, Days to heading 7, a major quantitative locus determining photoperiod sensitivity and regional adaptation in rice., We show that in long days DTH7 acts downstream of the photoreceptor phytochrome B to repress the expression of Ehd1, an up-regulator of the "florigen" genes (Hd3a and RFT1), leading to delayed flowering
- Hd5~DTH8~Ghd8~OsHAP3H~LHD1~EF8~CAR8~OsNF-YB11, RFT1, EF8 is involved in photoperiodic flowering pathway and chlorophyll biogenesis in rice., Our data showed that EF8 delayed flowering time under long-day conditions by altering the rhythmic expression patterns of ‘florigen’ genes Hd3a and RFT1
- OsCCT01, RFT1, Three CCT domain-containing genes were identified to regulate heading date by candidate gene-based association mapping and transformation in rice., The overexpression of OsCCT01 delayed flowering through suppressing the expression of Ehd1, Hd3a and RFT1 under both long day and short day conditions
- MRG702, RFT1, MRG702, a reader protein of H3K4me3 and H3K36me3, is involved in brassinosteroid-regulated growth and flowering time control in rice., Gene transcription analyses showed that MRG702 knock-down resulted in the down-regulation of BR-related genes, including D11, BRI1, and BU1, and several flowering genes including Ehd1, Ehd2/OsID1/RID1, Ehd3,OsMADS50, Hd3a, and RFT1
- Ehd1, RFT1, Genetic interactions between diverged alleles of Early heading date 1 Ehd1 and Heading date 3a Hd3a/ RICE FLOWERING LOCUS T1 RFT1 control differential heading and contribute to regional adaptation in rice Oryza sativa., Genetic interactions between diverged alleles of Early heading date 1 (Ehd1) and Heading date 3a (Hd3a)/ RICE FLOWERING LOCUS T1 (RFT1) control differential heading and contribute to regional adaptation in rice (Oryza sativa).
- Ehd1, RFT1, Genetic interactions between diverged alleles of Early heading date 1 Ehd1 and Heading date 3a Hd3a/ RICE FLOWERING LOCUS T1 RFT1 control differential heading and contribute to regional adaptation in rice Oryza sativa., Early heading date 1 (Ehd1) regulates Hd3a and RFT1
- Ehd1, RFT1, Genetic interactions between diverged alleles of Early heading date 1 Ehd1 and Heading date 3a Hd3a/ RICE FLOWERING LOCUS T1 RFT1 control differential heading and contribute to regional adaptation in rice Oryza sativa., We demonstrated that, in an ehd1 mutant background, Hd3a was silenced, but RFT1 was expressed (although at lower levels than in plants with a functional Ehd1) under short-day (SD) and long-day (LD) conditions
- Ehd1, RFT1, Genetic interactions between diverged alleles of Early heading date 1 Ehd1 and Heading date 3a Hd3a/ RICE FLOWERING LOCUS T1 RFT1 control differential heading and contribute to regional adaptation in rice Oryza sativa., We identified a nonfunctional RFT1 allele (rft1); the lines carrying homozygous ehd1 and Hd3a/rft1 failed to induce the floral transition under SD and LD conditions
- RFT1, SDG708, SET DOMAIN GROUP 708, a histone H3 lysine 36-specific methyltransferase, controls flowering time in rice Oryza sativa, Compared with the wild-type, SDG708-knockdown rice mutants displayed a late-flowering phenotype under both long-day and short-day conditions because of the down-regulation of the key flowering regulatory genes Heading date 3a (Hd3a), RICE FLOWERING LOCUS T1 (RFT1), and Early heading date 1 (Ehd1).
- OsCOL10, RFT1, OsCOL10, a CONSTANS-like gene, functions as a flowering-time repressor downstream of Ghd7 in rice., Further studies show that OsCOL10 represses the expression of the FT-like genes RFT1 and Hd3a through Ehd1
- HDR1, RFT1, The Oryza sativa Regulator HDR1 Associates with the Kinase OsK4 to Control Photoperiodic Flowering., We determined that HDR1 is a novel suppressor of flowering that upregulates Hd1 and downregulates Ehd1, leading to the downregulation of Hd3a and RFT1 under LDs
- Hd3a, RFT1, Hd3a, RFT1 and Ehd1 integrate photoperiodic and drought stress signals to delay the floral transition in rice., Hd3a, RFT1 and Ehd1 integrate photoperiodic and drought stress signals to delay the floral transition in rice.
- Hd3a, RFT1, Hd3a, RFT1 and Ehd1 integrate photoperiodic and drought stress signals to delay the floral transition in rice., Exposure to drought stress under floral-inductive photoperiods strongly reduced transcription of EARLY HEADING DATE 1 (Ehd1), HEADING DATE 3a (Hd3a) and RICE FLOWERING LOCUS T 1 (RFT1), primary integrators of day length signals, providing a molecular connection between stress and the photoperiodic pathway
- RFT1, Se14, Se14, encoding a JmjC domain-containing protein, plays key roles in long-day suppression of rice flowering through the demethylation of H3K4me3 of RFT1., Se14, encoding a JmjC domain-containing protein, plays key roles in long-day suppression of rice flowering through the demethylation of H3K4me3 of RFT1.
- RFT1, Se14, Se14, encoding a JmjC domain-containing protein, plays key roles in long-day suppression of rice flowering through the demethylation of H3K4me3 of RFT1., We conclude that Se14 is a novel photoperiod-sensitivity gene that has a suppressive effect on floral transition (flowering time) under long day-length conditions through the modification of chromatin structure by H3K4me3 demethylation in the promoter region of RFT1
- Hd18, RFT1, Hd18, encoding histone acetylase related to Arabidopsis FLOWERING LOCUS D, is involved in the control of flowering time in rice., Compared with those in Koshihikari, the expression levels of the flowering-time genes Early heading date 1 (Ehd1), Heading date 3a (Hd3a), and Rice flowering locus T1 (RFT1) were lower in a near-isogenic line with the Hayamasari Hd18 allele in a Koshihikari genetic background
- OsCOL13, RFT1, A CONSTANS-like transcriptional activator, OsCOL13, functions as a negative regulator of flowering downstream of OsphyB and upstream of Ehd1 in rice., OsCOL13 suppresses the florigen genes Hd3a and RFT1 by repressing Ehd1, but has no relationship with other known Ehd1 regulators as determined by using mutants or near isogenic lines
- OsHAPL1, RFT1, The OsHAPL1-DTH8-Hd1 complex functions as the transcription regulator to repress heading date in rice., Further studies showed that OsHAPL1 represses the expression of the florigen genes and FLOWERING LOCUS T 1 (RFT1) and Hd3a through Early heading date 1 (Ehd1)
- OsHAPL1, RFT1, The OsHAPL1-DTH8-Hd1 complex functions as the transcription regulator to repress heading date in rice., We propose that OsHAPL1 functions as a transcriptional regulator and, together with DTH8, Hd1, the HAP complex, and general transcription factors, regulates the expression of target genes and then affects heading date by influencing the expression of Hd3a and RFT1 through Ehd1
- OsCOL10, RFT1, Flowering time regulation by the CONSTANS-Like gene OsCOL10., Through transgenic analysis, we have showed that OsCOL10 repress flowering by reducing expression of the FT-like genes RFT1 and Hd3a through Ehd1
- RFT1, SID1~OsIDD4, Suppressor of rid1 SID1 shares common targets with RID1 on florigen genes to initiate floral transition in rice., Further analyses showed SID1 and RID1 directly target the promoter regions of Hd3a and RFT1, two florigen genes in rice
- OsFTIP1, RFT1, OsFTIP1-Mediated Regulation of Florigen Transport in Rice Is Negatively Regulated by a Ubiquitin-like Domain Kinase OsUbDKÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂó4., Here we show that rice FT-INTERACTING PROTEIN 1 (OsFTIP1), a member of the family of multiple C2 domain and transmembrane region proteins (MCTPs) and the closest ortholog of Arabidopsis FTIP1, is required for export of RICE FLOWERING LOCUS T 1 (RFT1) from companion cells to sieve elements
- OsFTIP1, RFT1, OsFTIP1-Mediated Regulation of Florigen Transport in Rice Is Negatively Regulated by a Ubiquitin-like Domain Kinase OsUbDKÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂó4., We further reveal that a ubiquitin-like domain kinase ÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂó4, OsUbDKÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂó4, interacts with OsFTIP1, and modulates its degradation in leaves through the 26S proteasome, which in turn affects RFT1 transport to the SAM
- OsFTIP1, RFT1, OsFTIP1-Mediated Regulation of Florigen Transport in Rice Is Negatively Regulated by a Ubiquitin-like Domain Kinase OsUbDKÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂó4., Thus, dynamic modulation of OsFTIP1 abundance in leaves by a negative regulator OsUbDKÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂó4 is integral to the role of OsFTIP1 in mediating RFT1 transport in rice, and provide key evidence for a conserved role of FTIP1-like MCTPs in mediating florigen transport in flowering plants
- PLA3~OsLBD3-7~OsLBD37, RFT1, OsLBD37 and OsLBD38, two class II type LBD proteins, are involved in the regulation of heading date by controlling the expression of Ehd1 in rice., Further analysis revealed that OsLBD37 and OsLBD38 delayed heading date by down-regulating the expression of the florigen genes Hd3a and RFT1 through key regulator of heading date Ehd1
- OsLBD38, RFT1, OsLBD37 and OsLBD38, two class II type LBD proteins, are involved in the regulation of heading date by controlling the expression of Ehd1 in rice., Further analysis revealed that OsLBD37 and OsLBD38 delayed heading date by down-regulating the expression of the florigen genes Hd3a and RFT1 through key regulator of heading date Ehd1
- OsMADS7~OsMADS45, RFT1, Ectopic expression of OsMADS45 activates the upstream genes Hd3a and RFT1 at an early development stage causing early flowering in rice., Ectopic expression of OsMADS45 activates the upstream genes Hd3a and RFT1 at an early development stage causing early flowering in rice.
- OsMADS7~OsMADS45, RFT1, Ectopic expression of OsMADS45 activates the upstream genes Hd3a and RFT1 at an early development stage causing early flowering in rice., OsMADS45 overexpression did not alter the oscillating rhythm of the examined floral regulatory genes but advanced (by approximately 20 days) the up-regulate of two florigens, Hd3a (Heading Date 3a) and RFT1 (RICE FLOWERING LOCUS T1) and suppressed the expression of Hd1 at the juvenile stage
- OsMADS7~OsMADS45, RFT1, Ectopic expression of OsMADS45 activates the upstream genes Hd3a and RFT1 at an early development stage causing early flowering in rice., These results indicate that in transgenic rice, OsMADS45 overexpressing ectopically activates the upstream genes Hd3a and RFT1 at early development stage and up-regulates the expression of OsMADS14 and OsMADS18, which induces early flowering
- RFT1, SDG701, SET DOMAIN GROUP701 encodes a H3K4-methytransferase and regulates multiple key processes of rice plant development., Consistently, the SDG701 protein was found to bind chromatin to promote H3K4me3 and to enhance expression of the rice Hd3a and RFT1 florigens
- OsCOL16, RFT1, OsCOL16, encoding a CONSTANS-like protein, represses flowering by up-regulating Ghd7 expression in rice., We determined that OsCOL16 up-regulates the expression of the floral repressor Ghd7, leading to down-regulation of the expression of Ehd1, Hd3a, and RFT1
- HBF1, RFT1, Antagonistic Transcription Factor Complexes Modulate the Floral Transition in Rice., However, additional bZIPs, including Hd3a BINDING REPRESSOR FACTOR 1 (HBF1) and HBF2 form repressor complexes that reduce Hd3a and RFT1 expression to delay flowering
- HBF2, RFT1, Antagonistic Transcription Factor Complexes Modulate the Floral Transition in Rice., However, additional bZIPs, including Hd3a BINDING REPRESSOR FACTOR 1 (HBF1) and HBF2 form repressor complexes that reduce Hd3a and RFT1 expression to delay flowering
Prev Next