- Information
- Symbol: RH2
- MSU: LOC_Os01g32460
- RAPdb: Os01g0508500
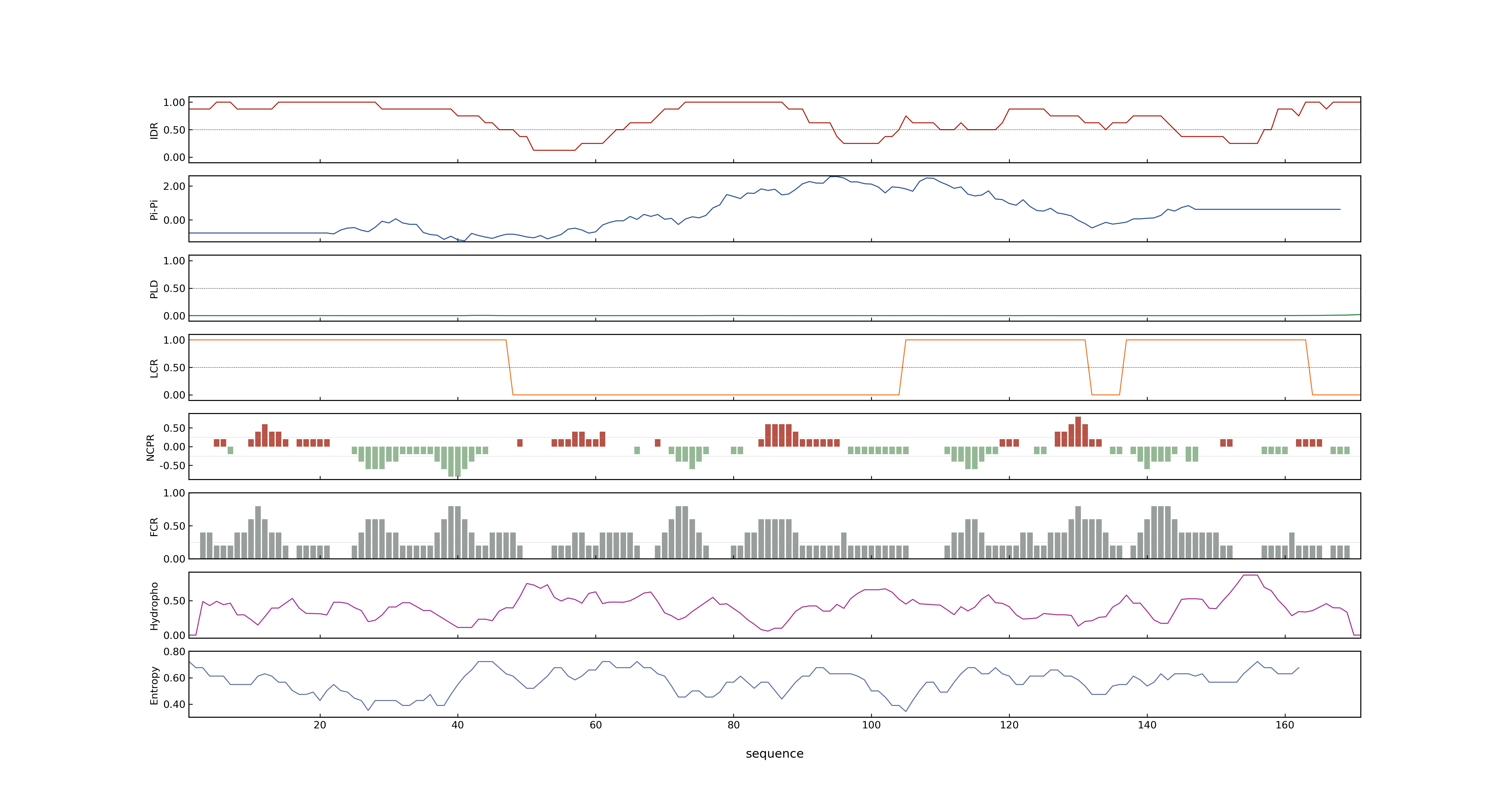
- PSP score
- LOC_Os01g32460.1: 0.1265
- PLAAC score
- LOC_Os01g32460.1: 0
- pLDDT score
- 62.78
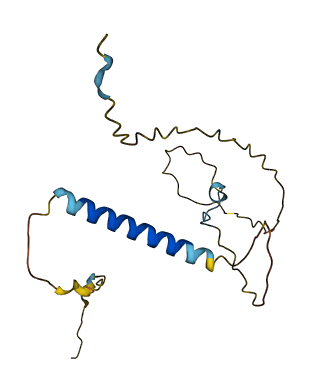
- Protein Structure from AlphaFold and UniProt
- MolPhase score
- LOC_Os01g32460.1: 0.98506146
- MolPhase Result
- Publication
-
Genbank accession number
-
Key message
- Connection
- RH1, RH2, A rice transient assay system identifies a novel domain in NRR required for interaction with NH1/OsNPR1 and inhibition of NH1-mediated transcriptional activation, We identified three NRR homologues (RH1, RH2, and RH3)
- RH1, RH2, A rice transient assay system identifies a novel domain in NRR required for interaction with NH1/OsNPR1 and inhibition of NH1-mediated transcriptional activation, RH1 and RH3, but not RH2, also effectively repress NH1-mediated transcriptional activation
- RH1, RH2, A rice transient assay system identifies a novel domain in NRR required for interaction with NH1/OsNPR1 and inhibition of NH1-mediated transcriptional activation, NRR, RH1, RH2, and RH3 share sequence similarity in a region beyond the previously identified NPR1-interacting domain
- RH1, RH2, A rice transient assay system identifies a novel domain in NRR required for interaction with NH1/OsNPR1 and inhibition of NH1-mediated transcriptional activation, RH2 carries a deviation (amino acids AV) in this region as compared to consensus sequences (amino acids ED) among NRR, RH1, and RH3
- OsNPR1~NH1, RH2, A rice transient assay system identifies a novel domain in NRR required for interaction with NH1/OsNPR1 and inhibition of NH1-mediated transcriptional activation, RH1 and RH3, but not RH2, also effectively repress NH1-mediated transcriptional activation
- OsNPR1~NH1, RH2, A rice transient assay system identifies a novel domain in NRR required for interaction with NH1/OsNPR1 and inhibition of NH1-mediated transcriptional activation, A substitution (AV to ED) in RH2 results in strong binding of mutant RH2ED to NH1 and effective repression of NH1-mediated activation
- OsNPR1~NH1, RH2, A rice transient assay system identifies a novel domain in NRR required for interaction with NH1/OsNPR1 and inhibition of NH1-mediated transcriptional activation, NRR, RH1, RH2, and RH3 share sequence similarity in a region beyond the previously identified NPR1-interacting domain
- RH2, RH3, A rice transient assay system identifies a novel domain in NRR required for interaction with NH1/OsNPR1 and inhibition of NH1-mediated transcriptional activation, We identified three NRR homologues (RH1, RH2, and RH3)
- RH2, RH3, A rice transient assay system identifies a novel domain in NRR required for interaction with NH1/OsNPR1 and inhibition of NH1-mediated transcriptional activation, RH1 and RH3, but not RH2, also effectively repress NH1-mediated transcriptional activation
- RH2, RH3, A rice transient assay system identifies a novel domain in NRR required for interaction with NH1/OsNPR1 and inhibition of NH1-mediated transcriptional activation, NRR, RH1, RH2, and RH3 share sequence similarity in a region beyond the previously identified NPR1-interacting domain
- RH2, RH3, A rice transient assay system identifies a novel domain in NRR required for interaction with NH1/OsNPR1 and inhibition of NH1-mediated transcriptional activation, RH2 carries a deviation (amino acids AV) in this region as compared to consensus sequences (amino acids ED) among NRR, RH1, and RH3
- NRR~CRCT, RH2, A rice transient assay system identifies a novel domain in NRR required for interaction with NH1/OsNPR1 and inhibition of NH1-mediated transcriptional activation, We identified three NRR homologues (RH1, RH2, and RH3)
- NRR~CRCT, RH2, A rice transient assay system identifies a novel domain in NRR required for interaction with NH1/OsNPR1 and inhibition of NH1-mediated transcriptional activation, NRR, RH1, RH2, and RH3 share sequence similarity in a region beyond the previously identified NPR1-interacting domain
- NRR~CRCT, RH2, A rice transient assay system identifies a novel domain in NRR required for interaction with NH1/OsNPR1 and inhibition of NH1-mediated transcriptional activation, RH2 carries a deviation (amino acids AV) in this region as compared to consensus sequences (amino acids ED) among NRR, RH1, and RH3
Prev Next