- Information
- Symbol: RNRL1,V3
- MSU: LOC_Os06g07210
- RAPdb: Os06g0168600
- PSP score
- LOC_Os06g07210.1: 0.1181
- PLAAC score
- LOC_Os06g07210.1: 0
- pLDDT score
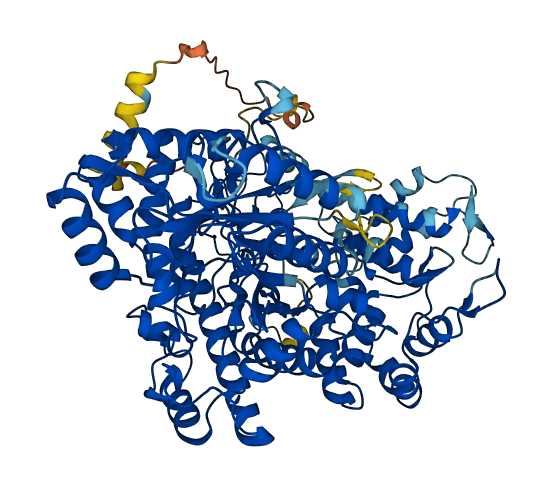
- 91.12
- Protein Structure from AlphaFold and UniProt
- MolPhase score
- LOC_Os06g07210.1: 0.92010444
- MolPhase Result
- Publication
- Genbank accession number
- Key message
- The virescent3 (v3) and stripe1 (st1) mutants in rice (Oryza sativa) produce chlorotic leaves in a growth stage-dependent manner under field conditions
- Moreover, wild-type plants exposed to a low concentration of an RNR inhibitor, hydroxyurea, produce chlorotic leaves without growth retardation, reminiscent of v3 and st1 mutants
- RNRL1 and RNRS1 are highly expressed in the shoot base and in young leaves, and the expression of the genes that function in plastid transcription/translation and in photosynthesis is altered in v3 and st1 mutants, indicating that a threshold activity of RNR is required for chloroplast biogenesis in developing leaves
- Connection
- RNRL1~V3, RNRL2, Rice virescent3 and stripe1 encoding the large and small subunits of ribonucleotide reductase are required for chloroplast biogenesis during early leaf development, In yeast, RNRL1 interacts with RNRS1 (RNRL1:RNRS1) and RNRL2:RNRS2, but no interaction occurs between other combinations of the large and small subunits
- RNRL1~V3, RNRS1~St1~SDL, Rice virescent3 and stripe1 encoding the large and small subunits of ribonucleotide reductase are required for chloroplast biogenesis during early leaf development, Here, we show V3 and St1, which encode the large and small subunits of ribonucleotide reductase (RNR), RNRL1, and RNRS1, respectively
- RNRL1~V3, RNRS1~St1~SDL, Rice virescent3 and stripe1 encoding the large and small subunits of ribonucleotide reductase are required for chloroplast biogenesis during early leaf development, RNRL1 and RNRS1 are highly expressed in the shoot base and in young leaves, and the expression of the genes that function in plastid transcription/translation and in photosynthesis is altered in v3 and st1 mutants, indicating that a threshold activity of RNR is required for chloroplast biogenesis in developing leaves
- RNRL1~V3, RNRS1~St1~SDL, Rice virescent3 and stripe1 encoding the large and small subunits of ribonucleotide reductase are required for chloroplast biogenesis during early leaf development, In yeast, RNRL1 interacts with RNRS1 (RNRL1:RNRS1) and RNRL2:RNRS2, but no interaction occurs between other combinations of the large and small subunits
- RNRL1~V3, RNRS1~St1~SDL, Rice virescent3 and stripe1 encoding the large and small subunits of ribonucleotide reductase are required for chloroplast biogenesis during early leaf development, The interacting activities are RNRL1:RNRS1 > RNRL1:rnrs1(st1) > rnrl1(v3):RNRS1 > rnrl1(v3):rnrs1(st1), which correlate with the degree of chlorosis for each genotype
- RNRL1~V3, RNRS1~St1~SDL, Rice virescent3 and stripe1 encoding the large and small subunits of ribonucleotide reductase are required for chloroplast biogenesis during early leaf development, This suggests that missense mutations in rnrl1(v3) and rnrs1(st1) attenuate the first alphabeta dimerization
- RNRL1~V3, RNRS1~St1~SDL, Rice virescent3 and stripe1 encoding the large and small subunits of ribonucleotide reductase are required for chloroplast biogenesis during early leaf development, The virescent3 (v3) and stripe1 (st1) mutants in rice (Oryza sativa) produce chlorotic leaves in a growth stage-dependent manner under field conditions
- RNRL1~V3, RNRS1~St1~SDL, Rice virescent3 and stripe1 encoding the large and small subunits of ribonucleotide reductase are required for chloroplast biogenesis during early leaf development, Moreover, wild-type plants exposed to a low concentration of an RNR inhibitor, hydroxyurea, produce chlorotic leaves without growth retardation, reminiscent of v3 and st1 mutants
- RNRL1~V3, RNRS2, Rice virescent3 and stripe1 encoding the large and small subunits of ribonucleotide reductase are required for chloroplast biogenesis during early leaf development, In yeast, RNRL1 interacts with RNRS1 (RNRL1:RNRS1) and RNRL2:RNRS2, but no interaction occurs between other combinations of the large and small subunits
Prev Next