- Information
- Symbol: SDG725
- MSU: LOC_Os02g34850
- RAPdb: Os02g0554000
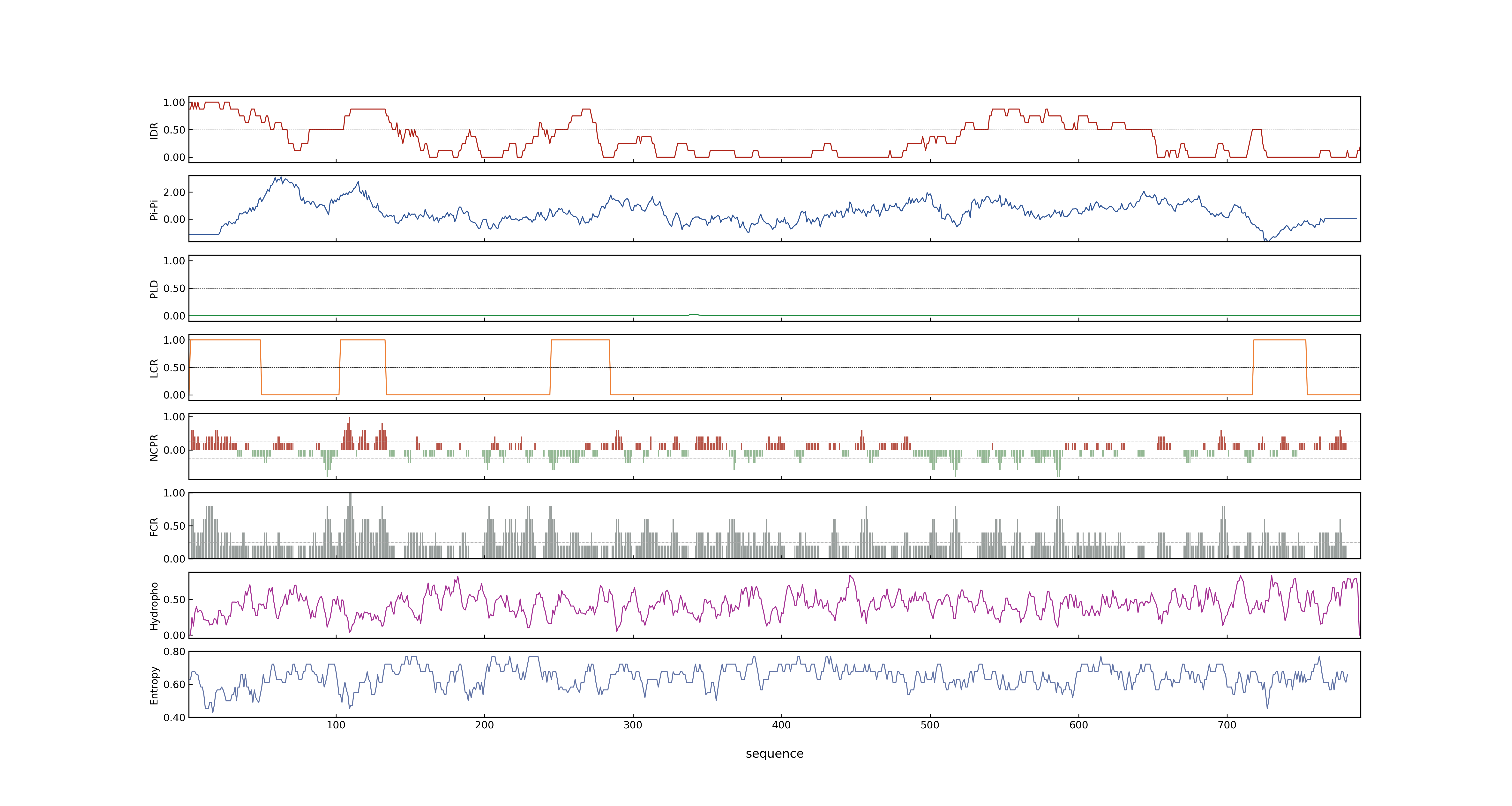
- PSP score
- LOC_Os02g34850.1: 0.9805
- PLAAC score
- LOC_Os02g34850.1: 0
- pLDDT score
- 34.6
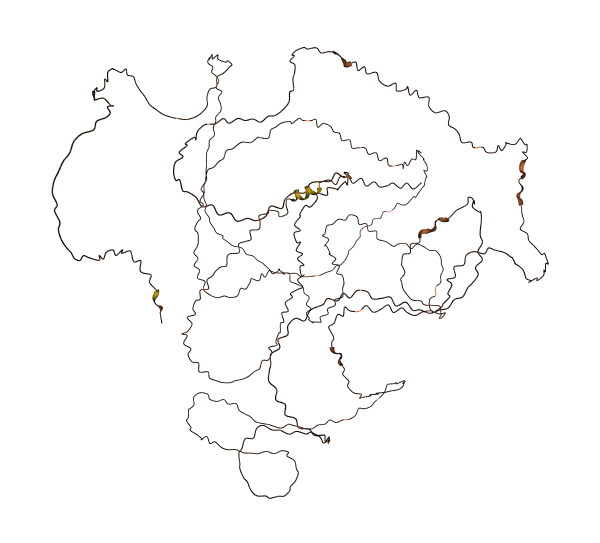
- Protein Structure from AlphaFold and UniProt
- MolPhase score
- LOC_Os02g34850.1: 0.99940693
- MolPhase Result
- Publication
- Genbank accession number
- Key message
- Here, we report that rice SDG725 encodes a H3K36 methyltransferase, and its down-regulation causes wide-ranging defects, including dwarfism, shortened internodes, erect leaves and small seeds
- Taken together, our data indicate that SDG725-mediated H3K36 methylation modulates brassinosteroid-related gene expression, playing an important role in rice plant growth and development
- Consistently, transcriptome analyses revealed that SDG725 depletion results in down-regulation by more than two-fold of over 1000 genes, including D11, BRI1 and BU1, which are known to be involved in brassinosteroid biosynthesis or signaling pathways
- Chromatin immunoprecipitation analyses showed that levels of H3K36me2/3 are reduced in chromatin at some regions of these brassinosteroid-related genes in SDG725 knockdown plants, and that SDG725 protein is able to directly bind to these target genes
- Connection
- BU1, SDG725, H3K36 methylation is critical for brassinosteroid-regulated plant growth and development in rice, Consistently, transcriptome analyses revealed that SDG725 depletion results in down-regulation by more than two-fold of over 1000 genes, including D11, BRI1 and BU1, which are known to be involved in brassinosteroid biosynthesis or signaling pathways
- D11~CPB1~CYP724B1~GNS4, SDG725, H3K36 methylation is critical for brassinosteroid-regulated plant growth and development in rice, Consistently, transcriptome analyses revealed that SDG725 depletion results in down-regulation by more than two-fold of over 1000 genes, including D11, BRI1 and BU1, which are known to be involved in brassinosteroid biosynthesis or signaling pathways
- D61~OsBRI1, SDG725, H3K36 methylation is critical for brassinosteroid-regulated plant growth and development in rice, Consistently, transcriptome analyses revealed that SDG725 depletion results in down-regulation by more than two-fold of over 1000 genes, including D11, BRI1 and BU1, which are known to be involved in brassinosteroid biosynthesis or signaling pathways
- MRG702, SDG725, MRG702, a reader protein of H3K4me3 and H3K36me3, is involved in brassinosteroid-regulated growth and flowering time control in rice., Similar to the loss-of-function mutants of the rice H3K36 methyltransferase gene SDG725, the MRG702 knock-down mutants displayed typical BR-deficient mutant and late-flowering phenotypes
- MRG702, SDG725, MRG702, a reader protein of H3K4me3 and H3K36me3, is involved in brassinosteroid-regulated growth and flowering time control in rice., Together, our results demonstrate that MRG702 acts as a reader protein of H3K4me3 and H3K36me3 and deciphers the H3K36 methylation information set by SDG725
Prev Next