- Information
- Symbol: Sdr4
- MSU: LOC_Os07g39700
- RAPdb: Os07g0585700
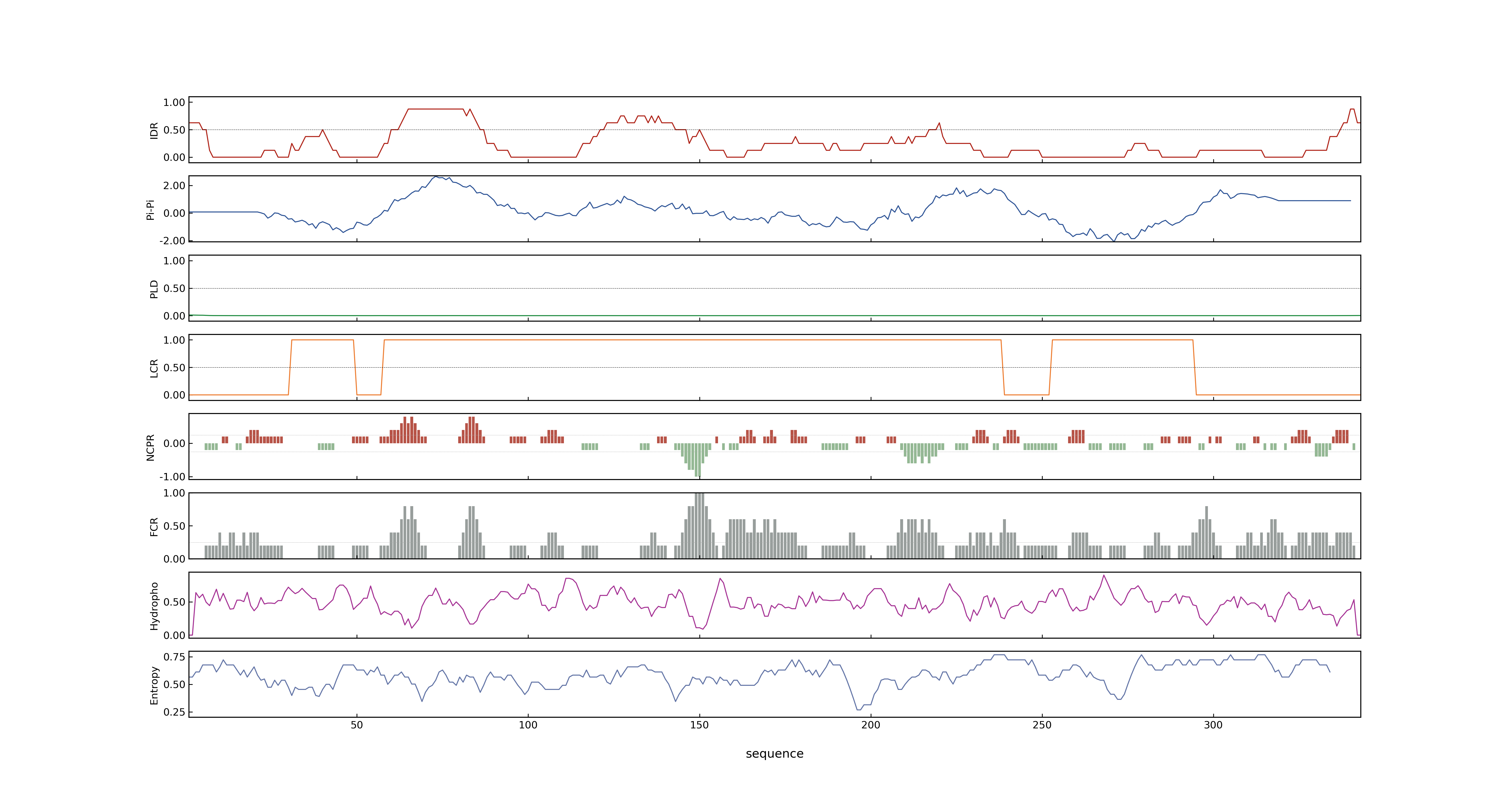
- PSP score
- LOC_Os07g39700.1: 0.6419
- PLAAC score
- LOC_Os07g39700.1: 0
- pLDDT score
- 62.24
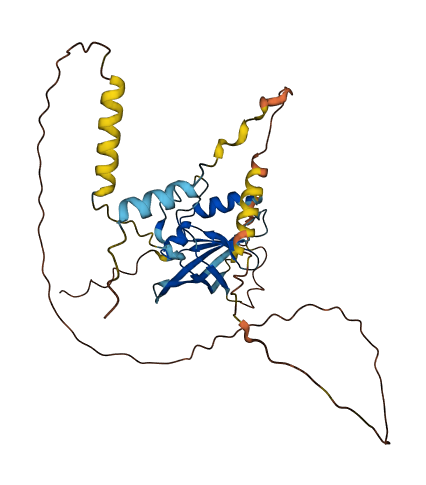
- Protein Structure from AlphaFold and UniProt
- MolPhase score
- LOC_Os07g39700.1: 0.99533230
- MolPhase Result
- Publication
- Molecular cloning of Sdr4, a regulator involved in seed dormancy and domestication of rice, 2010, Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A.
- Genbank accession number
- Key message
- We cloned a rice quantitative trait locus, Sdr4, which contributes substantially to differences in seed dormancy between japonica (Nipponbare) and indica (Kasalath) cultivars
- Sdr4 expression is positively regulated by OsVP1, a global regulator of seed maturation, and in turn positively regulates potential regulators of seed dormancy and represses the expression of postgerminative genes, suggesting that Sdr4 acts as an intermediate regulator of dormancy in the seed maturation program
- Japonica cultivars have only the Nipponbare allele (Sdr4-n), which endows reduced dormancy, whereas both the Kasalath allele (Srd4-k) and Sdr4-n are widely distributed in the indica group, indicating prevalent introgression
- Molecular cloning of Sdr4, a regulator involved in seed dormancy and domestication of rice
- Connection
- OSVP1~VP1, Sdr4, Molecular cloning of Sdr4, a regulator involved in seed dormancy and domestication of rice, Sdr4 expression is positively regulated by OsVP1, a global regulator of seed maturation, and in turn positively regulates potential regulators of seed dormancy and represses the expression of postgerminative genes, suggesting that Sdr4 acts as an intermediate regulator of dormancy in the seed maturation program
Prev Next