- Information
- Symbol: Xa26,Xa3
- MSU: LOC_Os11g47210
- RAPdb: None
- PSP score
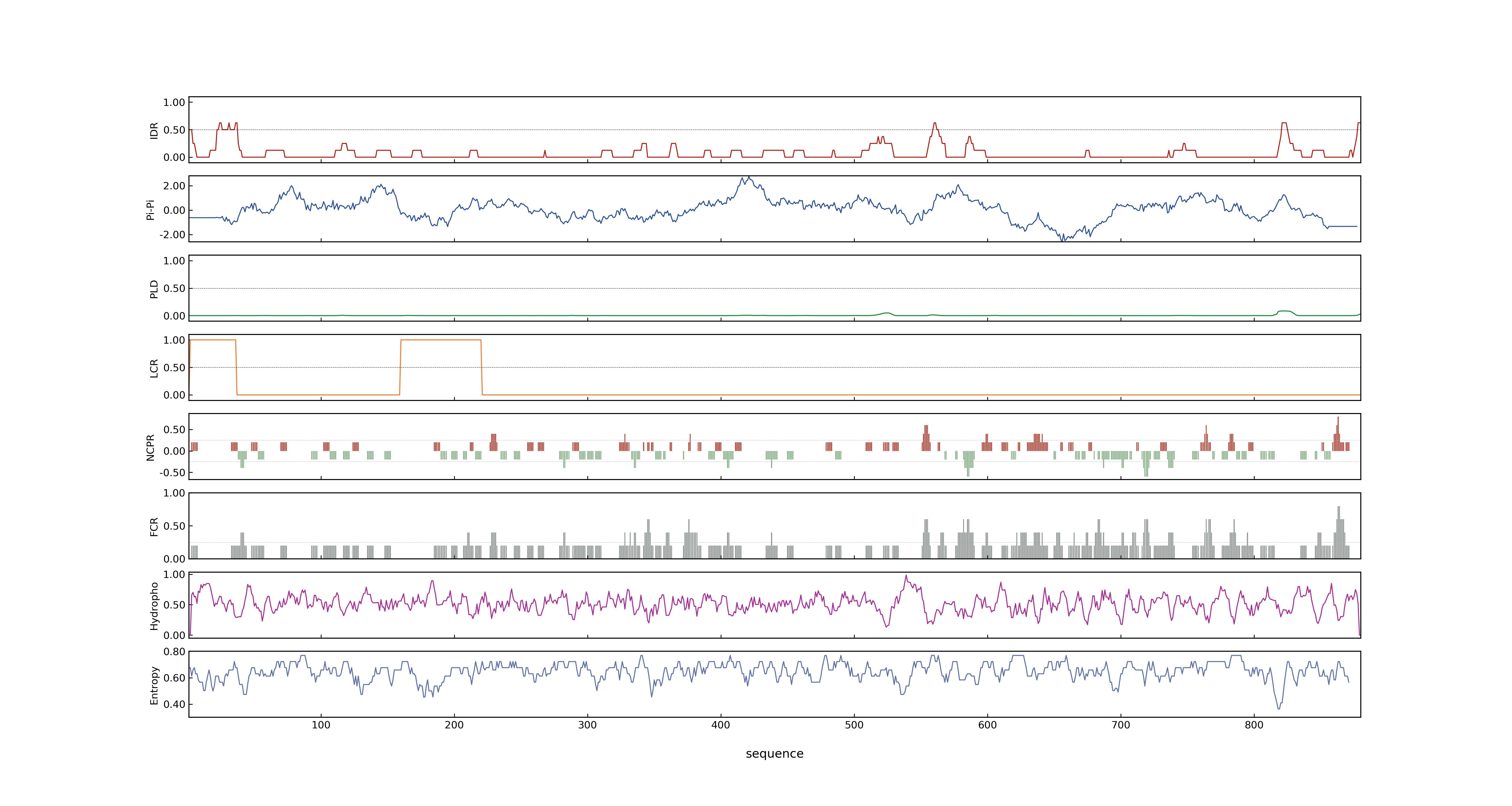
- LOC_Os11g47210.1: 0.5827
- PLAAC score
- LOC_Os11g47210.1: 0
- pLDDT score
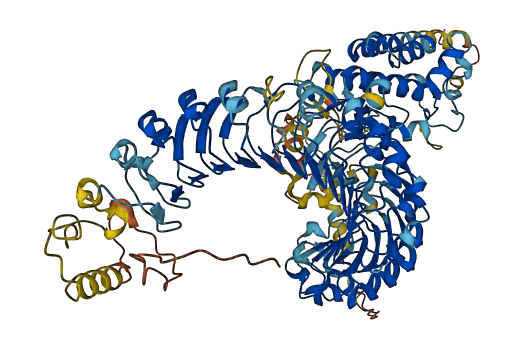
- 80.36
- Protein Structure from AlphaFold and UniProt
- MolPhase score
- LOC_Os11g47210.1: 0.64225566
- MolPhase Result
- Publication
- Xa3, conferring resistance for rice bacterial blight and encoding a receptor kinase-like protein, is the same as Xa26, 2006, Theor Appl Genet.
- A pair of orthologs of a leucine-rich repeat receptor kinase-like disease resistance gene family regulates rice response to raised temperature, 2011, BMC Plant Biol.
- The expression pattern of a rice disease resistance gene xa3/xa26 is differentially regulated by the genetic backgrounds and developmental stages that influence its function, 2007, Genetics.
- Functional analysis of Xa3/Xa26 family members in rice resistance to Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae, 2007, Theor Appl Genet.
- An XA21-associated kinase OsSERK2 regulates immunity mediated by the XA21 and XA3 immune receptors, 2014, Mol Plant.
- Ortholog alleles at Xa3/Xa26 locus confer conserved race-specific resistance against Xanthomonas oryzae in rice, 2012, Mol Plant.
- Xa26, a gene conferring resistance toXanthomonas oryzaepv.oryzaein rice, encodes an LRR receptor kinase-like protein, 2004, The Plant Journal.
- Multiple gene loci affecting genetic background-controlled disease resistance conferred by R gene Xa3/Xa26 in rice, 2009, Theor Appl Genet.
- Genetic and physical mapping of a new gene for bacterial blight resistance in rice, 2003, Theor Appl Genet.
- Small RNAs and Gene Network in a Durable Disease Resistance Gene-Mediated Defense Responses in Rice., 2015, PLoS One.
- Genbank accession number
- Key message
- Multiple gene loci affecting genetic background-controlled disease resistance conferred by R gene Xa3/Xa26 in rice
- The function of bacterial-blight resistance gene Xa3/Xa26 in rice is influenced by genetic background; the Oryza sativa L
- Xa3 is genetically tightly linked to Xa26, another gene for bacterial blight resistance
- Xa3, conferring resistance for rice bacterial blight and encoding a receptor kinase-like protein, is the same as Xa26
- The Xa26( t) locus is tightly linked to another bacterial blight resistance gene locus, Xa4
- Sequence analysis revealed that IRBB3 and Zhachanglong lines that are resistant to a broad range of Xoo strains, also carry Xa26
- BACKGROUND: Rice Xa3/Xa26 disease-resistance gene encodes a leucine-rich repeat (LRR) receptor kinase-type protein against Xanthomonas oryzae pv
- The RKe-involved temperature-related pathway and Xa3/Xa26-mediated disease-resistance pathway may partially overlap
- The expression pattern of a rice disease resistance gene xa3/xa26 is differentially regulated by the genetic backgrounds and developmental stages that influence its function
- Some F(2) individuals showed significantly increased Xa3/Xa26 transcripts, but the increased transcripts did not completely correlate with the reduced disease in this population
- Xa3-mediated resistance for rice bacterial blight, one of the most devastating rice diseases worldwide, is influenced by genetic background
- The rice disease resistance (R) gene Xa3/Xa26 (having also been named Xa3 and Xa26) against Xanthomonas oryzae pv
- Xa3/Xa26-2 and Xa3/Xa26-3 conferred resistance to 16 of the 18 Xoo strains examined
- Transgenic plants carrying a single copy of Xa3/Xa26, Xa3/Xa26-2, or Xa3/Xa26-3, in the same genetic background, showed a similar resistance spectrum to a set of Xoo strains, although plants carrying Xa3/Xa26-2 or Xa3/Xa26-3 showed lower resistance levels than the plants carrying Xa3/Xa26
- Phenotypic comparison showed that all the rice lines carrying either Xa3 or Xa26 developed dark brown deposition at the border between the lesion caused by incompatible-pathogen infection and health leaf tissue, while other rice lines did not show this dark brown deposition in either incompatible or compatible interactions
- Xa3 expression gradually increases from early seedling stage to adult stage
- A rice gene, Xa26, conferring resistance against Xoo at both seedling and adult stages was isolated by map-based cloning strategies from the rice cultivar Minghui 63
- A new dominant gene against a Chinese Xoo strain JL691 in both the seedling and adult stages was identified in Minghui 63 and designated as Xa26( t)
- , further reduced lesion length), and whole-growth-stage resistance compared to the indica rice; this enhanced resistance was associated with an increased expression of Xa3 throughout the growth stages in the japonica plants, which resulted in enhanced expression of defense-responsive genes
- Moreover, transgenic plants carrying Xa26 showed enhanced resistance compared with the donor line of the gene in both seedling and adult stages
- Connection
- RKe, Xa26~Xa3, A pair of orthologs of a leucine-rich repeat receptor kinase-like disease resistance gene family regulates rice response to raised temperature, Transgenic plants carrying a chimeric protein consisting of the LRR domain of NRKe and the kinase domain of Xa3/Xa26 developed the same lesion mimics as the NRKe-transgenic plants, whereas transgenic plants carrying another chimeric protein consisting of the LRR domain of Xa3/Xa26 and the kinase domain of NRKe were free of lesion mimic
- RKe, Xa26~Xa3, A pair of orthologs of a leucine-rich repeat receptor kinase-like disease resistance gene family regulates rice response to raised temperature, The RKe-involved temperature-related pathway and Xa3/Xa26-mediated disease-resistance pathway may partially overlap
- OsFLS2, Xa26~Xa3, An XA21-associated kinase OsSERK2 regulates immunity mediated by the XA21 and XA3 immune receptors, Here we report the isolation of OsSERK2 (rice somatic embryogenesis receptor kinase 2) and demonstrate that OsSERK2 positively regulates immunity mediated by XA21 and XA3 as well as the rice immune receptor FLS2 (OsFLS2)
- OsFLS2, Xa26~Xa3, An XA21-associated kinase OsSERK2 regulates immunity mediated by the XA21 and XA3 immune receptors, Taken together, our findings suggest that the mechanism of OsSERK2-meditated regulation of rice XA21, XA3, and FLS2 differs from that of AtSERK3/BAK1-mediated regulation of Arabidopsis FLS2 and EFR
- OsSERK2, Xa26~Xa3, An XA21-associated kinase OsSERK2 regulates immunity mediated by the XA21 and XA3 immune receptors, Here we report the isolation of OsSERK2 (rice somatic embryogenesis receptor kinase 2) and demonstrate that OsSERK2 positively regulates immunity mediated by XA21 and XA3 as well as the rice immune receptor FLS2 (OsFLS2)
- OsSERK2, Xa26~Xa3, An XA21-associated kinase OsSERK2 regulates immunity mediated by the XA21 and XA3 immune receptors, Taken together, our findings suggest that the mechanism of OsSERK2-meditated regulation of rice XA21, XA3, and FLS2 differs from that of AtSERK3/BAK1-mediated regulation of Arabidopsis FLS2 and EFR
- OsSERK2, Xa26~Xa3, An XA21-associated kinase OsSERK2 regulates immunity mediated by the XA21 and XA3 immune receptors, An XA21-associated kinase (OsSERK2) regulates immunity mediated by the XA21 and XA3 immune receptors
- xa21, Xa26~Xa3, An XA21-associated kinase OsSERK2 regulates immunity mediated by the XA21 and XA3 immune receptors, The rice XA21 immune receptor kinase and the structurally related XA3 receptor confer immunity to Xanthomonas oryzae pv
- xa21, Xa26~Xa3, An XA21-associated kinase OsSERK2 regulates immunity mediated by the XA21 and XA3 immune receptors, Here we report the isolation of OsSERK2 (rice somatic embryogenesis receptor kinase 2) and demonstrate that OsSERK2 positively regulates immunity mediated by XA21 and XA3 as well as the rice immune receptor FLS2 (OsFLS2)
- xa21, Xa26~Xa3, An XA21-associated kinase OsSERK2 regulates immunity mediated by the XA21 and XA3 immune receptors, Taken together, our findings suggest that the mechanism of OsSERK2-meditated regulation of rice XA21, XA3, and FLS2 differs from that of AtSERK3/BAK1-mediated regulation of Arabidopsis FLS2 and EFR
- xa21, Xa26~Xa3, An XA21-associated kinase OsSERK2 regulates immunity mediated by the XA21 and XA3 immune receptors, An XA21-associated kinase (OsSERK2) regulates immunity mediated by the XA21 and XA3 immune receptors
Prev Next